Environmental and Ecosystem Processes
... The Mantle region lies under the crust and is approximately 2900 km thick. The mantle is much denser than the crust (which is why the crust floats on top) and has a texture much like tar. The rock in this region is rich in compounds made from iron, magnesium, and silicon, therefore it is denser than ...
... The Mantle region lies under the crust and is approximately 2900 km thick. The mantle is much denser than the crust (which is why the crust floats on top) and has a texture much like tar. The rock in this region is rich in compounds made from iron, magnesium, and silicon, therefore it is denser than ...
Ecology Worksheets The Science of Ecology Principles of Ecology True or False
... ______ 1. Ecology is usually considered to be a branch of biology. ______ 2. The environment of an organism includes only nonliving physical factors. ______ 3. The biosphere extends from sea level to about 11,000 meters above sea level. ______ 4. An important ecological issue is the rapid growth of ...
... ______ 1. Ecology is usually considered to be a branch of biology. ______ 2. The environment of an organism includes only nonliving physical factors. ______ 3. The biosphere extends from sea level to about 11,000 meters above sea level. ______ 4. An important ecological issue is the rapid growth of ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF
... dimorphism in the shell structure. Virtually nothing is known about this species’ natural life traits. However this poorly studied freshwater snail has recently been targeted by the freshwater ornamental industry, due to its predation abilities on other snail species that frequently became aquarium ...
... dimorphism in the shell structure. Virtually nothing is known about this species’ natural life traits. However this poorly studied freshwater snail has recently been targeted by the freshwater ornamental industry, due to its predation abilities on other snail species that frequently became aquarium ...
Chapter 11: Wolves Student notes Chapter 11 takes the wolf as the
... reproductive success and survival. a. Only one female per year has pups, but the entire pack will help raise them. b. They learn how to play, hunt, defend territory, and raise pups collectively. The ecological role of the wolf 1. Every ecosystem contains multiple trophic levels, which are basically ...
... reproductive success and survival. a. Only one female per year has pups, but the entire pack will help raise them. b. They learn how to play, hunt, defend territory, and raise pups collectively. The ecological role of the wolf 1. Every ecosystem contains multiple trophic levels, which are basically ...
ppt - eweb.furman.edu
... types of animals. We tend to see this diversity evolving by sister species using slightly different resources. This should make sense; sister species are probably very similar, and so they would have to partition some important resources in order to coexist without competitive exclusion. ...
... types of animals. We tend to see this diversity evolving by sister species using slightly different resources. This should make sense; sister species are probably very similar, and so they would have to partition some important resources in order to coexist without competitive exclusion. ...
A Biodiversity Primer for Ontario
... Genetic diversity. It’s what fuels evolution – the variability among individuals within a species, based on variations in genes, that natural selection can act on. That variability increases the chance that a species will adapt to changing environmental conditions or impacts, since some individuals ...
... Genetic diversity. It’s what fuels evolution – the variability among individuals within a species, based on variations in genes, that natural selection can act on. That variability increases the chance that a species will adapt to changing environmental conditions or impacts, since some individuals ...
4.3 Succession File
... Primary succession begins in an area with no remnants of an older community Pioneer species: The first species to colonize lifeless ...
... Primary succession begins in an area with no remnants of an older community Pioneer species: The first species to colonize lifeless ...
Ecosystem Resistance and Resilience
... Insect and disease of white pine white pine: less pest damage in partial shade and with structure of natural ...
... Insect and disease of white pine white pine: less pest damage in partial shade and with structure of natural ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... uncertain. For example, scientists found that seabirds (penguins) in high-latitude Antarctica tended to prefer warm climate (Sun et al. 2000). In contrast, a cool climate seemed more favorable to seabirds in tropical areas (Liu et al. 2006). Some key issues remain unclear. For instance, coupling bet ...
... uncertain. For example, scientists found that seabirds (penguins) in high-latitude Antarctica tended to prefer warm climate (Sun et al. 2000). In contrast, a cool climate seemed more favorable to seabirds in tropical areas (Liu et al. 2006). Some key issues remain unclear. For instance, coupling bet ...
Report - Indiana University Southeast
... One section of forest occupies roughly the northern half of the preserve. The oldest part, with mature hardwoods and native shrub layer, is centered around a ravine carved by two streams, including one fed by a small waterfall. Historically, it was not suitable for cultivation. In the 30 years since ...
... One section of forest occupies roughly the northern half of the preserve. The oldest part, with mature hardwoods and native shrub layer, is centered around a ravine carved by two streams, including one fed by a small waterfall. Historically, it was not suitable for cultivation. In the 30 years since ...
Chapter 3 and 4 Study Guide Ecology is the study of interactions
... Physcial factors: temperature, nutrients, camouflage, place to live, etc. Biological factors- competition within a populations, competition within a community, prey, predators, offspring, Competition exclusion principle states that no two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same ...
... Physcial factors: temperature, nutrients, camouflage, place to live, etc. Biological factors- competition within a populations, competition within a community, prey, predators, offspring, Competition exclusion principle states that no two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same ...
Predator - Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies
... from exotic species invasions, such as lake whitefish, should evolve through natural selection or undergo decline. For example, it is especially difficult for small whitefish to consume larger, more energetically profitable zebra mussels (Pothoven and Nalepa 2006). In this case, then, whitefish indi ...
... from exotic species invasions, such as lake whitefish, should evolve through natural selection or undergo decline. For example, it is especially difficult for small whitefish to consume larger, more energetically profitable zebra mussels (Pothoven and Nalepa 2006). In this case, then, whitefish indi ...
Colony–colony interactions between highly invasive ants
... introductions are exploding (Essl et al., 2011). As a result, biological invasions are increasingly threatening biodiversity. Among invasive species, ants (Formicidae) are a particularly prominent group. Owing to their small size, they can be easily transported by accident on plants, fresh products, ...
... introductions are exploding (Essl et al., 2011). As a result, biological invasions are increasingly threatening biodiversity. Among invasive species, ants (Formicidae) are a particularly prominent group. Owing to their small size, they can be easily transported by accident on plants, fresh products, ...
- Wiley Online Library
... location of migratory species. Such systems offer an opportunity to empirically investigate cyclic population density effects on short-term food web interactions by taking advantage of the large seasonal shifts in migratory prey biomass. 2. We utilized a large-mammal predator–prey savanna food we ...
... location of migratory species. Such systems offer an opportunity to empirically investigate cyclic population density effects on short-term food web interactions by taking advantage of the large seasonal shifts in migratory prey biomass. 2. We utilized a large-mammal predator–prey savanna food we ...
empirical approaches to quantifying interaction intensity: competition
... about interaction strength and the metrics that are used to test these hypotheses are often not explicit. We describe criteria for choosing appropriate metrics and methods for comparing them among studies at three stages of designing a meta-analysis to test hypotheses about variation in interaction ...
... about interaction strength and the metrics that are used to test these hypotheses are often not explicit. We describe criteria for choosing appropriate metrics and methods for comparing them among studies at three stages of designing a meta-analysis to test hypotheses about variation in interaction ...
Biodiversity: Structure and Function
... Stefan Porembski University of Rostock, Institute for Biodiversity Research, Germany ...
... Stefan Porembski University of Rostock, Institute for Biodiversity Research, Germany ...
Decline in top predator body size and changing climate alter trophic
... Top predators affect planktivores through predation, and affect small benthivores through predation and competition, but consumption of lobsters by top predators has long been questioned. Convincing evidence was provided from the Gulf of Maine area where predation pressure on larger lobster (50–78 m ...
... Top predators affect planktivores through predation, and affect small benthivores through predation and competition, but consumption of lobsters by top predators has long been questioned. Convincing evidence was provided from the Gulf of Maine area where predation pressure on larger lobster (50–78 m ...
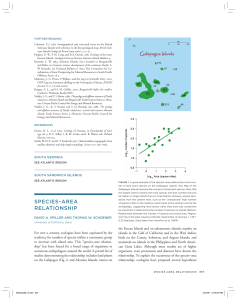
species–area relationship
... by water), the species–area relationship has been well documented for many types of “island analogues” (patches of suitable habitat for species isolated by unsuitable habitat) on mainlands. Knowledge of the factors that shape the species–area relationship can be used to evaluate different strategies ...
... by water), the species–area relationship has been well documented for many types of “island analogues” (patches of suitable habitat for species isolated by unsuitable habitat) on mainlands. Knowledge of the factors that shape the species–area relationship can be used to evaluate different strategies ...
Colonization in metapopulations: a review of
... heterogeneous demography. Regarding Ps(X,x) this model gave qualitatively the same predictions as the two preceding models (colonization success depends on Alp and propagule size), but for similar values of Alp and x, the Ebenhard model predicted much lower colonization probabilities. As heterogeneo ...
... heterogeneous demography. Regarding Ps(X,x) this model gave qualitatively the same predictions as the two preceding models (colonization success depends on Alp and propagule size), but for similar values of Alp and x, the Ebenhard model predicted much lower colonization probabilities. As heterogeneo ...
Food Webs, Competition Graphs, and Habitat Formation
... discrete, this data does not have to be smoothed out, or points eliminated, to allow for mathematical models to be applied. One example of a discrete mathematical model used in biology is that of a food web. The first biology courses in high school and in college present the fundamental nature of a ...
... discrete, this data does not have to be smoothed out, or points eliminated, to allow for mathematical models to be applied. One example of a discrete mathematical model used in biology is that of a food web. The first biology courses in high school and in college present the fundamental nature of a ...
Powerpoint
... 5. Poking holes in the species niche concept • Confusion as to whether niches are species or community specific (Schoener 1989) • Empty niches (advocated by Tilman and Bastow Wilson): Communities will exclude an invader if its niche is already filled • Neutral theory: species’ characteristics, and ...
... 5. Poking holes in the species niche concept • Confusion as to whether niches are species or community specific (Schoener 1989) • Empty niches (advocated by Tilman and Bastow Wilson): Communities will exclude an invader if its niche is already filled • Neutral theory: species’ characteristics, and ...
Dual phase evolution a mechanism for self
... Phase changes in the connectivity of a landscape can potentially explain both punctuated equilibria and pollen zones. Sites in a landscape are connected by processes, such as dispersal, that involve movement from place to place. In evolution and ecology, this means that individuals can migrate betwe ...
... Phase changes in the connectivity of a landscape can potentially explain both punctuated equilibria and pollen zones. Sites in a landscape are connected by processes, such as dispersal, that involve movement from place to place. In evolution and ecology, this means that individuals can migrate betwe ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.