eandb2 15 kb eandb2
... Define “frequency dependent selection”, and describe some of the ways it can arise in nature. Give examples whenever possible. In the natural habitats of populations of organisms, there are always many different reasons behind a change in the frequency of a particular phenotype, whether there are sp ...
... Define “frequency dependent selection”, and describe some of the ways it can arise in nature. Give examples whenever possible. In the natural habitats of populations of organisms, there are always many different reasons behind a change in the frequency of a particular phenotype, whether there are sp ...
In the Wild - Maryland Zoo
... o Also sometimes hunt cooperatively which increases survival rates o Establish and defend large territories (range from 0.2-5.5 square kilometers) – territory size depends on the availability of food and other resources Lifespan: Highest recorded age of 14 years 11 months Ecosystem relationships: Pr ...
... o Also sometimes hunt cooperatively which increases survival rates o Establish and defend large territories (range from 0.2-5.5 square kilometers) – territory size depends on the availability of food and other resources Lifespan: Highest recorded age of 14 years 11 months Ecosystem relationships: Pr ...
allopatric speciation
... • Certain kinds of individuals will have greater reproductive success; these kinds will become more common in the population after many generations Fossils & Evolution—Chapter 3 ...
... • Certain kinds of individuals will have greater reproductive success; these kinds will become more common in the population after many generations Fossils & Evolution—Chapter 3 ...
Brush-tailed rock-wallaby Petrogale penicillata
... Change 2008) generated a high level of community interest. Its objectives are to: • increase recruitment at priority sites • decrease the rate of decline in range and abundance • prevent the decline of the species to a level at which it would risk becoming extinct in the wild • increase knowledg ...
... Change 2008) generated a high level of community interest. Its objectives are to: • increase recruitment at priority sites • decrease the rate of decline in range and abundance • prevent the decline of the species to a level at which it would risk becoming extinct in the wild • increase knowledg ...
Interactions Study Guide
... have to go and find it (all animals with the exception of the bacteria—as far as we know, which isn’t that far). Consumers are classified according to what they eat and how far up they are on the food chain. a. Primary or first-order consumers eat only plants (producers). These are also called herbi ...
... have to go and find it (all animals with the exception of the bacteria—as far as we know, which isn’t that far). Consumers are classified according to what they eat and how far up they are on the food chain. a. Primary or first-order consumers eat only plants (producers). These are also called herbi ...
Ch. 3—Key concepts
... • Certain kinds of individuals will have greater reproductive success; these kinds will become more common in the population after many generations Fossils & Evolution—Chapter 3 ...
... • Certain kinds of individuals will have greater reproductive success; these kinds will become more common in the population after many generations Fossils & Evolution—Chapter 3 ...
Iconic species project: brush-tailed rock
... Change 2008) generated a high level of community interest. Its objectives are to: • increase recruitment at priority sites • decrease the rate of decline in range and abundance • prevent the decline of the species to a level at which it would risk becoming extinct in the wild • increase knowledg ...
... Change 2008) generated a high level of community interest. Its objectives are to: • increase recruitment at priority sites • decrease the rate of decline in range and abundance • prevent the decline of the species to a level at which it would risk becoming extinct in the wild • increase knowledg ...
Trophic Structure & Food Webs
... Food Chains: short, direct transfer of energy from phytoplankton to apex predators ...
... Food Chains: short, direct transfer of energy from phytoplankton to apex predators ...
MESOSTIGMATA
... depend on the phytoseiid species, prey species, population density of the prey, environmental conditions (climate, alternative food). Usually males develop more quickly than females. ...
... depend on the phytoseiid species, prey species, population density of the prey, environmental conditions (climate, alternative food). Usually males develop more quickly than females. ...
11-Summary, Outline, End Ch Questions
... A. One way to prevent overfishing is to develop better ways to protect fish populations. The maximum sustained yield mathematical model is used, but indications are that it has hastened the collapse of most commercially valuable stocks for several reasons. B. Optimum sustained yield is a concept tha ...
... A. One way to prevent overfishing is to develop better ways to protect fish populations. The maximum sustained yield mathematical model is used, but indications are that it has hastened the collapse of most commercially valuable stocks for several reasons. B. Optimum sustained yield is a concept tha ...
What is Biodiversity? www.syngenta.co.uk/learningzone Farmland
... Biodiversity is about a sustainable future. It is the starting point for many of the things we use every day, whether it is the food we eat, the medicines we use or the leisure pursuits we enjoy. It is also responsible for regulating key aspects of the Earth’s ecological balance, for example, nutrie ...
... Biodiversity is about a sustainable future. It is the starting point for many of the things we use every day, whether it is the food we eat, the medicines we use or the leisure pursuits we enjoy. It is also responsible for regulating key aspects of the Earth’s ecological balance, for example, nutrie ...
Biotic and abiotic factors interact in complex ways in communities
... What are the interactions between the levels of biological communities? What is the difference between an organism’s habitat and its niche? ...
... What are the interactions between the levels of biological communities? What is the difference between an organism’s habitat and its niche? ...
Biology Big Ideas
... Organisms in an ecosystem constantly interact. The interactions among the organisms generate stability within ecosystems. o Predation is an interaction between species in which one species (the predator) eats the other (the prey). Fluctuations in predator–prey populations are predictable. At some ...
... Organisms in an ecosystem constantly interact. The interactions among the organisms generate stability within ecosystems. o Predation is an interaction between species in which one species (the predator) eats the other (the prey). Fluctuations in predator–prey populations are predictable. At some ...
ECOSYSTEMS AND BIODIVERSITY
... A forest is an area with a high density of trees. World’s total land area is 13,076 million hectares - (Source: FAO; 1989) Of which total forests account for about 31% of the world’s land area. In India, the forest cover is roughly 19% of the total land area. The forest ecosystems are of g ...
... A forest is an area with a high density of trees. World’s total land area is 13,076 million hectares - (Source: FAO; 1989) Of which total forests account for about 31% of the world’s land area. In India, the forest cover is roughly 19% of the total land area. The forest ecosystems are of g ...
Lesson Description
... SIS1. Make observations, raise questions, and formulate hypotheses. Pose questions and form hypotheses based on personal observations, scientific articles, experiments, an SIS2. Design and conduct scientific investigations. Articulate and explain the major concepts being investigated and the pur ...
... SIS1. Make observations, raise questions, and formulate hypotheses. Pose questions and form hypotheses based on personal observations, scientific articles, experiments, an SIS2. Design and conduct scientific investigations. Articulate and explain the major concepts being investigated and the pur ...
Amassing Efforts against Alien Invasive Species in Europe
... newspaper articles voicing concerns about alien species and their impacts on native biodiversity, economic resources, and human health. Alien or non-native species introductions by humans rank as one of the two top factors (after habitat loss) leading to declines in biological diversity [1]. Their s ...
... newspaper articles voicing concerns about alien species and their impacts on native biodiversity, economic resources, and human health. Alien or non-native species introductions by humans rank as one of the two top factors (after habitat loss) leading to declines in biological diversity [1]. Their s ...
Assembly Models - Ecology - Oxford
... since the foundation of the discipline. It concerns basic questions such as how do we start from a regional species pool to assemble a structured community? How many species should be found at a given location? What is the relationship between community structure and the environment? Studying the di ...
... since the foundation of the discipline. It concerns basic questions such as how do we start from a regional species pool to assemble a structured community? How many species should be found at a given location? What is the relationship between community structure and the environment? Studying the di ...
Cross-Feeding Dynamics Described by a Series Expansion of the
... To summarise, the previous attempts at modelling cross-feeding have been constrained either to systems assuming linear metabolic chains or individual-based models with limited analytical insight. Our aim with the current paper is to present a general framework in which cross-feeding dynamics can be ...
... To summarise, the previous attempts at modelling cross-feeding have been constrained either to systems assuming linear metabolic chains or individual-based models with limited analytical insight. Our aim with the current paper is to present a general framework in which cross-feeding dynamics can be ...
TT ECOL
... dependent and independent juveniles, and observation of nesting activity. The few nests that were seen were 15-20 meters high and in dense cover. One of the nests was in an excavated tree hole, which is not typical with thrush species. Breeding occurred all year round, with notable increase in . In ...
... dependent and independent juveniles, and observation of nesting activity. The few nests that were seen were 15-20 meters high and in dense cover. One of the nests was in an excavated tree hole, which is not typical with thrush species. Breeding occurred all year round, with notable increase in . In ...
Community ecology from a functional perspective
... similar niche (say, similar climatic conditions) become available in both locations, one of the species is likely to fill that niche. Thus, as time passes, the adaptations that make the species successful in that niche in that particular environment add up producing similar traits for two species th ...
... similar niche (say, similar climatic conditions) become available in both locations, one of the species is likely to fill that niche. Thus, as time passes, the adaptations that make the species successful in that niche in that particular environment add up producing similar traits for two species th ...
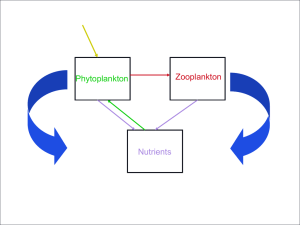
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.