Ecosystems
... Community Interactions Community: all the LIVING organisms in an ecosystem that live and interact together 3 types of interactions: 1. Competition 2. Predation (predator/prey) 3. Symbiosis ...
... Community Interactions Community: all the LIVING organisms in an ecosystem that live and interact together 3 types of interactions: 1. Competition 2. Predation (predator/prey) 3. Symbiosis ...
Ecology - Humble ISD
... ocean organisms like whales. However, they do not help or cause any harm to them. B). Make up one of your own. ...
... ocean organisms like whales. However, they do not help or cause any harm to them. B). Make up one of your own. ...
u tigLe thai e - Mrs. Moore`s Advisory Page
... Some biologists think that certain species, such as alligators and wolves, help maintain biological diversity in their ecosystems. Predict what might happen to other organisms, such as gar fish or herons, if alligators were to become extinct in the Florida Everglades. ...
... Some biologists think that certain species, such as alligators and wolves, help maintain biological diversity in their ecosystems. Predict what might happen to other organisms, such as gar fish or herons, if alligators were to become extinct in the Florida Everglades. ...
Habitat
... 1. What kind of symbiotic relationship does a lichen exhibit? 2. Identify 2 organisms that have a predator/prey relationship? 3. Two male gorillas compete for territory. Is this interspecific or intra-specific competition? 4. The competitive exclusion principle says that no 2 species can occupy the ...
... 1. What kind of symbiotic relationship does a lichen exhibit? 2. Identify 2 organisms that have a predator/prey relationship? 3. Two male gorillas compete for territory. Is this interspecific or intra-specific competition? 4. The competitive exclusion principle says that no 2 species can occupy the ...
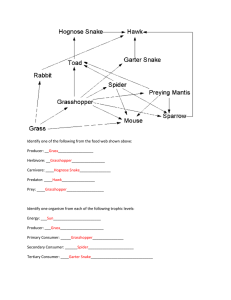
Identify one of the following from the food web shown above
... Explain how the development of agriculture can be harmful to the environment even though it is beneficial to society. A. Deforestation for farming destroys natural habitats and can cause habitat fragmentation B. Deforestation can cause desertification if the soil is allowed to erode C. Chemical pest ...
... Explain how the development of agriculture can be harmful to the environment even though it is beneficial to society. A. Deforestation for farming destroys natural habitats and can cause habitat fragmentation B. Deforestation can cause desertification if the soil is allowed to erode C. Chemical pest ...
Week 2-3 Notes File
... One species (parasite) obtains energy by living off of another species. EX: Tapeworms live in the intestines of a dog, absorbing nutrients from the food it eats ...
... One species (parasite) obtains energy by living off of another species. EX: Tapeworms live in the intestines of a dog, absorbing nutrients from the food it eats ...
Grade 9 Science – Biology - Frontenac Secondary School
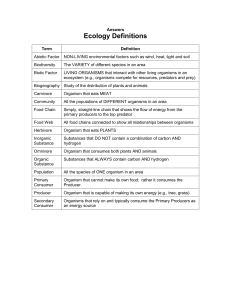
... NON-LIVING environmental factors such as wind, heat, light and soil Biotic Factor LIVING ORGANISMS that interact with other living organisms in an ecosystem (e.g., organisms compete for resources, predators and prey) Habitat Environmental area that is inhabited by a particular species Niche ...
... NON-LIVING environmental factors such as wind, heat, light and soil Biotic Factor LIVING ORGANISMS that interact with other living organisms in an ecosystem (e.g., organisms compete for resources, predators and prey) Habitat Environmental area that is inhabited by a particular species Niche ...
Exam 4 Review Part I
... b. Warm air has a greater ability to hold water c. Warm air cools as it rises d. Descending air absorbs moisture e. Atmospheric air holds more water than air near Earth 14. One species in a given space and time is called a ___. a. Population b. Community c. Ecosystem d. Biome e. Biosphere ...
... b. Warm air has a greater ability to hold water c. Warm air cools as it rises d. Descending air absorbs moisture e. Atmospheric air holds more water than air near Earth 14. One species in a given space and time is called a ___. a. Population b. Community c. Ecosystem d. Biome e. Biosphere ...
AP Biology - Christian Unified Schools
... Pick one of the case studies presented in the chapter (greater prairie chickens, recockaded woodpeckers, or grizzly bears). Explain why the population was threatened and how conservation efforts were aimed towards helping the struggling population. ...
... Pick one of the case studies presented in the chapter (greater prairie chickens, recockaded woodpeckers, or grizzly bears). Explain why the population was threatened and how conservation efforts were aimed towards helping the struggling population. ...
• The study of the interactions between organisms and their
... • One mechanism for evolution • Requires the following be true – Populations are variable – Variations are heritable – Variations affect individuals ability to acquire resources – Resources are limited, individuals compete, and those who are best at getting resources reproduce the most -> are most f ...
... • One mechanism for evolution • Requires the following be true – Populations are variable – Variations are heritable – Variations affect individuals ability to acquire resources – Resources are limited, individuals compete, and those who are best at getting resources reproduce the most -> are most f ...
Name
... 12E: Describe the flow of matter through the carbon and nitrogen cycles and explain the consequences of disrupting ...
... 12E: Describe the flow of matter through the carbon and nitrogen cycles and explain the consequences of disrupting ...
Adaptations - cloudfront.net
... The change that makes organisms better suited to their environments develop through a process called Natural selection. ...
... The change that makes organisms better suited to their environments develop through a process called Natural selection. ...
Ecology Unit - Houston ISD
... 2) Ecosystem = all organisms and nonliving components in a particular place 3) Community = all interacting organisms living in an area - includes only living things 4) Population = all the members of a species that live in one place at one time 5) Organism = one of that species Components of the Env ...
... 2) Ecosystem = all organisms and nonliving components in a particular place 3) Community = all interacting organisms living in an area - includes only living things 4) Population = all the members of a species that live in one place at one time 5) Organism = one of that species Components of the Env ...
NICHE CONCEPT Every organism has a place to live in nature, a
... Every organism has a place to live in nature, a functional role in that place, and a complex set of adaptations for reproducing its kind. On the surface, this observation might seem to be obvious, even trivial. However, in order to understand our biological world—the biosphere, how it operates and u ...
... Every organism has a place to live in nature, a functional role in that place, and a complex set of adaptations for reproducing its kind. On the surface, this observation might seem to be obvious, even trivial. However, in order to understand our biological world—the biosphere, how it operates and u ...
Ecology
... is lost to heat from one level to the next. Only 10% of your food is actually incorporated into making you! ...
... is lost to heat from one level to the next. Only 10% of your food is actually incorporated into making you! ...
Science 10 Chapter 1.2
... The organism that is harmed is call the ‘host’ host is not usually killed (unintentionally) ...
... The organism that is harmed is call the ‘host’ host is not usually killed (unintentionally) ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.