SA Ecology
... roughly 10% of the chemical energy that the trophic level immediately below it receives in the same time-period. OR Other statement explaining the relation between productivity rates at successive levels of a food chain. B: Frogs are one trophic level above the grasshoppers in the pyramid, so by the ...
... roughly 10% of the chemical energy that the trophic level immediately below it receives in the same time-period. OR Other statement explaining the relation between productivity rates at successive levels of a food chain. B: Frogs are one trophic level above the grasshoppers in the pyramid, so by the ...
Ecology - Aurora City Schools
... 1. Exponential Growth Phase-When the population first starts growing, population growth is close to exponential growth 2. Transitional Phase- The population growth starts to slow 3. Plateau Phase- Carrying capacity is reached and the population is as big as it can theoretically get in its envi ...
... 1. Exponential Growth Phase-When the population first starts growing, population growth is close to exponential growth 2. Transitional Phase- The population growth starts to slow 3. Plateau Phase- Carrying capacity is reached and the population is as big as it can theoretically get in its envi ...
Populations
... tend to reduce population growth rates 6.7 S curve: Population growth and stabilization in response to environmental resistance ...
... tend to reduce population growth rates 6.7 S curve: Population growth and stabilization in response to environmental resistance ...
Population Dynamics Notes
... • As early as Darwin, scientists have realized that populations have the ability to grow exponentially • All populations have this ability, although not all populations realized this type of growth • Darwin pondered the question of exponential growth. He knew that all species had the potential to gr ...
... • As early as Darwin, scientists have realized that populations have the ability to grow exponentially • All populations have this ability, although not all populations realized this type of growth • Darwin pondered the question of exponential growth. He knew that all species had the potential to gr ...
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
... Installing ___________________ or nets in the populated region Counting the ____________________ animals and __________________ them with ________________, _________________, __________________ or ___________________ _______________________ the marked animals Reinstalling __________________ ...
... Installing ___________________ or nets in the populated region Counting the ____________________ animals and __________________ them with ________________, _________________, __________________ or ___________________ _______________________ the marked animals Reinstalling __________________ ...
Chapter 6 - ltcconline.net
... previous formula to: dN/dt=rN The d is for delta which represents change. Thus the formula would read: ―the change in the population (dN) per change in time (dt) is equal to the rate of change (r) times the population size (N).‖ This is a simple mathematical model of population ...
... previous formula to: dN/dt=rN The d is for delta which represents change. Thus the formula would read: ―the change in the population (dN) per change in time (dt) is equal to the rate of change (r) times the population size (N).‖ This is a simple mathematical model of population ...
Understanding Our Environment
... previous formula to: dN/dt=rN The d is for delta which represents change. Thus the formula would read: “the change in the population (dN) per change in time (dt) is equal to the rate of change (r) times the population size (N).” This is a simple mathematical model of population ...
... previous formula to: dN/dt=rN The d is for delta which represents change. Thus the formula would read: “the change in the population (dN) per change in time (dt) is equal to the rate of change (r) times the population size (N).” This is a simple mathematical model of population ...
Ch 9 ppt
... Combination of all the biotic and abiotic factors that may limit a population’s increase Replacement Level: when recruitment (young) = adults that have died ...
... Combination of all the biotic and abiotic factors that may limit a population’s increase Replacement Level: when recruitment (young) = adults that have died ...
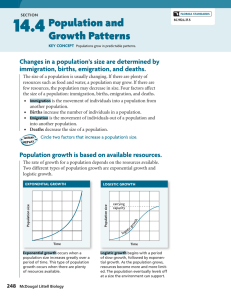
14.4 Population and Growth Patterns TEKS 11B, 12A, 12D
... Changes in a population’s size are determined by immigration, births, emigration, and deaths. • The size of a population is always changing. • Four factors affect the size of a population. – immigration – births – emigration – deaths ...
... Changes in a population’s size are determined by immigration, births, emigration, and deaths. • The size of a population is always changing. • Four factors affect the size of a population. – immigration – births – emigration – deaths ...
Mechanisms of Growth Regulation
... environment does not change, which is not the case. The carrying capacity varies annually: for example, some summers are hot and dry whereas others are cold and wet. In many areas, the carrying capacity during the winter is much lower than it is during the summer. Also, natural events such as earthq ...
... environment does not change, which is not the case. The carrying capacity varies annually: for example, some summers are hot and dry whereas others are cold and wet. In many areas, the carrying capacity during the winter is much lower than it is during the summer. Also, natural events such as earthq ...
Chapter 11
... Populations are also influenced by disease, predation, habitat quality, bad weather, etc. The best estimate of K is obtained by averaging the population size over time, which provides a mean population size. Populations tend towards this equilibrium through density-dependent factors. Regulatory fact ...
... Populations are also influenced by disease, predation, habitat quality, bad weather, etc. The best estimate of K is obtained by averaging the population size over time, which provides a mean population size. Populations tend towards this equilibrium through density-dependent factors. Regulatory fact ...
I can compare 2 different biomes by explaining how they are similar
... 15. Describe the three main properties of a population. 16. Describe exponential population growth. 17. Describe how the reproductive behavior of individuals can affect the growth rate of their population. 18. Explain how population sizes in nature are regulated. 19. Explain the difference between n ...
... 15. Describe the three main properties of a population. 16. Describe exponential population growth. 17. Describe how the reproductive behavior of individuals can affect the growth rate of their population. 18. Explain how population sizes in nature are regulated. 19. Explain the difference between n ...
Population-Limiting Factors
... What are the differences between density-independent and densitydependent limiting factors? What are the similarities between the different models used to quantify the growth of a population? ...
... What are the differences between density-independent and densitydependent limiting factors? What are the similarities between the different models used to quantify the growth of a population? ...
Population and Growth Patterns
... Ecological factors limit population growth. Many factors affect the carrying capacity of an environment for a population. The factor that has the greatest effect on limiting population growth is called the limiting factor. For example, if a lack of space is the biggest factor limiting population gro ...
... Ecological factors limit population growth. Many factors affect the carrying capacity of an environment for a population. The factor that has the greatest effect on limiting population growth is called the limiting factor. For example, if a lack of space is the biggest factor limiting population gro ...
Populations
... Like other organisms, the size of the human pop. tends to increase over time. Industrial Revolution begins ...
... Like other organisms, the size of the human pop. tends to increase over time. Industrial Revolution begins ...
Communities and Populations
... • Many species will show a characteristic “crash,” then the population will build back up right away, or stay low for some time • Environments are always changing, and most populations can adapt to a certain amount of change by growing or shrinking in size. • Major upsets in the ecosystem can lead t ...
... • Many species will show a characteristic “crash,” then the population will build back up right away, or stay low for some time • Environments are always changing, and most populations can adapt to a certain amount of change by growing or shrinking in size. • Major upsets in the ecosystem can lead t ...
Population Size and Limiting Factors
... particular species that the environment can normally and consistently support • An environment has a specific carrying capacity for each different species ...
... particular species that the environment can normally and consistently support • An environment has a specific carrying capacity for each different species ...
Chapter 4 Population Biology
... A. refers to the proportions of the population that are in different age levels B. shows the proportions of males and females in each age group and those within child bearing age and elderly (can help us predict trends in population growth) C. if the percentage of people in each age category is fair ...
... A. refers to the proportions of the population that are in different age levels B. shows the proportions of males and females in each age group and those within child bearing age and elderly (can help us predict trends in population growth) C. if the percentage of people in each age category is fair ...
Examining the Stages in Ecological Succession
... population of the Nitella was decreasing but the population of the snails kept increasing because they were still feeding on the Nitella present before they experienced a decrease in food supply. There was a competition within the species of snails and only the ‘fittest’ survived and the ‘not fit’ d ...
... population of the Nitella was decreasing but the population of the snails kept increasing because they were still feeding on the Nitella present before they experienced a decrease in food supply. There was a competition within the species of snails and only the ‘fittest’ survived and the ‘not fit’ d ...
Population Ecology notes
... He used elephants as an example because elephants are one of the slowest breeders on the planet One female will produce 6 young over her 100 yr life span. In a population, this amounts to a growth rate of 2% ...
... He used elephants as an example because elephants are one of the slowest breeders on the planet One female will produce 6 young over her 100 yr life span. In a population, this amounts to a growth rate of 2% ...
Slide 1
... Carrying capacity: The maximum size of a population that can be supported by an environment. ...
... Carrying capacity: The maximum size of a population that can be supported by an environment. ...
Population Growth and Regulation
... individuals that do not form social groups; occurs when resources are not scarce enough to require territorial spacing • Examples: Trees and other plants in rain forests ...
... individuals that do not form social groups; occurs when resources are not scarce enough to require territorial spacing • Examples: Trees and other plants in rain forests ...
Population Biology
... Life expectancy—probable # of years survival for individual at given age +/- Population Size Life span—longest period of life reached by organism Wide variation—minutes (bacteria) to thousands of years (bristle cone pines in ...
... Life expectancy—probable # of years survival for individual at given age +/- Population Size Life span—longest period of life reached by organism Wide variation—minutes (bacteria) to thousands of years (bristle cone pines in ...