Limiting Resources - Marine Discovery at the University of Arizona
... the metapopulation as a whole Are extremely important in marine populations because of the life histories of many marine animals (larval dispersal). Examples where metapopulation dynamics are important include a large barrier reef with nearby smaller reefs; an organism with a widely dispersing lar ...
... the metapopulation as a whole Are extremely important in marine populations because of the life histories of many marine animals (larval dispersal). Examples where metapopulation dynamics are important include a large barrier reef with nearby smaller reefs; an organism with a widely dispersing lar ...
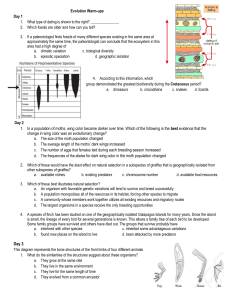
Unit 11 Evolution Warm ups
... Madagascar by floating across the Mozambique Channel on matted clumps of vegetation. 1. Lemur body types can vary widely. In addition to fossils and comparative anatomy, which of the following types of evidence can scientists reliably use to study the evolution of the variety of lemur body types? a. ...
... Madagascar by floating across the Mozambique Channel on matted clumps of vegetation. 1. Lemur body types can vary widely. In addition to fossils and comparative anatomy, which of the following types of evidence can scientists reliably use to study the evolution of the variety of lemur body types? a. ...
QA: Populations - Liberty Union High School District
... Exponential growth results in a graph of what shape? The change in population over time (growth rate) is represented by this letter? This equation/rule helps a scientist determine the amount of time required for a population to double in size? These factors affect populations randomly; examples incl ...
... Exponential growth results in a graph of what shape? The change in population over time (growth rate) is represented by this letter? This equation/rule helps a scientist determine the amount of time required for a population to double in size? These factors affect populations randomly; examples incl ...
Principles of Genetics, A BRIEF INTRODUCTION
... chromosomes; each chromosome exists in two homolohous forms, one of which is phenotypically realized. ...
... chromosomes; each chromosome exists in two homolohous forms, one of which is phenotypically realized. ...
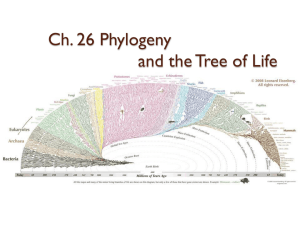
Ch 26 systematics phylogeny S
... change, based on genes that evolve at constant rates # nucleotide substitutions is proportional to elapsed time since species diverged from common ancestor Compare number of genetic differences with known evolutionary dates from fossil record to calibrate Average rate of genetic change can est ...
... change, based on genes that evolve at constant rates # nucleotide substitutions is proportional to elapsed time since species diverged from common ancestor Compare number of genetic differences with known evolutionary dates from fossil record to calibrate Average rate of genetic change can est ...
Evolution
... Hutton and Darwin proposed that geological processes were gradual and took many years to change, but they believed these processes are occurring today. True/False Lamarck believed that evolution occurred through the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Describe the difference between artificial ...
... Hutton and Darwin proposed that geological processes were gradual and took many years to change, but they believed these processes are occurring today. True/False Lamarck believed that evolution occurred through the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Describe the difference between artificial ...
APES Study Guide Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology
... 2. What do scientists study at each level of complexity? ...
... 2. What do scientists study at each level of complexity? ...
Chapter 17 evol of population Notes
... Because all members of a population can interbreed, they share a common group of genes, called a gene pool. Gene Pool – the combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population. ...
... Because all members of a population can interbreed, they share a common group of genes, called a gene pool. Gene Pool – the combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population. ...
1 Natural hybridization – crossings in nature between individuals
... The majority of the studies on natural hybridization has been focused on one pair of species, in the case of genus Quercus, on pedunculate (Quercus robur) and sessile oak (Q. petraea) (e.g. Bacilieri et al. 1996, Evolution; Gugerli et al. 2007, Annals of Botany). A few studies have investigated the ...
... The majority of the studies on natural hybridization has been focused on one pair of species, in the case of genus Quercus, on pedunculate (Quercus robur) and sessile oak (Q. petraea) (e.g. Bacilieri et al. 1996, Evolution; Gugerli et al. 2007, Annals of Botany). A few studies have investigated the ...
Characteristics of Populations
... Density-Dependent Limiting Factors • Factors that are related to the density of a population: 1. Competition •Organisms compete for food, water, space, sunlight, and other essentials 2. Predation •Population control caused by predator-prey relationships 3. Parasitism and disease •Robs organisms of ...
... Density-Dependent Limiting Factors • Factors that are related to the density of a population: 1. Competition •Organisms compete for food, water, space, sunlight, and other essentials 2. Predation •Population control caused by predator-prey relationships 3. Parasitism and disease •Robs organisms of ...
Ch. 21-Forces within Populations Notesheet
... Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution Natural selection acts on phenotypic variations within populations. Evolutionary change is also driven by random processes. Biological evolution is supported by scientific evidence from many disciplines including mathematics Organisms share many co ...
... Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution Natural selection acts on phenotypic variations within populations. Evolutionary change is also driven by random processes. Biological evolution is supported by scientific evidence from many disciplines including mathematics Organisms share many co ...
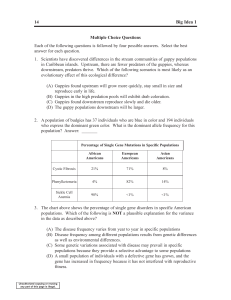
Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
... (B) The species will repopulate in the same manner as prior to the natural disaster. (C) Post extinction species may fail to diversify due to the changes in the ecosystem that are not suited to their survival. (D) The genetic diversity of the population will decrease, as a bottleneck was incurred. ...
... (B) The species will repopulate in the same manner as prior to the natural disaster. (C) Post extinction species may fail to diversify due to the changes in the ecosystem that are not suited to their survival. (D) The genetic diversity of the population will decrease, as a bottleneck was incurred. ...
Evolution: A history and a process
... a. Which color moth would have a better chance of surviving predation (better camoflage to hide from predators) on this dark surface? b.How does this help explain the change in the colors of the moth population shown in the graph? c. Clean Air Acts were passed by governments of industrialized nation ...
... a. Which color moth would have a better chance of surviving predation (better camoflage to hide from predators) on this dark surface? b.How does this help explain the change in the colors of the moth population shown in the graph? c. Clean Air Acts were passed by governments of industrialized nation ...
3.1 Notes ws
... 6. Which level of organization contains all of the organisms of one species that live in a certain area? 7. What is the highest level of organization studied by ecologists? 8. A group of populations is called a(n) 9. Which includes animals of different species living together? Circle the correct ans ...
... 6. Which level of organization contains all of the organisms of one species that live in a certain area? 7. What is the highest level of organization studied by ecologists? 8. A group of populations is called a(n) 9. Which includes animals of different species living together? Circle the correct ans ...
Introduction to Biology II - University of Houston–Downtown
... – Gene diversity – Nucleotide diversity ...
... – Gene diversity – Nucleotide diversity ...
Evolution (Speciation)
... evolutionary relationships. 8.g* Students know how several independent molecular clocks, calibrated against each other and combined with evidence from the fossil record, can help to estimate how long ago various groups of organisms diverged evolutionarily from one another. ...
... evolutionary relationships. 8.g* Students know how several independent molecular clocks, calibrated against each other and combined with evidence from the fossil record, can help to estimate how long ago various groups of organisms diverged evolutionarily from one another. ...
Ch 25 and 26 Phylogeny and The History of Life on Earth
... Evaluating Molecular Homologies • The more time that has passed, the more mutations in the DNA sequences of organisms and the less closely related they are. • This can be used as a fairly accurate “molecular clock” since the rate of some gene mutations is constant. ...
... Evaluating Molecular Homologies • The more time that has passed, the more mutations in the DNA sequences of organisms and the less closely related they are. • This can be used as a fairly accurate “molecular clock” since the rate of some gene mutations is constant. ...
Limiting Factors- Anything that prevents a population sized form
... Exotic species – species that are not naturally native – brought in by humans Rabbits in Australia – see text book ...
... Exotic species – species that are not naturally native – brought in by humans Rabbits in Australia – see text book ...
Document
... is land, water, air pollution. • Global climate change is a very great challenge. The changes we are experiencing today are a result of human activities. The planet’s climate change had impacted types of organisms. Water shortages are becoming more common. Diseases can spread more rapidly with incre ...
... is land, water, air pollution. • Global climate change is a very great challenge. The changes we are experiencing today are a result of human activities. The planet’s climate change had impacted types of organisms. Water shortages are becoming more common. Diseases can spread more rapidly with incre ...
USA Science and Engineering Festival Expo 2012
... evolutionary ”Tree of Life”. You will use some molecular biological knowledge of DNA and use some of its powerful tools to answer the question “How can a gene from a jellyfish make bacteria and fish glow?” The answer lies in creating an artificial genetically engineered piece of DNA called a plasmid ...
... evolutionary ”Tree of Life”. You will use some molecular biological knowledge of DNA and use some of its powerful tools to answer the question “How can a gene from a jellyfish make bacteria and fish glow?” The answer lies in creating an artificial genetically engineered piece of DNA called a plasmid ...