* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 05 Populations and Demography
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
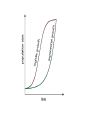
Chapter 5 Populations Photo 5-1 How Populations Grow How do researchers study populations? Researchers focus on 4 major groups when they study populations: 1. Geographic Range 2. Density and Distribution 3. Growth rate 4. Age structure 1. This is the area in which a population inhabits. Geographic range can vary enormously in size depending on the species. Think bacteria in a given area compared to people. 2. Population density refers to the number of individuals per unit area. This like #1 is dependant on species. (Duck in on a pond compared to fish in it) Distribution refers to how individuals in a population are spaced out. There are three recognized distribution types: 1. Random- Spaced out sporadically in an area (flowers in a field) 2. Uniform- Set distance between each (nesting sites) 3. Clumped- tightly packed pods or groups (school of fish) 3. The populations growth rate determines whether the size of the population will increase, decrease, or stay the same. Again this is mainly decided by the species type. 4. Age structure is a breakdown of how many males and females of the population at specific ages. This is important because most species have a certain age they can begin to reproduce at. Population Growth •Number of births •Number of deaths •Emigration (out) & Immigration (in) In Springfield, 45 babies are born in the year 2008. 15 people died that same year. What is the growth rate for the city? Positive Growth rate = population increase Negative Growth rate = decrease Exponential Growth –reproduce at a constant rate. Occurs under ideal conditions (no limits) J-shape curve Logistic Growth – resources become less available, growth slows or stops S-shape curve Carrying Capacity – the number an environment can support 5-2 Limits to Growth Limiting Factor – causes population growth to decrease Most common are: Density-Dependent Factors – Population size depends on: • Competition • Predation • Parasitism and disease • Human disturbances DensityIndependent Factors – does not depend on population size 1. Unusual weather 2. Natural disasters 3. Some human activities 5.3 DEMOGRAPHY •the study of human population growth - explains how populations change over time. Change in our world population over time Page 143 Graph •Agriculture •Irrigation •Plagues •Industrial revolution Demographic Transition – a dramatic change in birth and death rates •United States, Japan, and Europe population growth has stopped •ZERO POPULATION GROWTH In order to achieve ZPG, each couple has only 2 children AGE STRUCTURE DIAGRAMS •Show percentage of people alive at each age group Choose two and draw a diagram that would fit each: •1. A country where the king orders the deaths of all the baby boys •2. A country at war, many young men die in that war •3. A country with poor health care for women, many die in childbirth •4. A country where AIDS kills people in their 30s