TISBE: TAXONOMIC INFORMATION SYSTEM FOR THE BELGIAN CONTINENTAL SHELF
... Register of Marine Species, the Biodiversity Database and CD ROM series of ETI). The TISBE database is integrated in the other databases of VLIZ: literature, databases, experts and institutions will be taken from the Integrated Marine Information System (IMIS). The objective of TISBE is to become a ...
... Register of Marine Species, the Biodiversity Database and CD ROM series of ETI). The TISBE database is integrated in the other databases of VLIZ: literature, databases, experts and institutions will be taken from the Integrated Marine Information System (IMIS). The objective of TISBE is to become a ...
Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of
... Although natural selection is usually the major mechanism for evolution, genetic variation in populations can occur through other processes, including mutation, genetic drift, sexual selection and artificial selection. Inbreeding, small population size, nonrandom mating, the absence of migration, an ...
... Although natural selection is usually the major mechanism for evolution, genetic variation in populations can occur through other processes, including mutation, genetic drift, sexual selection and artificial selection. Inbreeding, small population size, nonrandom mating, the absence of migration, an ...
IB Biology Ecology Exam 2004
... B) herbivores. C) carnivores. D) detritivores. E) saprotrophs. 27_______Organisms that feed on dead organic matter by digesting it outside their bodies before absorbing it are known as A) producers. B) herbivores. C) carnivores. D) detritivores. E) saprotrophs. 28_______A term which includes an orga ...
... B) herbivores. C) carnivores. D) detritivores. E) saprotrophs. 27_______Organisms that feed on dead organic matter by digesting it outside their bodies before absorbing it are known as A) producers. B) herbivores. C) carnivores. D) detritivores. E) saprotrophs. 28_______A term which includes an orga ...
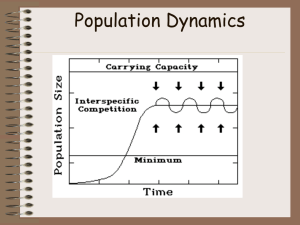
Population Dynamics
... Examples: For Neodiprion sawflies, winter surviorship is greatly affected by the weather, which is density-independent. During the summer, however, parasitic wasps impose very high density-dependent mortality. Pacific mussels, Mytillus sp., are largely limited by density-dependent competition for sp ...
... Examples: For Neodiprion sawflies, winter surviorship is greatly affected by the weather, which is density-independent. During the summer, however, parasitic wasps impose very high density-dependent mortality. Pacific mussels, Mytillus sp., are largely limited by density-dependent competition for sp ...
now we have the mechanism for natural selection
... make sense of how evolution worked. • Building on Mendel’s genetics, studies showed how characteristics in a population could be selected by environmental pressures which causes a population to become progressively adapted. • This Modern Synthesis, as Julian Huxley called it, brought Darwin’s Natura ...
... make sense of how evolution worked. • Building on Mendel’s genetics, studies showed how characteristics in a population could be selected by environmental pressures which causes a population to become progressively adapted. • This Modern Synthesis, as Julian Huxley called it, brought Darwin’s Natura ...
Chapter Sixteen ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS d, b, a, e, c, f
... phenotype, which is what natural selection acts upon. 14. Data are missing, and many trees can account for limited data. 15. Y chromosome and mitochondrial DNA sequences enable researchers to trace the genetic contributions of paternal and maternal relatives, but represent only some of a person’s an ...
... phenotype, which is what natural selection acts upon. 14. Data are missing, and many trees can account for limited data. 15. Y chromosome and mitochondrial DNA sequences enable researchers to trace the genetic contributions of paternal and maternal relatives, but represent only some of a person’s an ...
CH 17: Populations
... A typical two-week course of antibiotics can exert selection pressure on over a thousand generations of bacteria. If ANY remain, they do so because they may have a mutated gene that causes a resistance to these antibiotics. Antibiotic resistant strains are now found everywhere, in hospitals and s ...
... A typical two-week course of antibiotics can exert selection pressure on over a thousand generations of bacteria. If ANY remain, they do so because they may have a mutated gene that causes a resistance to these antibiotics. Antibiotic resistant strains are now found everywhere, in hospitals and s ...
1. Information about the target species or related species List and
... If there is certainty about the species and the source, and the trade involves a low risk activity, then its relatively easy to make an NDF from basic sources (e.g. Distribution range, Population size, conservation status, trade frequency and intensity, basic life history information on vulnerable s ...
... If there is certainty about the species and the source, and the trade involves a low risk activity, then its relatively easy to make an NDF from basic sources (e.g. Distribution range, Population size, conservation status, trade frequency and intensity, basic life history information on vulnerable s ...
CP Biology - Northern Highlands
... interact to affect the survival of organisms? 2. What is a trophic level? What is meant by “The 10% Rule” and why does it limit the total number of trophic levels in an ecosystem? 3. How does the way that matter (chemicals) moves through the biosphere differ from the way energy flows? 4. List four s ...
... interact to affect the survival of organisms? 2. What is a trophic level? What is meant by “The 10% Rule” and why does it limit the total number of trophic levels in an ecosystem? 3. How does the way that matter (chemicals) moves through the biosphere differ from the way energy flows? 4. List four s ...
effects of anthropogenic disturbance on habitat and life history
... and mitigating controllable threats where possible. As a large portion of S. jejuna’s habitat has been anthropogenically-disturbed, understanding the effects of disturbance on species persistence are central to promoting species recovery. An assessment of habitat features revealed that anthropogenic ...
... and mitigating controllable threats where possible. As a large portion of S. jejuna’s habitat has been anthropogenically-disturbed, understanding the effects of disturbance on species persistence are central to promoting species recovery. An assessment of habitat features revealed that anthropogenic ...
01 - cloudfront.net
... 17. Mutualism and commensalism are two types of ______________________. 18. In the face of competition, an organism may occupy only part of its fundamental niche. That part is called its ______________________ ______________________. 19. A characteristic of ______________________ is that these organ ...
... 17. Mutualism and commensalism are two types of ______________________. 18. In the face of competition, an organism may occupy only part of its fundamental niche. That part is called its ______________________ ______________________. 19. A characteristic of ______________________ is that these organ ...
Ecology Unit Test Study Guide
... Plants produce their own food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight (photosynthesis). This is different than ...
... Plants produce their own food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight (photosynthesis). This is different than ...
Set 1 - Edquest Science
... TAXONOMY The two-name Latin naming system for all living things was developed by Carolus Linnaeus. This classification system was much more reliable than previous systems, because he used structure, rather than habitat. Two words identify each organism. The 1st represents the organisms genus and the ...
... TAXONOMY The two-name Latin naming system for all living things was developed by Carolus Linnaeus. This classification system was much more reliable than previous systems, because he used structure, rather than habitat. Two words identify each organism. The 1st represents the organisms genus and the ...
Jeopardy - Mr. Manskopf Environmental Science
... b. secondary succession. c. tertiary succession. d. a climax community. ...
... b. secondary succession. c. tertiary succession. d. a climax community. ...
Ecosystem Interactions
... competitive relationships are Understand the concept of equilibrium and how limiting factors contribute to creating it (e.g. carrying capacity) ...
... competitive relationships are Understand the concept of equilibrium and how limiting factors contribute to creating it (e.g. carrying capacity) ...
Ecology Unit Exam - Ecology Unit Plan
... Niche: all strategies and adaptations a species uses in its environment (how it meets its specific needs for food and shelter, how and where it survives [habitat], and where it reproduces. In essence, a species' niche includes all of its interactions with the biotic and abiotic parts of its environm ...
... Niche: all strategies and adaptations a species uses in its environment (how it meets its specific needs for food and shelter, how and where it survives [habitat], and where it reproduces. In essence, a species' niche includes all of its interactions with the biotic and abiotic parts of its environm ...
Population Dynamics
... available (Slows population growth rate) Slow population growth rate due to 1. Decrease in birthrate 2. Increase in deathrate 3. Immigration decreases 4. Emigration increases ...
... available (Slows population growth rate) Slow population growth rate due to 1. Decrease in birthrate 2. Increase in deathrate 3. Immigration decreases 4. Emigration increases ...
I. What is Ecology? A. Definition: The study of the interactions of
... So, that's what "nature" does; it might be important to understand how these systems operate and respond to change. 2. Humans have always affected these systems - In the past, humans affected local ecosystems and were never able to sustain an equilibrium with their environment. They either moved (An ...
... So, that's what "nature" does; it might be important to understand how these systems operate and respond to change. 2. Humans have always affected these systems - In the past, humans affected local ecosystems and were never able to sustain an equilibrium with their environment. They either moved (An ...
B 262, F 2007
... bacterium and prescribes penicillin. The infection symptoms disappeared after taking the antibiotic for about 4 days and Edna stopped taking the penicillin (long before the end of her prescription). The infection again returned a little more than a week after she stopped the penicillin, so Edna took ...
... bacterium and prescribes penicillin. The infection symptoms disappeared after taking the antibiotic for about 4 days and Edna stopped taking the penicillin (long before the end of her prescription). The infection again returned a little more than a week after she stopped the penicillin, so Edna took ...
Ecology 2.1
... pattern over time. The number of individuals in the population may rise and fall, depending on the season or other conditions, or as a result of interactions with other organisms. Patterns in Living Space The patterns formed by a population often show how the population meets its needs. For example, ...
... pattern over time. The number of individuals in the population may rise and fall, depending on the season or other conditions, or as a result of interactions with other organisms. Patterns in Living Space The patterns formed by a population often show how the population meets its needs. For example, ...