Population Structures
... distribution of conditions to which individuals of the species were well adapted. If these conditions are common population should also be common Plus: a species should be more abundant at the center of its ...
... distribution of conditions to which individuals of the species were well adapted. If these conditions are common population should also be common Plus: a species should be more abundant at the center of its ...
Genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity
... determines the characteristics of all species and individuals that make up the diversity of the living world. The number of possible combinations of genes and of the molecules making up genes is immense - much larger than the number of individuals making up a species. Genetic diversity refers to the ...
... determines the characteristics of all species and individuals that make up the diversity of the living world. The number of possible combinations of genes and of the molecules making up genes is immense - much larger than the number of individuals making up a species. Genetic diversity refers to the ...
Interspecific Communication
... gradually developing the ability to discriminate. (Hauser 2000:302-306). Recognition of interspecific alarm calls: vervets • Vervets, even infants, recognize alarm calls of many birds (e.g. superb starling, Spreo superbus) (Hauser 1988). • Vervets listen more attentively to interspecific vocalizatio ...
... gradually developing the ability to discriminate. (Hauser 2000:302-306). Recognition of interspecific alarm calls: vervets • Vervets, even infants, recognize alarm calls of many birds (e.g. superb starling, Spreo superbus) (Hauser 1988). • Vervets listen more attentively to interspecific vocalizatio ...
Lecture 30
... Mustard is not grazed by indigenous herbivores so dead plant material is leading to high fuel loads . . . . . and fire Plant ecologists fear the formerly saguarodominated landscapes may morph into something that more closely resembles savannah as native plants with no defense to fire are killed ...
... Mustard is not grazed by indigenous herbivores so dead plant material is leading to high fuel loads . . . . . and fire Plant ecologists fear the formerly saguarodominated landscapes may morph into something that more closely resembles savannah as native plants with no defense to fire are killed ...
Relationships between organisms
... Experiment: Interspecific Competition • The distribution of these two barnacles is a result of a combination of: – Interspecific competition: Chthamalus is excluded from the lower zone by Balanus – Adaptations to dryness and heat: Balanus cannot survive in the upper zone but ...
... Experiment: Interspecific Competition • The distribution of these two barnacles is a result of a combination of: – Interspecific competition: Chthamalus is excluded from the lower zone by Balanus – Adaptations to dryness and heat: Balanus cannot survive in the upper zone but ...
Biodiversity and Endangered Species Review Sheet
... about $1000000 on the red wolf for a few years. Recent DNA studies reveal that the red wolf is really a hybrid of the coyote and timber wolf and not a separate species at all. Any time you need a red wolf, just cross a coyote and a wolf. Red wolves are smaller than wolves, unable to bring down large ...
... about $1000000 on the red wolf for a few years. Recent DNA studies reveal that the red wolf is really a hybrid of the coyote and timber wolf and not a separate species at all. Any time you need a red wolf, just cross a coyote and a wolf. Red wolves are smaller than wolves, unable to bring down large ...
Document
... Hunting and fishing - Extermination of passenger pigeon Over Fishing has depleted the stock of cod, salmon, haddock, grouper, anchovies and sardines are in sharp decline. In the late 1800s, the passenger pigeon flocks were in the millions. They were good to eat, their feathers made good pillows and ...
... Hunting and fishing - Extermination of passenger pigeon Over Fishing has depleted the stock of cod, salmon, haddock, grouper, anchovies and sardines are in sharp decline. In the late 1800s, the passenger pigeon flocks were in the millions. They were good to eat, their feathers made good pillows and ...
Master spécialité Ecologie, Biodiversité et Evolution (EBE)
... Exotic weedy plants and Eurasian earthworms are invading many forests and natural areas in North America. These organisms are having serious impacts, reducing native plant cover and diversity and perhaps changing soil conditions and interactions with mycorrhizae. It is thus of considerable interest ...
... Exotic weedy plants and Eurasian earthworms are invading many forests and natural areas in North America. These organisms are having serious impacts, reducing native plant cover and diversity and perhaps changing soil conditions and interactions with mycorrhizae. It is thus of considerable interest ...
CH 43 Populations Notes - Lincoln Park High School
... In stressful conditions, more resources go to maintaining homeostasis Life-history tradeoffs—negative relationships among growth, reproduction, and survival Ex: investments in reproduction may be at the expense of survivorship or growth; age at first reproduction is younger in large clutch size ...
... In stressful conditions, more resources go to maintaining homeostasis Life-history tradeoffs—negative relationships among growth, reproduction, and survival Ex: investments in reproduction may be at the expense of survivorship or growth; age at first reproduction is younger in large clutch size ...
Eating for Energy
... O How would the presence of wolves affect the organisms in their food web? O What do wolves eat? O What eats wolves? O Would this species affect the food web? ...
... O How would the presence of wolves affect the organisms in their food web? O What do wolves eat? O What eats wolves? O Would this species affect the food web? ...
In populations being controlled by density
... in harmony with the surrounding environment…in other words, reach its carrying capacity (K). If a population tends to B remain about the same size, then it is said to be stable. There are basically two different types of natural population regulation classified according to the types of factors that ...
... in harmony with the surrounding environment…in other words, reach its carrying capacity (K). If a population tends to B remain about the same size, then it is said to be stable. There are basically two different types of natural population regulation classified according to the types of factors that ...
Ch. 8: Survival of Species
... What Is a Species? • A species is a group of organisms that can reproduce with each other and create offspring (babies.) • Animals that are not part of the same species cannot have offspring. • If I were to attempt to mate a cat and a dog, they would not produce kittens or puppies. ...
... What Is a Species? • A species is a group of organisms that can reproduce with each other and create offspring (babies.) • Animals that are not part of the same species cannot have offspring. • If I were to attempt to mate a cat and a dog, they would not produce kittens or puppies. ...
How Introduced Species Affect Ecosystems
... • Many introduced species help or at least do not harm the ecosystem they come to. • However, some take over the habitat of the native species. These are called invasive species. • Invasive species often have high reproduction rates, are aggressive competitors, and lack natural predators. ...
... • Many introduced species help or at least do not harm the ecosystem they come to. • However, some take over the habitat of the native species. These are called invasive species. • Invasive species often have high reproduction rates, are aggressive competitors, and lack natural predators. ...
interspecies interaction - University of Minnesota Duluth
... The chance of a predator locating such a bird is probably less than when the bird is actively rearing the brood. Thus there is an actual density (this is difficult if not impossible to determine) and there is an apparent density, or a population level that appears to exist based on direct or indirec ...
... The chance of a predator locating such a bird is probably less than when the bird is actively rearing the brood. Thus there is an actual density (this is difficult if not impossible to determine) and there is an apparent density, or a population level that appears to exist based on direct or indirec ...
Interactions 1 in Ecosystems - Kossmann
... same resources, as shown in FIGURE 1.2. But when two species use the same resources in the same ways, one species will always be better adapted to the environment. The principle of competitive exclusion states that when two species are competing for the same resources, one species will be better sui ...
... same resources, as shown in FIGURE 1.2. But when two species use the same resources in the same ways, one species will always be better adapted to the environment. The principle of competitive exclusion states that when two species are competing for the same resources, one species will be better sui ...
Population Dynamics Notes
... Population Dispersion Uniform: Individuals are regularly spaced in the environment - ex. Creosote bush due to antagonism between individuals, or do to regular spacing of resources rare because resources are rarely evenly spaced Random: Individuals are randomly dispersed in the environment ex. Dande ...
... Population Dispersion Uniform: Individuals are regularly spaced in the environment - ex. Creosote bush due to antagonism between individuals, or do to regular spacing of resources rare because resources are rarely evenly spaced Random: Individuals are randomly dispersed in the environment ex. Dande ...
Figure 40-4
... strong effect on the species involved that each evolves ways to reduce any overlap in needs In other words, each species specializes within the community, developing its own well-defined, ecological niche ...
... strong effect on the species involved that each evolves ways to reduce any overlap in needs In other words, each species specializes within the community, developing its own well-defined, ecological niche ...
Math Topic 11
... 14. Megan’s dog Sparky eats 4_14 cups of food each day. Explain how Megan can determine how much food to give Sparky if she needs to feed him only _23 as much. Solve the problem. ...
... 14. Megan’s dog Sparky eats 4_14 cups of food each day. Explain how Megan can determine how much food to give Sparky if she needs to feed him only _23 as much. Solve the problem. ...
File - Brickell Academy Life Science
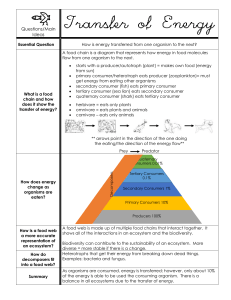
... diverse = more stable if there is a change. Heterotrophs that get their energy from breaking down dead things. Examples: bacteria and fungus. As organisms are consumed, energy is transferred; however, only about 10% of the energy is able to be used the consuming organism. There is a balance in all e ...
... diverse = more stable if there is a change. Heterotrophs that get their energy from breaking down dead things. Examples: bacteria and fungus. As organisms are consumed, energy is transferred; however, only about 10% of the energy is able to be used the consuming organism. There is a balance in all e ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.