Recombinant DNA Paper Lab_complete
... Bacteria have not only their normal DNA, they also have pieces of circular DNA called plasmids. Plasmids are a wonderfully ally for biologists who desire to get bacteria to produce very specific proteins. The plasmids conveniently can be cut, fused with other DNA and then reabsorbed by bacteria. The ...
... Bacteria have not only their normal DNA, they also have pieces of circular DNA called plasmids. Plasmids are a wonderfully ally for biologists who desire to get bacteria to produce very specific proteins. The plasmids conveniently can be cut, fused with other DNA and then reabsorbed by bacteria. The ...
Yr 10 Genetics File
... • DNA is made up of four bases. • These are A = adenine T = thymine C = cytosine G = guanine • These bases form a sequence along the DNA strand. Eg; This forms only one strand of DNA. DNA is a double helix strand. ...
... • DNA is made up of four bases. • These are A = adenine T = thymine C = cytosine G = guanine • These bases form a sequence along the DNA strand. Eg; This forms only one strand of DNA. DNA is a double helix strand. ...
Extraction of Plasmid DNA, Restriction Digest, and DNA Gel
... Biochemists study protein structure, function and activity. To study protein X, we need it in pure form rather than as a mixture of many proteins. It is not always easy to purify a protein from its natural source. For example, to purify bovine protein X (from cow), you might start by grinding up a p ...
... Biochemists study protein structure, function and activity. To study protein X, we need it in pure form rather than as a mixture of many proteins. It is not always easy to purify a protein from its natural source. For example, to purify bovine protein X (from cow), you might start by grinding up a p ...
Leukaemia Section t(10;11)(p11.2;q23) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... A. Partial Q-banded karyotype showing the t(10;11)(p11.2;q23), derivative chromosomes are on the right. B. FISH using RP13-31H8 (ABI1) shows one signal on the normal chromosome 10 and the another one split between the p arm of der(10) (arrowheads) and the q arm of der(11) (arrow). The BAC clone was ...
... A. Partial Q-banded karyotype showing the t(10;11)(p11.2;q23), derivative chromosomes are on the right. B. FISH using RP13-31H8 (ABI1) shows one signal on the normal chromosome 10 and the another one split between the p arm of der(10) (arrowheads) and the q arm of der(11) (arrow). The BAC clone was ...
Amino Acids and Proteins: →Protein Functions: enzymes, transport
... 4) Reactions of amino acids: The side chains exhibit specific chemical reactivities, depending on the nature of the functional group (see figure 4.8). It is the characteristic behavior of the side chain that governs the reactivity of amino acids incorporated into proteins. Polymerization of Amino Ac ...
... 4) Reactions of amino acids: The side chains exhibit specific chemical reactivities, depending on the nature of the functional group (see figure 4.8). It is the characteristic behavior of the side chain that governs the reactivity of amino acids incorporated into proteins. Polymerization of Amino Ac ...
CHAPTER 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules The
... Saturated = carbon skeleton is saturated with hydrogen atoms, NO double bonds so there is a very close association among lipid molecules. This is why saturated fats are solid at room temperature Unsaturated = carbon skeleton is NOT saturated with hydrogen atoms; double bonds are present in these mol ...
... Saturated = carbon skeleton is saturated with hydrogen atoms, NO double bonds so there is a very close association among lipid molecules. This is why saturated fats are solid at room temperature Unsaturated = carbon skeleton is NOT saturated with hydrogen atoms; double bonds are present in these mol ...
Lecture 27
... In mammals, found in the liver and small intestine mucosa XO is a homodimer with FAD, two [2Fe-2S] clusters and a molybdopterin complex (Mo-pt) that cycles between Mol (VI) and Mol (IV) oxidation states. Final electron acceptor is O2 which is converted to H2O2 XO is cleaved into 3 segments. The uncl ...
... In mammals, found in the liver and small intestine mucosa XO is a homodimer with FAD, two [2Fe-2S] clusters and a molybdopterin complex (Mo-pt) that cycles between Mol (VI) and Mol (IV) oxidation states. Final electron acceptor is O2 which is converted to H2O2 XO is cleaved into 3 segments. The uncl ...
Distrofie muscolari dei cingoli
... Description of nucleotide changes substitutions are designated by a “>”-character 76A>C denotes that at nucleotide 76 a A is changed to a C 88+1G>T (alternatively IVS2+1G>T) denotes the G to T substitution at nucleotide +1of intron 2, relative to the cDNA positioned between nucleotides 88 and 89 ...
... Description of nucleotide changes substitutions are designated by a “>”-character 76A>C denotes that at nucleotide 76 a A is changed to a C 88+1G>T (alternatively IVS2+1G>T) denotes the G to T substitution at nucleotide +1of intron 2, relative to the cDNA positioned between nucleotides 88 and 89 ...
File
... • Water helps stabilize the internal temperature of the body – Has high heat capacity—the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1°C ...
... • Water helps stabilize the internal temperature of the body – Has high heat capacity—the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1°C ...
Lecture#7 Microbial Biotechnology
... obtained by purifying it from the pancreas of cows & pigs slaughtered for food. This was expensive, difficult and the insulin could cause allergic reactions. ...
... obtained by purifying it from the pancreas of cows & pigs slaughtered for food. This was expensive, difficult and the insulin could cause allergic reactions. ...
A structural determinant in the uracil DNA glycosylase superfamily
... the genome during DNA replication. The implications of this study in the origin of life are discussed. INTRODUCTION Enzymes in the uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) superfamily are well known for their role in the removal of deaminated base damage in DNA repair. So far, six families in the superfamily ha ...
... the genome during DNA replication. The implications of this study in the origin of life are discussed. INTRODUCTION Enzymes in the uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) superfamily are well known for their role in the removal of deaminated base damage in DNA repair. So far, six families in the superfamily ha ...
Food Safety & Toxicology (3) - Share My Knowledge & Experience
... • Reduction: Consumption of foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products and seafood, and enhanced vitamin D intake ...
... • Reduction: Consumption of foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products and seafood, and enhanced vitamin D intake ...
Biotechnology
... Overview: The DNA Toolbox • In recombinant DNA, nucleotide sequences from two different sources, often two species, are combined in vitro into the same DNA molecule • Methods for making recombinant DNA are central to genetic engineering, the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes • DNA ...
... Overview: The DNA Toolbox • In recombinant DNA, nucleotide sequences from two different sources, often two species, are combined in vitro into the same DNA molecule • Methods for making recombinant DNA are central to genetic engineering, the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes • DNA ...
nucleicacidmetabolism
... dephosphorylations can and do occur ADP and GDP can be reduced to dADP and dGDP AMP can deaminated to IMP (new) IMP can be aminated to AMP IMP can oxidized to XMP XMP can be aminated to GMP Guanine, adenine can be phosphoribosylated to GMP and AMP Nucleic Acid Metabolism ...
... dephosphorylations can and do occur ADP and GDP can be reduced to dADP and dGDP AMP can deaminated to IMP (new) IMP can be aminated to AMP IMP can oxidized to XMP XMP can be aminated to GMP Guanine, adenine can be phosphoribosylated to GMP and AMP Nucleic Acid Metabolism ...
catalyst
... When you are finished, put your pencil down and look up. Remain silent to allow others to finish. Answer the following questions: ...
... When you are finished, put your pencil down and look up. Remain silent to allow others to finish. Answer the following questions: ...
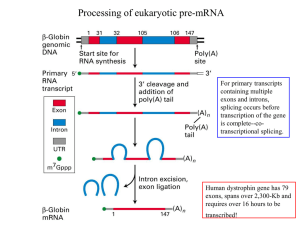
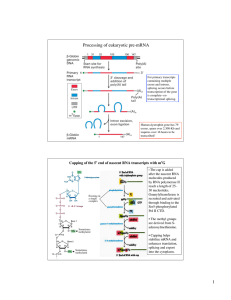
1 Processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA
... splicing cycle and experimental demonstration that the base pairing between U1 and the 5’ splice site in pre-mRNA is important ...
... splicing cycle and experimental demonstration that the base pairing between U1 and the 5’ splice site in pre-mRNA is important ...
Cycles in Nature PowerPoint
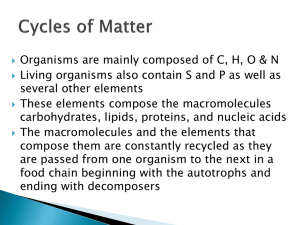
... Organisms are mainly composed of C, H, O & N Living organisms also contain S and P as well as several other elements These elements compose the macromolecules carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids The macromolecules and the elements that compose them are constantly recycled as they are ...
... Organisms are mainly composed of C, H, O & N Living organisms also contain S and P as well as several other elements These elements compose the macromolecules carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids The macromolecules and the elements that compose them are constantly recycled as they are ...
Chapter 19 Biochemistry - American Public University System
... • The cell is the smallest structural unit of living organisms that has the properties traditionally associated with life. • A cell can be an independent living organism or a building block of a more complex organism. • Some cells contain a nucleus, the part of the cell that contains genetic materia ...
... • The cell is the smallest structural unit of living organisms that has the properties traditionally associated with life. • A cell can be an independent living organism or a building block of a more complex organism. • Some cells contain a nucleus, the part of the cell that contains genetic materia ...
Sequencing genomes
... And the same is true for Dayhoff’s model of evolution. If we need to obtain probability matrices for higher percentage of accepted mutations (i.e. covering longer evolutionary time), we do matrix powers. Let’s say we want PAM120 – 120 mutations fixed on average per 100 residues. We do PAM1120. ...
... And the same is true for Dayhoff’s model of evolution. If we need to obtain probability matrices for higher percentage of accepted mutations (i.e. covering longer evolutionary time), we do matrix powers. Let’s say we want PAM120 – 120 mutations fixed on average per 100 residues. We do PAM1120. ...
Slide 1
... Hence the code appears to minimize translational error with respect to randomly reshuffled codes, even though translational error was not the main factor being selected. ...
... Hence the code appears to minimize translational error with respect to randomly reshuffled codes, even though translational error was not the main factor being selected. ...
Microbiology - Imperial Valley College
... double-stranded DNA at its particular recognition sites, shown in blue. ...
... double-stranded DNA at its particular recognition sites, shown in blue. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.