slides - István Albert
... SNP calling checklist • Unique sample or pooled samples? – unique samples à the expecta9on for each allele will be 50% ...
... SNP calling checklist • Unique sample or pooled samples? – unique samples à the expecta9on for each allele will be 50% ...
Intensity-Dependent Normalization
... Introduction to Genetics DNA - A nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell. DNA consists of two long chains of nucleotides joined by hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine. The sequence of nucleotides determines individual here ...
... Introduction to Genetics DNA - A nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell. DNA consists of two long chains of nucleotides joined by hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine. The sequence of nucleotides determines individual here ...
Employing Cell-free DNA from Maternal Plasma for
... using sequences from the Y chromosome. For example, DYS14 (a sequence located on the testis-specific Y encoded protein 1 (TSPY) gene, or the SRY (sex-determining region Y) gene can be used to detect a male fetus. The absence of these sequences is used to infer a rhesus negative or female fetus respe ...
... using sequences from the Y chromosome. For example, DYS14 (a sequence located on the testis-specific Y encoded protein 1 (TSPY) gene, or the SRY (sex-determining region Y) gene can be used to detect a male fetus. The absence of these sequences is used to infer a rhesus negative or female fetus respe ...
Chapter 4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
Document
... Scalable purification of archive-quality DNA from 100 to 5 x 108 cultured cells using the Gentra® Puregene® Cell Kit This protocol provides information about scaling of reagents required for purification of DNA from 100 to 5 x 108 cultured cells using the Gentra Puregene Cell Kit. The Gentra Puregen ...
... Scalable purification of archive-quality DNA from 100 to 5 x 108 cultured cells using the Gentra® Puregene® Cell Kit This protocol provides information about scaling of reagents required for purification of DNA from 100 to 5 x 108 cultured cells using the Gentra Puregene Cell Kit. The Gentra Puregen ...
A CAAT–Box Binding Factor Gene That Regulates Seed Development
... •Transcription is initiated at regions of DNA called promoters. Specific sequences of nucleotide bases at a promoter are recognized by both transcription factors and RNA polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes RNA. The mRNA strand produced is complementary to the transcribed strand (the antisense st ...
... •Transcription is initiated at regions of DNA called promoters. Specific sequences of nucleotide bases at a promoter are recognized by both transcription factors and RNA polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes RNA. The mRNA strand produced is complementary to the transcribed strand (the antisense st ...
No Slide Title
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
103 final review worksheet
... 94. Draw a diagram of ATP synthase, showing the two subunits, F0 an F1. Show where the protein crosses the intermitochondrial membrane and label the intermembrane space and the matrix. Show where the protons enter, where they leave and where the ATP is synthesized. ...
... 94. Draw a diagram of ATP synthase, showing the two subunits, F0 an F1. Show where the protein crosses the intermitochondrial membrane and label the intermembrane space and the matrix. Show where the protons enter, where they leave and where the ATP is synthesized. ...
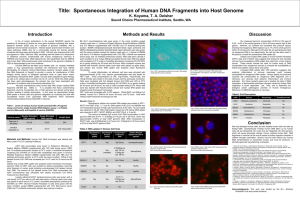
Title: Spontaneous Integration of Human DNA Fragments into Host
... free DNA fragments is thought to provide a source for maintenance of DNA integrity during rescue of collapsed replication forks or base lesion repair. Spontaneous extracellular DNA uptake has also been exploited for gene therapy as well as for cellular gene correction (2,4,5,7,8, and 9). While free ...
... free DNA fragments is thought to provide a source for maintenance of DNA integrity during rescue of collapsed replication forks or base lesion repair. Spontaneous extracellular DNA uptake has also been exploited for gene therapy as well as for cellular gene correction (2,4,5,7,8, and 9). While free ...
DNA Analysis Chapter 11
... – Four base nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) dangle off of each sugar molecule – A and T will bond with one another – C and G will bond with one another ...
... – Four base nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) dangle off of each sugar molecule – A and T will bond with one another – C and G will bond with one another ...
Chapter 2b Packet
... 14. A ______________ is a large molecule formed by linked smaller molecules called amino acids. 15. ____________ ____________are the building blocks of proteins. ______ different amino acids are found in proteins. 16. Proteins have many different functions such as (list 3) __________________________ ...
... 14. A ______________ is a large molecule formed by linked smaller molecules called amino acids. 15. ____________ ____________are the building blocks of proteins. ______ different amino acids are found in proteins. 16. Proteins have many different functions such as (list 3) __________________________ ...
Efficient whole-genome DNA methylation analysis of the Human
... efficiently survey DNA methylation patterns genome-wide is the objective of the work presented. The method combines the power of methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) proteins to sensitively and selectively bind methylated DNA sequences with the coverage, precision, and accuracy provided by highthroughput ...
... efficiently survey DNA methylation patterns genome-wide is the objective of the work presented. The method combines the power of methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) proteins to sensitively and selectively bind methylated DNA sequences with the coverage, precision, and accuracy provided by highthroughput ...
structural investigation on cation recognition molecules
... Many spectroscopic methods (IR, Raman, EPR, NMR) were used for the structural investigation of the chelator desferrioxamine B and its Fe(III) complex, ferrioxamine B. The “recognition” properties of some molecules are very important for many biological processes and generally for life [1]. The prote ...
... Many spectroscopic methods (IR, Raman, EPR, NMR) were used for the structural investigation of the chelator desferrioxamine B and its Fe(III) complex, ferrioxamine B. The “recognition” properties of some molecules are very important for many biological processes and generally for life [1]. The prote ...
RNA-Seq Sample Recommendations (Craig Praul, PSU and Caitlyn
... concentration measured by our facility with calibrated NanoDrops or other techniques such as Bioanalzyer or Qubit discussed below. If you are using your own spectrophotometer please check that it is calibrated by measuring the concentration of commercially obtained standards, use calibrated pipettor ...
... concentration measured by our facility with calibrated NanoDrops or other techniques such as Bioanalzyer or Qubit discussed below. If you are using your own spectrophotometer please check that it is calibrated by measuring the concentration of commercially obtained standards, use calibrated pipettor ...
B. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases
... a) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase b) Four ribonucleoside triphosphates (1) ATP, GTP, CTP, and UTP c) DNA template (1) The enzyme that performs transcription is referred to as a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (a) Here we will refer to it simply as RNA polymerase d) No primer (1) No primers are needed for ...
... a) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase b) Four ribonucleoside triphosphates (1) ATP, GTP, CTP, and UTP c) DNA template (1) The enzyme that performs transcription is referred to as a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (a) Here we will refer to it simply as RNA polymerase d) No primer (1) No primers are needed for ...
Section 13.2 Summary – pages 341
... cloned using PCR. Then, the strands are separated from each other. • The single-stranded fragments are placed in four different test tubes, one for each DNA base. ...
... cloned using PCR. Then, the strands are separated from each other. • The single-stranded fragments are placed in four different test tubes, one for each DNA base. ...
Chapter 5 - My Teacher Site
... monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages – Some polysaccharides are used for storage and then hydrolyzed as needed to provide sugar for the cell • Other polysaccharides serve as building material for structures that protect cell or whole organism – The structure and function of polysaccharides ...
... monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages – Some polysaccharides are used for storage and then hydrolyzed as needed to provide sugar for the cell • Other polysaccharides serve as building material for structures that protect cell or whole organism – The structure and function of polysaccharides ...
Chapter 13
... Any other sugar must be converted to glucose before it can enter the glycolysis pathway & this takes energy. It is advantageous to have the potential to utilize other sugars (carbon sources), but want to only synthesize the proteins necessary for utilization of these sugars only when glucose is abse ...
... Any other sugar must be converted to glucose before it can enter the glycolysis pathway & this takes energy. It is advantageous to have the potential to utilize other sugars (carbon sources), but want to only synthesize the proteins necessary for utilization of these sugars only when glucose is abse ...
Conditional (if else) lecture
... • Create a hash table for converting DNA condons (3 bases) into amino acids • Display all the enteries to the user • Continually ssk the user to entered three bases and display the corresponding Amino Acid (AA); e.g. aug met…. Repeat the process until a “stop” codon is entered. Display the AA sequ ...
... • Create a hash table for converting DNA condons (3 bases) into amino acids • Display all the enteries to the user • Continually ssk the user to entered three bases and display the corresponding Amino Acid (AA); e.g. aug met…. Repeat the process until a “stop” codon is entered. Display the AA sequ ...
Question 1 _____/ 30 points Question 2 _____/ 20 points Question 3
... The pattern of transcripts would most likely look like wildtype. In this case, the Mediator complex is not being recruited by the activator, rather TFIID is, so phosphorylation of the CTD is not as important for release of RNA Pol II from the promoter. ...
... The pattern of transcripts would most likely look like wildtype. In this case, the Mediator complex is not being recruited by the activator, rather TFIID is, so phosphorylation of the CTD is not as important for release of RNA Pol II from the promoter. ...
1. Amino Acids,Peptides, Proteins
... Ch. 24. Metabolism of Acylglycerols & Sphingolipids - to the p. 249 (to the “All Sphingolipids...”) - without „ Biosynthesis of Glycerol Ether Phospholipids”, but with Figure 24-6. Ch. 25. Lipid Transport & Storage - from p. 260 (from “Clinical aspects...”) to the end Repetition of Fatty Acids Metab ...
... Ch. 24. Metabolism of Acylglycerols & Sphingolipids - to the p. 249 (to the “All Sphingolipids...”) - without „ Biosynthesis of Glycerol Ether Phospholipids”, but with Figure 24-6. Ch. 25. Lipid Transport & Storage - from p. 260 (from “Clinical aspects...”) to the end Repetition of Fatty Acids Metab ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.