Human impacts on ecosystems
... other ecosystems within Canada. Free from predation and competition many invasive species reproduce rapidly and damage, displace or destroy native species ...
... other ecosystems within Canada. Free from predation and competition many invasive species reproduce rapidly and damage, displace or destroy native species ...
Chapter 2: Living Things in Ecosystems Notes
... C. Section 2.3 (Adapting to the Environment) Goals ...
... C. Section 2.3 (Adapting to the Environment) Goals ...
Notes Part 3 A habitat differs from a niche. A habitat is all aspects of
... Competition occurs when two species use ...
... Competition occurs when two species use ...
Patches - carmelacanzonieri.com
... • Convoluted forms are effective in enhancing interactions with the surroundings. A long common boundary provides a greater probability of movements across • A compact patch contains higher species richness than an elongated patch that has fewer interior species ...
... • Convoluted forms are effective in enhancing interactions with the surroundings. A long common boundary provides a greater probability of movements across • A compact patch contains higher species richness than an elongated patch that has fewer interior species ...
What is population ecology? - Mrs. Cindy Williams Biology website
... • What affect population ecology? • density • age • distribution • growth • competition • predation ...
... • What affect population ecology? • density • age • distribution • growth • competition • predation ...
Ecosystems
... If the population's needs are not met, it will move to a better habitat. Two different populations can not occupy the same niche at the same time, however. So the processes of competition, predation, cooperation, and symbiosis occur. ...
... If the population's needs are not met, it will move to a better habitat. Two different populations can not occupy the same niche at the same time, however. So the processes of competition, predation, cooperation, and symbiosis occur. ...
Slide 1
... Hyperabundance phenomenon • Animal populations “trapped” on small & medium sized islands have high population densities – WHY? – Reduced competition? – Reduced predation? ...
... Hyperabundance phenomenon • Animal populations “trapped” on small & medium sized islands have high population densities – WHY? – Reduced competition? – Reduced predation? ...
Chapter 14 Review
... 14.4: Population Growth Patterns • Population growth is based on available resources. • Exponential growth is when a population size increases dramatically over time because resources are abundant. • Ecological factors limit population growth. • Logistic growth is when the growth of the population ...
... 14.4: Population Growth Patterns • Population growth is based on available resources. • Exponential growth is when a population size increases dramatically over time because resources are abundant. • Ecological factors limit population growth. • Logistic growth is when the growth of the population ...
Section 1 Summary Notes
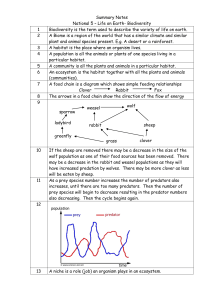
... If the sheep are removed there may be a decrease in the size of the wolf population as one of their food sources has been removed. There may be a decrease in the rabbit and weasel populations as they will have increased predation by wolves. There may be more clover as less will be eaten by sheep. As ...
... If the sheep are removed there may be a decrease in the size of the wolf population as one of their food sources has been removed. There may be a decrease in the rabbit and weasel populations as they will have increased predation by wolves. There may be more clover as less will be eaten by sheep. As ...
Ecosystem Connections: who, what, where, when Remember
... Are they temperate species adapted to the tropics or vice versa? What is the age structure of the population? How do they cope with predation? And many more ….!! ...
... Are they temperate species adapted to the tropics or vice versa? What is the age structure of the population? How do they cope with predation? And many more ….!! ...
1091-Lec9Edge
... higher edge:core ratios Fragmentation can have -ve and +ve effects The relative importance of habitat loss and habitat configuration can be assessed using ...
... higher edge:core ratios Fragmentation can have -ve and +ve effects The relative importance of habitat loss and habitat configuration can be assessed using ...
Ecosystems and Habitats
... • An ecosystem is all the living and nonliving things interacting in an environment. ...
... • An ecosystem is all the living and nonliving things interacting in an environment. ...
1 1 The greater a habitat`s biodiversity, the greater will be that
... support ecological succession from pond to marshland. ...
... support ecological succession from pond to marshland. ...
BCB322: Landscape Ecology
... follow IB predictions unless predatory lizards are present. Otherwise predation drives extinction rates (Toft & Schoener, 1983) ...
... follow IB predictions unless predatory lizards are present. Otherwise predation drives extinction rates (Toft & Schoener, 1983) ...
Document
... • An ecosystem’s function depends on the patches and the physical relationships with each other. Various relationships such as predators, herbivores, and mutualism need all need certain species in close areas. The ability for an organism to move can have a wide-ranging impact. The biogeochemical pro ...
... • An ecosystem’s function depends on the patches and the physical relationships with each other. Various relationships such as predators, herbivores, and mutualism need all need certain species in close areas. The ability for an organism to move can have a wide-ranging impact. The biogeochemical pro ...
powerpoint file - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary
... Not having evolved with a nighttime arboreal (tree climbing) predator, the native birds had no behavioral or physical defenses. As a result, birds began disappearing with the smaller species being affected first. By the mid 1980’s, 9 of 11 native forest birds were gone from Guam’s forests. Two of th ...
... Not having evolved with a nighttime arboreal (tree climbing) predator, the native birds had no behavioral or physical defenses. As a result, birds began disappearing with the smaller species being affected first. By the mid 1980’s, 9 of 11 native forest birds were gone from Guam’s forests. Two of th ...
Ecological effects of habitat fragmentation and edge creation
... not sharp. Rather, there is an edge zone of varying width for different factors. In forests, the altered environment of the edge zone favors shade intolerant plant species at the expense of the forest dominants and can also favor the proliferation of invasive species. Since the perimeter of a polygo ...
... not sharp. Rather, there is an edge zone of varying width for different factors. In forests, the altered environment of the edge zone favors shade intolerant plant species at the expense of the forest dominants and can also favor the proliferation of invasive species. Since the perimeter of a polygo ...
1091-Lec10(TrapA)
... What are the issues about using presence/absence/abundance data to identify critical habitat? What data is needed to determine whether a habitat acts as a source or a sink? ...
... What are the issues about using presence/absence/abundance data to identify critical habitat? What data is needed to determine whether a habitat acts as a source or a sink? ...
metapopulations
... local patch persistence patch size local populations population persistence Larger patches patch heterogeneity If environment is variable, If species is sensitive to changing environment, If a patch has greater variety of habitats for it to use, -expect less extinction in that patch Kindv ...
... local patch persistence patch size local populations population persistence Larger patches patch heterogeneity If environment is variable, If species is sensitive to changing environment, If a patch has greater variety of habitats for it to use, -expect less extinction in that patch Kindv ...