Food Webs, Competition Graphs, and Habitat Formation
... discrete, this data does not have to be smoothed out, or points eliminated, to allow for mathematical models to be applied. One example of a discrete mathematical model used in biology is that of a food web. The first biology courses in high school and in college present the fundamental nature of a ...
... discrete, this data does not have to be smoothed out, or points eliminated, to allow for mathematical models to be applied. One example of a discrete mathematical model used in biology is that of a food web. The first biology courses in high school and in college present the fundamental nature of a ...
Framework - CCE LTER
... B. How does land use change interact with other press/pulse disturbances? C. How do storms and SST or sea level rise interact In coastal ...
... B. How does land use change interact with other press/pulse disturbances? C. How do storms and SST or sea level rise interact In coastal ...
A Cultural Niche Construction Theory of Initial
... 2011), are based on a ‘‘unidirectional’’ definition of adaptation that was the consensus within evolutionary theory up through the 1970s and still dominates today. According to this traditional definition, adaptation is a one-way street in which environments change and species adapt: ‘‘Adaptation is ...
... 2011), are based on a ‘‘unidirectional’’ definition of adaptation that was the consensus within evolutionary theory up through the 1970s and still dominates today. According to this traditional definition, adaptation is a one-way street in which environments change and species adapt: ‘‘Adaptation is ...
Scavenging: how carnivores and carrion structure communities
... between trophic levels distinct from the predation, parasitism and disease that are more commonly considered in theoretical and empirical studies. Here, we propose a new framework for improving food-web analyses by including scavenging. We outline how scavenging fits into food-web theory, assess its ...
... between trophic levels distinct from the predation, parasitism and disease that are more commonly considered in theoretical and empirical studies. Here, we propose a new framework for improving food-web analyses by including scavenging. We outline how scavenging fits into food-web theory, assess its ...
Determination of Primary Placeholder Habitat Associations in a Kelp
... should be noted that the branching reds may exhibit competitive superiority or have less specific recruitment cues, in that they strongly associate to both boulder and bedrock substrate. The strongly positive association of cup coral to bedrock and high relief reflects its preference for rocky areas ...
... should be noted that the branching reds may exhibit competitive superiority or have less specific recruitment cues, in that they strongly associate to both boulder and bedrock substrate. The strongly positive association of cup coral to bedrock and high relief reflects its preference for rocky areas ...
Network position of hosts in food webs and their parasite diversity
... in different hosts or environments making it difficult to compile a comprehensive host list for the parasite life cycle. Different stages may thus also have different trophic positions in the food web raising the question of whether a parasite species is a single trophic component or several tropho- ...
... in different hosts or environments making it difficult to compile a comprehensive host list for the parasite life cycle. Different stages may thus also have different trophic positions in the food web raising the question of whether a parasite species is a single trophic component or several tropho- ...
14 -The Tidelands
... freshwater species, which lack adaptations for dealing with salt, can survive well here either. • It has been also suggested that the critical salinity range has very unusual ratios of common inorganic elements (e.g., Cl, Na), which creates further physiological difficulties ...
... freshwater species, which lack adaptations for dealing with salt, can survive well here either. • It has been also suggested that the critical salinity range has very unusual ratios of common inorganic elements (e.g., Cl, Na), which creates further physiological difficulties ...
otter
... martens. Otters are semi-aquatic carnivores which obtain most if not all their food in the water. In appearance they are small to medum sized animals with short legs, long slender bodies and a lengthy tapering tail. Their well developed senses make them expert hunters while their natural curiosity s ...
... martens. Otters are semi-aquatic carnivores which obtain most if not all their food in the water. In appearance they are small to medum sized animals with short legs, long slender bodies and a lengthy tapering tail. Their well developed senses make them expert hunters while their natural curiosity s ...
The Human Population
... i. The maximum rate that a population could increase under ideal conditions is its intrinsic rate of increase (biotic potential) 1. Several factors influence biotic potential a. Age that reproduction begins b. Fraction of the life span during which an individual can reproduce c. Number of reproducti ...
... i. The maximum rate that a population could increase under ideal conditions is its intrinsic rate of increase (biotic potential) 1. Several factors influence biotic potential a. Age that reproduction begins b. Fraction of the life span during which an individual can reproduce c. Number of reproducti ...
community assembly and structure of tropical leaf
... these concepts was assessed. Null model tests of niche and size overlap revealed that the observed multivariate structure was only weakly influenced by biotic interactions, and therefore is most likely not the sole result of present species interactions. Non-metric multidimensional scaling and quadr ...
... these concepts was assessed. Null model tests of niche and size overlap revealed that the observed multivariate structure was only weakly influenced by biotic interactions, and therefore is most likely not the sole result of present species interactions. Non-metric multidimensional scaling and quadr ...
Competitive relationships of Andropogon gerardii (Big Bluestem
... field conditions Andropogon from non-local provenances were consistently smaller than the local provenance plants, which supports the long-held belief that plant populations are adapted to their local environmental conditions (Turesson 1922). These results are consistent with previous field research ...
... field conditions Andropogon from non-local provenances were consistently smaller than the local provenance plants, which supports the long-held belief that plant populations are adapted to their local environmental conditions (Turesson 1922). These results are consistent with previous field research ...
Ground Rules, exams, etc. (no “make up” exams) Text: read
... “tit for tat” strategy can lead to cooperation (“the future casts a long shadow back on the present” -- Axelrod) Evolutionarily stable strategies = ESS (a tactic that when present in a population, cannot be beaten) ...
... “tit for tat” strategy can lead to cooperation (“the future casts a long shadow back on the present” -- Axelrod) Evolutionarily stable strategies = ESS (a tactic that when present in a population, cannot be beaten) ...
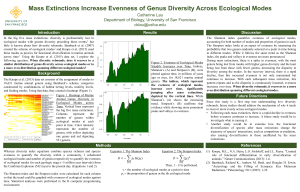
Mass Extinctions Increase Evenness of Genus Diversity Across
... The Shannon index quantifies evenness of ecological modes, accounting for both number of modes and proportion of genera in each. The Simpson index looks at an aspect of evenness by measuring the probability that two genera randomly selected at a point in time belong to different modes. While it foll ...
... The Shannon index quantifies evenness of ecological modes, accounting for both number of modes and proportion of genera in each. The Simpson index looks at an aspect of evenness by measuring the probability that two genera randomly selected at a point in time belong to different modes. While it foll ...
Explaining the global biodiversity gradient: energy, area, history and
... species–area curve (Hubbell, 2001). The first two are purely matters of sampling, but the third is clearly a relevant biological parameter. As a first approximation, we can think of y as highly correlated with species richness, and note that Hubbell’s theorem predicts that species richness will ther ...
... species–area curve (Hubbell, 2001). The first two are purely matters of sampling, but the third is clearly a relevant biological parameter. As a first approximation, we can think of y as highly correlated with species richness, and note that Hubbell’s theorem predicts that species richness will ther ...
Theory and its correction
... maximum benefit-cost ratio has been reached, then put all available energy into reproduction. Under these circumstances the semelparity is optimum. That includes the case where profit and cost are both linear. There is no change in cost per unit with effort,and we now know the advantage of early rep ...
... maximum benefit-cost ratio has been reached, then put all available energy into reproduction. Under these circumstances the semelparity is optimum. That includes the case where profit and cost are both linear. There is no change in cost per unit with effort,and we now know the advantage of early rep ...
APESD - Syllabi
... and grow to be stewards of the environment. The study of environmental science, in relation to the earth, is a combination of the physical, chemical, earth, and biological sciences. A variety of topics covered include: ecosystems, biodiversity, population, resources, energy, pollution, urban plannin ...
... and grow to be stewards of the environment. The study of environmental science, in relation to the earth, is a combination of the physical, chemical, earth, and biological sciences. A variety of topics covered include: ecosystems, biodiversity, population, resources, energy, pollution, urban plannin ...
Behavioral Types of Predator and Prey Jointly Determine Prey Survival
... studies simultaneously examine variation in multiple interacting species, despite the potential for coevolutionary responses to work to either maintain or eliminate variation in interacting populations. Here, we investigate how individual differences in behavioral types of both predators (ocher sea ...
... studies simultaneously examine variation in multiple interacting species, despite the potential for coevolutionary responses to work to either maintain or eliminate variation in interacting populations. Here, we investigate how individual differences in behavioral types of both predators (ocher sea ...
Something Stinks: the Effect of Predator Scent Cues on
... assumption is that mammalian prey species will want to avoid the predator cue, this may be a mistaken assumption as many other studies have shown non-significant responses to these cues (Wasko et al. 2013; Spencer et al. 2014; Sivy et al. 2010; Starke III and Ferkin 2012). There may also be a partic ...
... assumption is that mammalian prey species will want to avoid the predator cue, this may be a mistaken assumption as many other studies have shown non-significant responses to these cues (Wasko et al. 2013; Spencer et al. 2014; Sivy et al. 2010; Starke III and Ferkin 2012). There may also be a partic ...
Evolutionary genetics of invasive species
... determine invasion success. Why is this topic of immediate importance? As impacts of invasions intensify, it is imperative to move beyond treating invasive species as genetic black boxes in mitigation and management strategies. For instance, demographic models that treat invasive species as homogene ...
... determine invasion success. Why is this topic of immediate importance? As impacts of invasions intensify, it is imperative to move beyond treating invasive species as genetic black boxes in mitigation and management strategies. For instance, demographic models that treat invasive species as homogene ...
Lee, CE. 2002 - Carol Eunmi LEE
... determine invasion success. Why is this topic of immediate importance? As impacts of invasions intensify, it is imperative to move beyond treating invasive species as genetic black boxes in mitigation and management strategies. For instance, demographic models that treat invasive species as homogene ...
... determine invasion success. Why is this topic of immediate importance? As impacts of invasions intensify, it is imperative to move beyond treating invasive species as genetic black boxes in mitigation and management strategies. For instance, demographic models that treat invasive species as homogene ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.