Chaotic Red Queen coevolution in three
... acting on variants of the traits. Under the assumption that mutations have very small effects, the long-term coevolutionary process can be modeled as a trait substitution sequence in each species (Metz et al., 1992, 1996), the dynamics of which are captured by a set of three deterministic differenti ...
... acting on variants of the traits. Under the assumption that mutations have very small effects, the long-term coevolutionary process can be modeled as a trait substitution sequence in each species (Metz et al., 1992, 1996), the dynamics of which are captured by a set of three deterministic differenti ...
Population Size - cloudfront.net
... only two pounds of butter. You can make four batches of cookies, with butter as the limiting factor. If you get more butter, some other ingredient will be limiting. Species ordinarily produce more offspring than their habitat can support ( Figure 1.2). If conditions improve, more young survive and t ...
... only two pounds of butter. You can make four batches of cookies, with butter as the limiting factor. If you get more butter, some other ingredient will be limiting. Species ordinarily produce more offspring than their habitat can support ( Figure 1.2). If conditions improve, more young survive and t ...
Ziv 2000
... 1. The value 0 indicates no match at all (i.e., a population of that species in that habitat cannot persist), while 1 indicates a perfect match (i.e., a population of that species in that habitat can experience its maximal growth). It may be calculated empirically if the major factors limiting parti ...
... 1. The value 0 indicates no match at all (i.e., a population of that species in that habitat cannot persist), while 1 indicates a perfect match (i.e., a population of that species in that habitat can experience its maximal growth). It may be calculated empirically if the major factors limiting parti ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... • The mate choice of one species can be mediated by the behavior of individuals of other species. For example, whether two plant species hybridize may depend on the preferences of their pollinators. • The evolution of floral traits that generate reproductive isolation has been studied in the columbi ...
... • The mate choice of one species can be mediated by the behavior of individuals of other species. For example, whether two plant species hybridize may depend on the preferences of their pollinators. • The evolution of floral traits that generate reproductive isolation has been studied in the columbi ...
Designing a Simple Biological Community
... decomposer/detritivore can be supported. These are subsisting off of consumer excrement. This relationship with consumer biomass should NOT be treated as consumption from that species’ trophic level! Assume biomass production is on an annual basis and that during this time there is a stable and cons ...
... decomposer/detritivore can be supported. These are subsisting off of consumer excrement. This relationship with consumer biomass should NOT be treated as consumption from that species’ trophic level! Assume biomass production is on an annual basis and that during this time there is a stable and cons ...
Biotic Factors
... Grazing -‐________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ -‐_______________________________ ...
... Grazing -‐________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ -‐_______________________________ ...
Ecological approaches to human nutrition
... Probably one of the best-known examples of such ecological complementarity that also results in net nutritional benefit comes from the Mesoamerican “three sisters.” The combination of corn (a grass), beans (a nitrogen-fixing legume), and squash (a low-lying creeper) maximizes trait differences for g ...
... Probably one of the best-known examples of such ecological complementarity that also results in net nutritional benefit comes from the Mesoamerican “three sisters.” The combination of corn (a grass), beans (a nitrogen-fixing legume), and squash (a low-lying creeper) maximizes trait differences for g ...
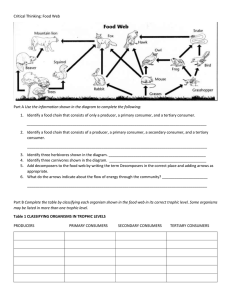
Critical Thinking: Food Web Part A Use the information shown in the
... the movement of matter (food) and energy through ecosystems are the food chain and the food web. You can think of both kinds of diagrams as flow charts that show the movement of food and energy through the following trophic levels: producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, and tertiary consume ...
... the movement of matter (food) and energy through ecosystems are the food chain and the food web. You can think of both kinds of diagrams as flow charts that show the movement of food and energy through the following trophic levels: producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, and tertiary consume ...
Lagomorphs
... throughout Europe (it was described in the 1980s from China, but genetic evidence suggests it was present in a milder form in Europe before that), European Rabbit populations were in a tailspin decline from habitat loss and habitat fragmentation, as well as overhunting, both legal and illegal. These ...
... throughout Europe (it was described in the 1980s from China, but genetic evidence suggests it was present in a milder form in Europe before that), European Rabbit populations were in a tailspin decline from habitat loss and habitat fragmentation, as well as overhunting, both legal and illegal. These ...
2005 summary
... useful and enjoyable and traditional math undergrads that biology is a great playland. ...
... useful and enjoyable and traditional math undergrads that biology is a great playland. ...
chart of the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
... populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would ...
... populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would ...
Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae
... pressure13. In this way, younger bats with a small body size and weight are potential ...
... pressure13. In this way, younger bats with a small body size and weight are potential ...
Decide whether the following relationships represent mutualism (M)
... The word commensalism means to _______________. It was named this because it originally described the relationship between animals that ate the “leftovers” of another animal’s hunt. Vultures may eat the remains of animal killed by a lion. Since the lion is done with its meal, the vulture is not hurt ...
... The word commensalism means to _______________. It was named this because it originally described the relationship between animals that ate the “leftovers” of another animal’s hunt. Vultures may eat the remains of animal killed by a lion. Since the lion is done with its meal, the vulture is not hurt ...
Biodiversity
... • Fewer species, fewer genes in the gene pool, and species can fall easier to disease and other problems. • An incredible number of species have already provided humans with medicines, food, clothing, and other items. How many more are able to do so that haven’t been discovered? Will they be lost be ...
... • Fewer species, fewer genes in the gene pool, and species can fall easier to disease and other problems. • An incredible number of species have already provided humans with medicines, food, clothing, and other items. How many more are able to do so that haven’t been discovered? Will they be lost be ...
New Title - cloudfront.net
... If an organism’s habitat is its address, its niche is its occupation. A niche (NITCH) is the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions. For instance, part of the description of an organism’s niche includes its ...
... If an organism’s habitat is its address, its niche is its occupation. A niche (NITCH) is the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions. For instance, part of the description of an organism’s niche includes its ...
Life history perspectives on pest insects: What`s the use?
... propensity to become a pest. I suggest that the former shortcoming is largely due to poor understanding of insect life history plasticity. This, in turn, may partly be due to a paucity of studies where reaction norms are investigated as putative adaptations. I suggest that the latter shortcoming is ...
... propensity to become a pest. I suggest that the former shortcoming is largely due to poor understanding of insect life history plasticity. This, in turn, may partly be due to a paucity of studies where reaction norms are investigated as putative adaptations. I suggest that the latter shortcoming is ...
Rhino poaching may cause atypical trophic cascades
... herbivores. We hypothesize that such cascades could result not only in the loss of other populations of endangered species but also in changes in vegetation structure and fire regimes; in addition, these cascades may interact with the actions of local poachers to create an ecological trap for an end ...
... herbivores. We hypothesize that such cascades could result not only in the loss of other populations of endangered species but also in changes in vegetation structure and fire regimes; in addition, these cascades may interact with the actions of local poachers to create an ecological trap for an end ...
Sample
... These activities deplete the environment and deprived the natural , leading the Earth become unsuitable for all forms of life, including the human himself. Conservation must be taken to save the ecosystem and human himself. ...
... These activities deplete the environment and deprived the natural , leading the Earth become unsuitable for all forms of life, including the human himself. Conservation must be taken to save the ecosystem and human himself. ...
Allee effects, extinctions, and chaotic transients in simple population
... In the case of essential extinction, the negative Schwartzian derivative hypothesis is necessary to ensure that almost every initial density goes to extinction. Without this condition, we are only assured that initial densities near C lead to extinction and other initial densities may lead to stable ...
... In the case of essential extinction, the negative Schwartzian derivative hypothesis is necessary to ensure that almost every initial density goes to extinction. Without this condition, we are only assured that initial densities near C lead to extinction and other initial densities may lead to stable ...
Advanced Model Checking
... Research Center for Modeling & Simulation (RCMS) National University of Sciences & Technology ...
... Research Center for Modeling & Simulation (RCMS) National University of Sciences & Technology ...
Carrying capacity
... capacity could support a positive natural increase, or could require a negative natural increase. Thus, the carrying capacity is the number of individuals an environment can support without significant negative impacts to the given organism and its environment. Below carrying capacity, populations t ...
... capacity could support a positive natural increase, or could require a negative natural increase. Thus, the carrying capacity is the number of individuals an environment can support without significant negative impacts to the given organism and its environment. Below carrying capacity, populations t ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.