05 Populations and Demography
... (flowers in a field) 2. Uniform- Set distance between each (nesting sites) 3. Clumped- tightly packed pods or groups (school of fish) ...
... (flowers in a field) 2. Uniform- Set distance between each (nesting sites) 3. Clumped- tightly packed pods or groups (school of fish) ...
5.3 Populations
... exponentially but conditions are never perfect. Food resources are limited, predation occurs, and abiotic conditions are factors. This limits population growth. ...
... exponentially but conditions are never perfect. Food resources are limited, predation occurs, and abiotic conditions are factors. This limits population growth. ...
Concept Review
... Fecundity is the physical ability to reproduce. Fertility is a measure of the number of offspring produced. Natality is the production of new individuals. Mortality is the death rate of a population. Major factors in mortality include predation, disease, accidents, and environmental influences. Life ...
... Fecundity is the physical ability to reproduce. Fertility is a measure of the number of offspring produced. Natality is the production of new individuals. Mortality is the death rate of a population. Major factors in mortality include predation, disease, accidents, and environmental influences. Life ...
2016-2017 Population Growrh and Urbanization
... supplies keep up with the demands of a growing population. ...
... supplies keep up with the demands of a growing population. ...
Unit 4 Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... Developing countries’ age structure diagrams look like __________________________________ Developed countries’ age structure diagrams look like rectangles; more even among age classes ...
... Developing countries’ age structure diagrams look like __________________________________ Developed countries’ age structure diagrams look like rectangles; more even among age classes ...
Populations
... 4. Density – Different species have different needs for space. The need for space determines an organism’s population density. Population density is how many individuals can live in an area at one time. If the population density increases beyond a suitable level for a particular species, it produce ...
... 4. Density – Different species have different needs for space. The need for space determines an organism’s population density. Population density is how many individuals can live in an area at one time. If the population density increases beyond a suitable level for a particular species, it produce ...
Envi Sci @ CHS
... unknown reasons. b. __________________ The population size of a species with a fairly unchanging population fluctuates slightly above and below its carrying capacity. c. __________________ The population undergoes sharp increases in size, followed by crashes over fairly regular time intervals. d. __ ...
... unknown reasons. b. __________________ The population size of a species with a fairly unchanging population fluctuates slightly above and below its carrying capacity. c. __________________ The population undergoes sharp increases in size, followed by crashes over fairly regular time intervals. d. __ ...
Review for Ecology Test
... ___________. The animals that feed on plants are called ___________ consumers and those that feed on the herbivores are called ______________ consumers. 16. What would happen to the populations of a specific roducers in a certain area if the primary consumer that feeds on that producer suddenly beca ...
... ___________. The animals that feed on plants are called ___________ consumers and those that feed on the herbivores are called ______________ consumers. 16. What would happen to the populations of a specific roducers in a certain area if the primary consumer that feeds on that producer suddenly beca ...
Ecosystems
... Logistic Growth Logistic Growth: as resources become limited, a population’s growth slows or stops The population reaches the limit the environment can support Produces a S-shaped curve ...
... Logistic Growth Logistic Growth: as resources become limited, a population’s growth slows or stops The population reaches the limit the environment can support Produces a S-shaped curve ...
PRESENTATION NAME
... When organism move out of a population When organisms move into a population ...
... When organism move out of a population When organisms move into a population ...
Chapter 5 Section 1 How Populations Grow
... Write these questions and your answers on a sheet of paper. • How many people are in this classroom? (include me because I am a person) • What is the room’s area? (there are 39.37 inches per meter)(area is length x width) • How many people are there in the room per square meter? (divide the number o ...
... Write these questions and your answers on a sheet of paper. • How many people are in this classroom? (include me because I am a person) • What is the room’s area? (there are 39.37 inches per meter)(area is length x width) • How many people are there in the room per square meter? (divide the number o ...
14.3: Factors Affecting Population Change pg. 671 Density
... Intraspecific Competition: an ecological interaction in which individuals of the same species or population compete for resources in their habitats. Limitations in population growth occur when the population size increases, causing the impact of the limitations to increase. Matlhus’ essay expressed ...
... Intraspecific Competition: an ecological interaction in which individuals of the same species or population compete for resources in their habitats. Limitations in population growth occur when the population size increases, causing the impact of the limitations to increase. Matlhus’ essay expressed ...
Presentation
... Occurs between same species and different species Causes starvation or emigration to decrease competition ...
... Occurs between same species and different species Causes starvation or emigration to decrease competition ...
New Title
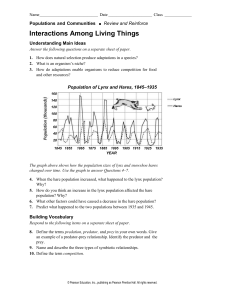
... The graph above shows how the population sizes of lynx and snowshoe hares changed over time. Use the graph to answer Questions 4–7. 4. When the hare population increased, what happened to the lynx population? Why? 5. How do you think an increase in the lynx population affected the hare population? W ...
... The graph above shows how the population sizes of lynx and snowshoe hares changed over time. Use the graph to answer Questions 4–7. 4. When the hare population increased, what happened to the lynx population? Why? 5. How do you think an increase in the lynx population affected the hare population? W ...
Carrying capacity
... Carrying capacity: The largest population of a species that can be supported by an environment ...
... Carrying capacity: The largest population of a species that can be supported by an environment ...
Competition Within a Population
... 2. Resource Limits A particular resource that is consumed by a particular species (food, water, etc) is called a “LIMITING FACTOR” CC is reached when the species is consuming it at the same rate it is being produced. ...
... 2. Resource Limits A particular resource that is consumed by a particular species (food, water, etc) is called a “LIMITING FACTOR” CC is reached when the species is consuming it at the same rate it is being produced. ...
Population Ecology - Madeira City Schools
... b. this growth cannot continue for a long time….why? c. idealized picture of unregulated growth d. G= rN (G = growth rate, N = population size, r = per person (capita) rate of increase) e. how do you get r? net increase total population 2. Logistical Growth – idealized picture of population growth t ...
... b. this growth cannot continue for a long time….why? c. idealized picture of unregulated growth d. G= rN (G = growth rate, N = population size, r = per person (capita) rate of increase) e. how do you get r? net increase total population 2. Logistical Growth – idealized picture of population growth t ...
Unit 5 Population Dynamics Expectations
... consuming more resources each year than Earth can produce. Sample questions: How does the Living Planet Index (LPI) help a nation to assess its ecological footprint and sustain its population? How does the planned obsolescence of electronic devices and appliances contribute to our ecological footpri ...
... consuming more resources each year than Earth can produce. Sample questions: How does the Living Planet Index (LPI) help a nation to assess its ecological footprint and sustain its population? How does the planned obsolescence of electronic devices and appliances contribute to our ecological footpri ...