Amino Acid Limitation Induces the Amino Acid
... 2004; Vattem & Wek, 2004). As a consequence of elevated ATF4 protein expression, multiple stress-induced genes are activated, including genes containing an amino acid response element (AARE) (Harding et al., 2003). C/EBPATF response element (CARE) refers to a genomic sequence that contains a half-si ...
... 2004; Vattem & Wek, 2004). As a consequence of elevated ATF4 protein expression, multiple stress-induced genes are activated, including genes containing an amino acid response element (AARE) (Harding et al., 2003). C/EBPATF response element (CARE) refers to a genomic sequence that contains a half-si ...
13.3 Mutations
... – Mutations that involve changes in one or a few nucleotides are known as point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. They generally occur during replication. – If a gene in one cell is altered, the alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the origin ...
... – Mutations that involve changes in one or a few nucleotides are known as point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. They generally occur during replication. – If a gene in one cell is altered, the alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the origin ...
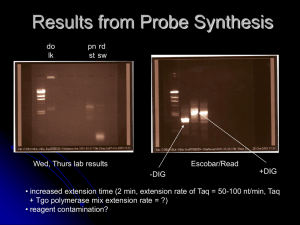
Southern Analysis: - California State University San Marcos
... Prehybridization: prehybridization solution contains a mix of proteins and nucleic acids that will bind to the membrane, covering regions where there is no fixed DNA (membrane blocking). This prevents the single stranded probe from binding nonspecifically to the membrane. ...
... Prehybridization: prehybridization solution contains a mix of proteins and nucleic acids that will bind to the membrane, covering regions where there is no fixed DNA (membrane blocking). This prevents the single stranded probe from binding nonspecifically to the membrane. ...
Dynamical scaling of the DNA unzipping transition
... [10–12] etc have been used to study DNA by pulling at one end. This has led to strand separation by force. In particular, AFM experiments reported hysteresis in the unzipping process, indicating the presence of a first order transition. These mechanical unzipping experiments have opened up new ways ...
... [10–12] etc have been used to study DNA by pulling at one end. This has led to strand separation by force. In particular, AFM experiments reported hysteresis in the unzipping process, indicating the presence of a first order transition. These mechanical unzipping experiments have opened up new ways ...
Section 2-3: Carbon Compounds (p. 44-48)
... – plants make polysaccharides, while animals make proteins. – proteins are made of monomers, while polysaccharides are not. – polysaccharides are made of monosaccharides, while proteins are made of amino acids. – proteins carry genetic information, while ...
... – plants make polysaccharides, while animals make proteins. – proteins are made of monomers, while polysaccharides are not. – polysaccharides are made of monosaccharides, while proteins are made of amino acids. – proteins carry genetic information, while ...
Huntingtin grabs a hammer: DNA repair in HD
... Truant’s team, helmed by postdoctoral researcher Tam Maiuri, used an innovative method to pursue their hypothesis, using molecules called “chromobodies.” These can attach to specific protein targets and emit fluorescent light, illuminating working proteins that can be tracked under a microscope. In ...
... Truant’s team, helmed by postdoctoral researcher Tam Maiuri, used an innovative method to pursue their hypothesis, using molecules called “chromobodies.” These can attach to specific protein targets and emit fluorescent light, illuminating working proteins that can be tracked under a microscope. In ...
invited talk
... (2004) SDPpred: a tool for prediction of amino acid residues that determine differences in functional specificity of homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids ...
... (2004) SDPpred: a tool for prediction of amino acid residues that determine differences in functional specificity of homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids ...
Slide 1
... killing the nonresistant cells, allowing only the preexisting resistant cells to survive. Mutations do not arise in particular genes as a direct response to environmental change Mutations occur randomly at any time ...
... killing the nonresistant cells, allowing only the preexisting resistant cells to survive. Mutations do not arise in particular genes as a direct response to environmental change Mutations occur randomly at any time ...
Epigenetics and its implications for Psychology
... among many other “abnormal” phenomena that complicate the traditional view of the gene as a discrete unit of heredity in DNA. Furthermore, a gene “may have no fixity at all; its existence is both transitory and contingent, depending critically on the functional dynamics of the entire organism” (Kell ...
... among many other “abnormal” phenomena that complicate the traditional view of the gene as a discrete unit of heredity in DNA. Furthermore, a gene “may have no fixity at all; its existence is both transitory and contingent, depending critically on the functional dynamics of the entire organism” (Kell ...
Molecular Basis of Evolution
... genes, but mitochondrial genes use slightly different genetic codes. The standard genetic code is presented in Table 1.1. In this table, amino acids are represented by three-letter codes (see Table 1.2). There are 43 5 64 possible codons for the four different nucleotides, uracil (U), cytosine (C), ...
... genes, but mitochondrial genes use slightly different genetic codes. The standard genetic code is presented in Table 1.1. In this table, amino acids are represented by three-letter codes (see Table 1.2). There are 43 5 64 possible codons for the four different nucleotides, uracil (U), cytosine (C), ...
ODE TO THE CODE - bit
... one of 20 amino acids or else serves as a punctuation mark signaling the end of a message. That’s all there is to the code. But a nagging question has never been put to rest: Why this particular code, rather than some other? Given 64 codons and 20 amino acids plus a punctuation mark, there are 1083 ...
... one of 20 amino acids or else serves as a punctuation mark signaling the end of a message. That’s all there is to the code. But a nagging question has never been put to rest: Why this particular code, rather than some other? Given 64 codons and 20 amino acids plus a punctuation mark, there are 1083 ...
Chapter 10 - Everglades High School
... Protein Synthesis in Prokaryotes • Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are able to regulate which genes are expressed and which are not, depending on the cell’s needs. • The piece of DNA that overlaps the promoter site and serves as the on-off switch is called an operator. • In bacteria, a group o ...
... Protein Synthesis in Prokaryotes • Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are able to regulate which genes are expressed and which are not, depending on the cell’s needs. • The piece of DNA that overlaps the promoter site and serves as the on-off switch is called an operator. • In bacteria, a group o ...
Question Paper Code 57/3
... Ans Stop codon - does not code for any amino acid / terminates the synthesis of polypeptide chain Unambiguous codon - one codon codes for one amino acid only Degenerate codon - some amino acid are coded by more than one codon Universal codon - genetic code is same for all organisms (bacteria to huma ...
... Ans Stop codon - does not code for any amino acid / terminates the synthesis of polypeptide chain Unambiguous codon - one codon codes for one amino acid only Degenerate codon - some amino acid are coded by more than one codon Universal codon - genetic code is same for all organisms (bacteria to huma ...
ppt - eweb.furman.edu
... the carbonate minerals precipitate into microporous chimneys. High flux of carbon and energy is channeled over inorganic catalysts Thermal currents through pores can concentrate organics 1000 – 106 fold Vents persist for millennia ...
... the carbonate minerals precipitate into microporous chimneys. High flux of carbon and energy is channeled over inorganic catalysts Thermal currents through pores can concentrate organics 1000 – 106 fold Vents persist for millennia ...
Nitrogen Metabolism Overview
... • Leucine is degraded to acetyl CoA and acetoacetate by a pathway whose first two seps are identical to those of valine degradation (Figure 18‐11). The third step is the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATP‐ dependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a ...
... • Leucine is degraded to acetyl CoA and acetoacetate by a pathway whose first two seps are identical to those of valine degradation (Figure 18‐11). The third step is the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATP‐ dependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a ...
national senior certificate grade 12
... (a) During meiosis the chromosome pair 21 does not separate/ there is non-disjunction Two gametes (M and N) will have an extra copy of chromosomenumber 21 and therefore the other gametes (O and P) do not have a copy of chromosome 21 ...
... (a) During meiosis the chromosome pair 21 does not separate/ there is non-disjunction Two gametes (M and N) will have an extra copy of chromosomenumber 21 and therefore the other gametes (O and P) do not have a copy of chromosome 21 ...
The Importance of Epigenetic Phenomena in Regulating Activity of
... methylation. Acetylation is of the lysine residue generally activates the chromatin by loosening the DNA around the histone and making the gene more readily available to be transcribed. Deacetylation is associated with the heterochromatin, which is a more condensed form of the chromatin that inhibit ...
... methylation. Acetylation is of the lysine residue generally activates the chromatin by loosening the DNA around the histone and making the gene more readily available to be transcribed. Deacetylation is associated with the heterochromatin, which is a more condensed form of the chromatin that inhibit ...
CONTROL OF THE ACTIVITY OF THE HUMAN MITOCHONDRIAL TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION FACTOR
... (Morris and Hollenbeck, 1993; Lee and Hollenbeck, 1995; Morris and Hollenbeck, 1995; Overly et al, 1996; Tanaka et al, 1998; Hurd and Saxton, 1996). Changes in shape and size can also be the consequence of processes like fusion or fission. Such events have been elegantly studied by time-lapse photog ...
... (Morris and Hollenbeck, 1993; Lee and Hollenbeck, 1995; Morris and Hollenbeck, 1995; Overly et al, 1996; Tanaka et al, 1998; Hurd and Saxton, 1996). Changes in shape and size can also be the consequence of processes like fusion or fission. Such events have been elegantly studied by time-lapse photog ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.