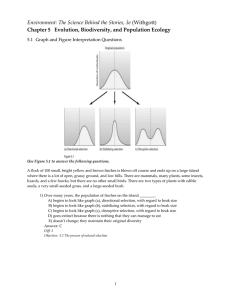
Carrying capacity
... capacity could support a positive natural increase, or could require a negative natural increase. Thus, the carrying capacity is the number of individuals an environment can support without significant negative impacts to the given organism and its environment. Below carrying capacity, populations t ...
... capacity could support a positive natural increase, or could require a negative natural increase. Thus, the carrying capacity is the number of individuals an environment can support without significant negative impacts to the given organism and its environment. Below carrying capacity, populations t ...
Parasitoids (insects whose larvae are the actual “predator”)
... released along with the mucous in the snails’ slime trails Ants pick up the parasite while feeding on the snail slime One of the parasites migrates to the ant’s “brain” [Ants normally retreat to their burrows late in the afternoon remaining there until the next day.] However, parasitized ants ...
... released along with the mucous in the snails’ slime trails Ants pick up the parasite while feeding on the snail slime One of the parasites migrates to the ant’s “brain” [Ants normally retreat to their burrows late in the afternoon remaining there until the next day.] However, parasitized ants ...
Science Lesson Planning Template
... Students will study animal/plant population graphs and hypothesize why population sizes increase/decrease repeatedly through the years. They will then research for their hypothesis if there were any environmental disasters that may have occurred to affect species survival and see if there is a corre ...
... Students will study animal/plant population graphs and hypothesize why population sizes increase/decrease repeatedly through the years. They will then research for their hypothesis if there were any environmental disasters that may have occurred to affect species survival and see if there is a corre ...
Ecosystems Project - SJFgrade7-8
... is where all types of life flourish and grow. It is a place where everything depends on each other and the way of life can change in an instant. While ecosystems are many in quantity and some are large in size, they are a complicated form of life and are hard to create, but easy to destroy. What is ...
... is where all types of life flourish and grow. It is a place where everything depends on each other and the way of life can change in an instant. While ecosystems are many in quantity and some are large in size, they are a complicated form of life and are hard to create, but easy to destroy. What is ...
When is a trophic cascade a trophic cascade?
... herbivores, thus indirectly allowing plants to grow unimpeded by predation. Since this seminal paper was published, trophic ecologists have elaborated hypotheses concerning the diversity and extent of indirect effects on food-web dynamics, with linear trophic cascades being one of many possible inte ...
... herbivores, thus indirectly allowing plants to grow unimpeded by predation. Since this seminal paper was published, trophic ecologists have elaborated hypotheses concerning the diversity and extent of indirect effects on food-web dynamics, with linear trophic cascades being one of many possible inte ...
Lecture 22: Coevolution
... Lag-Load Models 1. Contractionary • sp. w ↑ L : falls behind, goes extinct 2. Expansionary • sp. w ↓ L : outcompetes; increases these 2 models are unstable may fluctuate between 1 & 2 ...
... Lag-Load Models 1. Contractionary • sp. w ↑ L : falls behind, goes extinct 2. Expansionary • sp. w ↓ L : outcompetes; increases these 2 models are unstable may fluctuate between 1 & 2 ...
Water for Everyone - Wisconsin`s Citizen
... decisions about water • Create resources that are specific to Wisconsin streams & rivers ...
... decisions about water • Create resources that are specific to Wisconsin streams & rivers ...
Predator-prey interactions: lecture content
... return to prior state (equilibrium) after perturbation Elasticity ...
... return to prior state (equilibrium) after perturbation Elasticity ...
Ecosystem accounting in support of environmental management
... the linkages between environment and human activity. He considers that a systemic approach that encompasses both ecology and macro-economics is necessary to analyse changes in the capacity of ecosystems to generate ecosystem services at national or provincial scale. The System for Environmental Econ ...
... the linkages between environment and human activity. He considers that a systemic approach that encompasses both ecology and macro-economics is necessary to analyse changes in the capacity of ecosystems to generate ecosystem services at national or provincial scale. The System for Environmental Econ ...
Lesson 2 – Evolution of population
... a. genetic drift b. founder effect c. natural selection d. population bottleneck e. all of these 31. Genetic drift results in a change in gene frequencies because: a. gene flow within the population is less than gene flow between populations. b. reproduction is non-random within the population. c. t ...
... a. genetic drift b. founder effect c. natural selection d. population bottleneck e. all of these 31. Genetic drift results in a change in gene frequencies because: a. gene flow within the population is less than gene flow between populations. b. reproduction is non-random within the population. c. t ...
Four Central Points About Coevolution | SpringerLink
... coevolutionary relationships in these species at the base of the food web (Piculell et al. 2008). Similarly, coevolved interactions form the base of oceanic food webs. Much of the diversity of life in the oceans is clustered around reef-building corals that harbor mutualistic dinoflagellates. In fac ...
... coevolutionary relationships in these species at the base of the food web (Piculell et al. 2008). Similarly, coevolved interactions form the base of oceanic food webs. Much of the diversity of life in the oceans is clustered around reef-building corals that harbor mutualistic dinoflagellates. In fac ...
Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q
... The demand for resources, such as water, food, and shelter, in short supply in a community. ...
... The demand for resources, such as water, food, and shelter, in short supply in a community. ...
Integrating occupancy models and structural equation models to
... covariates are independent (i.e., indirect effects do not occur). Here, we combined structural equation and occupancy models to investigate complex influences on species occurrence while accounting for imperfect detection. These two methods are inherently compatible because they both provide means ...
... covariates are independent (i.e., indirect effects do not occur). Here, we combined structural equation and occupancy models to investigate complex influences on species occurrence while accounting for imperfect detection. These two methods are inherently compatible because they both provide means ...
December 2014 PP
... 2. It means zebra mussels have been better able to obtain and use resources than the native mussels. 3. Fundamental Niche is the full niche of the species—all the resources of a particular environment. The Realized Niche is the actual niche restricted by competition from other organisms. ...
... 2. It means zebra mussels have been better able to obtain and use resources than the native mussels. 3. Fundamental Niche is the full niche of the species—all the resources of a particular environment. The Realized Niche is the actual niche restricted by competition from other organisms. ...
05_3eTIF
... A) include the effects of a hard freeze on an entire community B) include the effects of a hard freeze on a single species within a community C) cause decreases in the number of species in an ecosystem D) include the effects of rainfall on an entire community E) include the effects of disease and pr ...
... A) include the effects of a hard freeze on an entire community B) include the effects of a hard freeze on a single species within a community C) cause decreases in the number of species in an ecosystem D) include the effects of rainfall on an entire community E) include the effects of disease and pr ...
ECOLOGY
... replacement of some or all of the species in a community. Ecological succession may take hundreds or thousands of years. Each new community that arises makes it harder for the previous community to survive, because of competition for resources. Succession provides opportunities for new resources and ...
... replacement of some or all of the species in a community. Ecological succession may take hundreds or thousands of years. Each new community that arises makes it harder for the previous community to survive, because of competition for resources. Succession provides opportunities for new resources and ...
B. Mutations
... d. An allele is the primary protein made by a gene found in a developing embryo. ...
... d. An allele is the primary protein made by a gene found in a developing embryo. ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.