Population Basics
... models of population variations after a few individuals initially colonize a new area. These curves are frequently seen in laboratory cultures of bacteria, wild sheep, barnacles, locusts, etc. However, in many more established populations, the situation becomes more complicated due to various shifts ...
... models of population variations after a few individuals initially colonize a new area. These curves are frequently seen in laboratory cultures of bacteria, wild sheep, barnacles, locusts, etc. However, in many more established populations, the situation becomes more complicated due to various shifts ...
Environmental Science
... rate at which individuals are born is called _________________________. The rate at which individuals die is called ___________________________. ...
... rate at which individuals are born is called _________________________. The rate at which individuals die is called ___________________________. ...
population ecology 2010
... • As early as Darwin, scientists have realized that populations have the ability to grow exponentially • All populations have this ability, although not all populations realized this type of growth • Darwin pondered the question of exponential growth. He knew that all species had the potential to gr ...
... • As early as Darwin, scientists have realized that populations have the ability to grow exponentially • All populations have this ability, although not all populations realized this type of growth • Darwin pondered the question of exponential growth. He knew that all species had the potential to gr ...
Unit 3 notes
... has too many people others feel that we can support billions of more people due to technological advances. Constant debate over need to reduce population growth Must consider moral, religious, personal freedom. ...
... has too many people others feel that we can support billions of more people due to technological advances. Constant debate over need to reduce population growth Must consider moral, religious, personal freedom. ...
Chapter 4 Population and Environment
... If, in a hypothetical population of size N, the birth rates (per capita) are represented as b and death rates (per capita) as d, then the increase or decrease in N during a time period t will be dN/dt = (b-d) N where (b-d) is called the 'intrinsic rate of natural increase’. Carrying capacity • In an ...
... If, in a hypothetical population of size N, the birth rates (per capita) are represented as b and death rates (per capita) as d, then the increase or decrease in N during a time period t will be dN/dt = (b-d) N where (b-d) is called the 'intrinsic rate of natural increase’. Carrying capacity • In an ...
Predator-prey interactions: lecture content
... Multiple factors control populations of most, if not all organisms, necessitating methods (like key-factor analysis) to assess relative strengths of control Key factors identify factors that perturb populations, density-dependence identifies those that regulate Metapopulations add spatial-temporal c ...
... Multiple factors control populations of most, if not all organisms, necessitating methods (like key-factor analysis) to assess relative strengths of control Key factors identify factors that perturb populations, density-dependence identifies those that regulate Metapopulations add spatial-temporal c ...
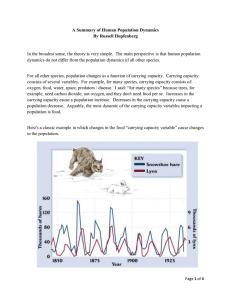
a Summary of Human Population Dynamics
... producing more hare-meat. In turn, the new increase in hare-meat supply would fuel more aggregate lynx population growth. Eventually, this cycle would be disastrous for the lynx as, at some point, the ecosystem could not sustain a world consisting of only lynx and hare. As people who have been born ...
... producing more hare-meat. In turn, the new increase in hare-meat supply would fuel more aggregate lynx population growth. Eventually, this cycle would be disastrous for the lynx as, at some point, the ecosystem could not sustain a world consisting of only lynx and hare. As people who have been born ...
Human Population Ecology
... Could the otters simply have migrated from one part of the region to another? To find out, the researchers analyzed populations over a 500mile-long stretch of the Aleutians from Kiska to Seguam …. By 1993 otter numbers in that whole stretch had been cut by half. Here the geographical scope of the r ...
... Could the otters simply have migrated from one part of the region to another? To find out, the researchers analyzed populations over a 500mile-long stretch of the Aleutians from Kiska to Seguam …. By 1993 otter numbers in that whole stretch had been cut by half. Here the geographical scope of the r ...
Unit_3_population
... Population experts believe that this graph will level out during the 21 century and represent an S-shaped curve. When this happens which individuals will be those dying and which will be those surviving??? ...
... Population experts believe that this graph will level out during the 21 century and represent an S-shaped curve. When this happens which individuals will be those dying and which will be those surviving??? ...
07_PopBio
... in a population may change over time. 3. Understand the different types of population growth curves 4. Understand the difference between Kselected and r-selected species ...
... in a population may change over time. 3. Understand the different types of population growth curves 4. Understand the difference between Kselected and r-selected species ...
CH 43 Populations Notes - Lincoln Park High School
... How has the human population typically changed throughout history? Has the growth rate changed in recent years? decades? centuries? Have we experienced logistic or exponential growth? Both? Neither? How much do you think the world population will change over the course of this class? (http://www.bre ...
... How has the human population typically changed throughout history? Has the growth rate changed in recent years? decades? centuries? Have we experienced logistic or exponential growth? Both? Neither? How much do you think the world population will change over the course of this class? (http://www.bre ...
Population Growth and Regulation Ecology Population Size
... • How did these humans exceed the carrying capacity of their island? ...
... • How did these humans exceed the carrying capacity of their island? ...
Populations and Communities
... Elephants in Africa’s wild game parks present another example of overpopulation. Elephant herds searching for food can cause tree damage. They push over trees to feed on treetops. Other animals that use those trees for food and shelter must compete with the elephants. Also, the loss of trees can dam ...
... Elephants in Africa’s wild game parks present another example of overpopulation. Elephant herds searching for food can cause tree damage. They push over trees to feed on treetops. Other animals that use those trees for food and shelter must compete with the elephants. Also, the loss of trees can dam ...
Population Ecology
... the young. b) It flattens out as death rates: decline for the few that do survive the early die-off. c) This would include organisms that produce: large numbers of offspring, but provide them with little or no care. d) Examples include: fishes, many plants, and most marine invertebrates. ...
... the young. b) It flattens out as death rates: decline for the few that do survive the early die-off. c) This would include organisms that produce: large numbers of offspring, but provide them with little or no care. d) Examples include: fishes, many plants, and most marine invertebrates. ...
Population Dynamics
... Notice that a population that has reached its carrying capacity still fluctuates, but averages out at the carrying capacity. ...
... Notice that a population that has reached its carrying capacity still fluctuates, but averages out at the carrying capacity. ...
Concepts and Principles of Population Dynamics
... dynamics of change in the population, an adaptation to the parasitic mode; diaIntrinsic features of populations: Nema- pause, aestivation, and cryptobiosis as todes, like other organisms, have definable mechanisms of survival of adverse condilife history strategies. These strategies can tions; and s ...
... dynamics of change in the population, an adaptation to the parasitic mode; diaIntrinsic features of populations: Nema- pause, aestivation, and cryptobiosis as todes, like other organisms, have definable mechanisms of survival of adverse condilife history strategies. These strategies can tions; and s ...
Population Biology
... Populations that seem to grow exponentially still have a carrying capacity - a population size that can be supported by prevailing conditions and resources. ...
... Populations that seem to grow exponentially still have a carrying capacity - a population size that can be supported by prevailing conditions and resources. ...
Biology Test
... _____41. What can cause a population to grow? a. The birthrate becomes higher than the death rate b. The birthrate stays the same, and the death rate increases. c. The birthrate becomes lower than the death rate d. The birthrate and the death rate remain the same. ____42. When individuals in a popul ...
... _____41. What can cause a population to grow? a. The birthrate becomes higher than the death rate b. The birthrate stays the same, and the death rate increases. c. The birthrate becomes lower than the death rate d. The birthrate and the death rate remain the same. ____42. When individuals in a popul ...
File
... population from increasing carrying capacity- largest population that an environment can support (based on limiting factors) There are three main limiting factors: 1- Food- if food is scarce, it becomes a limiting factor 2- Space- space is often a limiting factor for plants because it can determine ...
... population from increasing carrying capacity- largest population that an environment can support (based on limiting factors) There are three main limiting factors: 1- Food- if food is scarce, it becomes a limiting factor 2- Space- space is often a limiting factor for plants because it can determine ...
4. Population Dynamics new1
... 2.3.1: Construct simple keys and use published keys for the identification of organisms 2.3.2: Describe and evaluate methods for estimating abundance of organisms 2.6.1: Explain the concepts of limiting factors and carrying capacity in the context of population growth 2.6.2: Describe and explain s a ...
... 2.3.1: Construct simple keys and use published keys for the identification of organisms 2.3.2: Describe and evaluate methods for estimating abundance of organisms 2.6.1: Explain the concepts of limiting factors and carrying capacity in the context of population growth 2.6.2: Describe and explain s a ...
Chapter 5: Populations
... Limits To Growth • Limiting factors continued – Density-independent limiting factors do not rely on population size. • They include natural disasters and human activities such as damming rivers. • When such factors occur, many species show a rapid drop in population size. ...
... Limits To Growth • Limiting factors continued – Density-independent limiting factors do not rely on population size. • They include natural disasters and human activities such as damming rivers. • When such factors occur, many species show a rapid drop in population size. ...
Limiting Factors
... factors that prevent the continuous growth of a population. Because of limiting factors, the number of organisms in a population is often well below carrying capacity. ...
... factors that prevent the continuous growth of a population. Because of limiting factors, the number of organisms in a population is often well below carrying capacity. ...
EnvScisamplebooktestChp13Questions
... 2. The estimated smallest population that can maintain itself and its genetic variability indefinitely is termed: a) logistic carrying capacity b) maximum sustainable yield c) minimum viable population d) optimum sustainable population e) maximum sustainable population 3. The term for the maximum po ...
... 2. The estimated smallest population that can maintain itself and its genetic variability indefinitely is termed: a) logistic carrying capacity b) maximum sustainable yield c) minimum viable population d) optimum sustainable population e) maximum sustainable population 3. The term for the maximum po ...
LIMITING FACTORS QQ
... Unlike density independent factors, these will play are larger or smaller part in limiting growth depending on how dense the population is. Examples include: ...
... Unlike density independent factors, these will play are larger or smaller part in limiting growth depending on how dense the population is. Examples include: ...