Relative importance of resource quantity, isolation and habitat
... Only one recent P. coridon population is known to occur north of our study area (50 km from the most northern population of our study region). This is also the northern distribution limit of H. comosa (Hennenberg and Bruelheide 2003). There is a gap of at least 30 km with no populations of P. corido ...
... Only one recent P. coridon population is known to occur north of our study area (50 km from the most northern population of our study region). This is also the northern distribution limit of H. comosa (Hennenberg and Bruelheide 2003). There is a gap of at least 30 km with no populations of P. corido ...
On the bioeconomics of predator and prey fishing
... 2-year old cod and the lower for the 7 age group. Using Norwegian data on prices of ®sh and cost of effort for the years 1991±92, and data on stomach content 1984±92, it is shown that shrimp constitute 40±80% of the feed costs for all age groups of 2 years and older, whereas capelin constitutes onl ...
... 2-year old cod and the lower for the 7 age group. Using Norwegian data on prices of ®sh and cost of effort for the years 1991±92, and data on stomach content 1984±92, it is shown that shrimp constitute 40±80% of the feed costs for all age groups of 2 years and older, whereas capelin constitutes onl ...
What limits the Serengeti zebra population?
... similar-sized Artiodactyls. Such a constraint may strengthen the effect of other factors, like predation, to limit zebra population sizes. We therefore expect zebra to show dampened responses to environmental variations compared with the more productive wildebeest and buffalo, because variation in p ...
... similar-sized Artiodactyls. Such a constraint may strengthen the effect of other factors, like predation, to limit zebra population sizes. We therefore expect zebra to show dampened responses to environmental variations compared with the more productive wildebeest and buffalo, because variation in p ...
Chapter 15: Dynamics of Consumer-Resource
... Inefficient predators cannot maintain prey at low levels (prey primarily limited by resources). Increased predator efficiency adds a second stable point at low prey density. Further increases in predator functional and numerical responses may eliminate a stable point at high prey density Intense pre ...
... Inefficient predators cannot maintain prey at low levels (prey primarily limited by resources). Increased predator efficiency adds a second stable point at low prey density. Further increases in predator functional and numerical responses may eliminate a stable point at high prey density Intense pre ...
Building the bridge between animal movement and population
... of how individual decisions affect population demography parameters and ultimately translate into population dynamics. In this sense, animal movement is the long-sought bridge between behaviour, landscape ecology and population dynamics (Lima & Zollner 1996; Wiens 1997). Traditional models of popula ...
... of how individual decisions affect population demography parameters and ultimately translate into population dynamics. In this sense, animal movement is the long-sought bridge between behaviour, landscape ecology and population dynamics (Lima & Zollner 1996; Wiens 1997). Traditional models of popula ...
TEMPORAL VARIATION IN FITNESS COMPONENTS AND
... Large terrestrial mammalian herbivores (with an adult mass of ≥10 kg) are found in most ecosystems, from arctic tundra to tropical forest (134). They face not only very different climates, but also great variation in predation pressure, risk of disease, and human interference. Despite these potentia ...
... Large terrestrial mammalian herbivores (with an adult mass of ≥10 kg) are found in most ecosystems, from arctic tundra to tropical forest (134). They face not only very different climates, but also great variation in predation pressure, risk of disease, and human interference. Despite these potentia ...
Salt marsh harvest mouse abundance and site use in a managed
... instance, the house mouse (Mus musculus), an invasive species, uses habitat that is more patchily distributed than SMHM, which may result in the displacement of the SMHM from available habitat (Bias & Morrison, 2006). Salt marsh harvest mice need habitat for foraging, nesting, and cover from predato ...
... instance, the house mouse (Mus musculus), an invasive species, uses habitat that is more patchily distributed than SMHM, which may result in the displacement of the SMHM from available habitat (Bias & Morrison, 2006). Salt marsh harvest mice need habitat for foraging, nesting, and cover from predato ...
Stoichiometry and population dynamics
... green circles; POC (mg-atom L)1): open red circles] and Daphnia biomass (blue triangles, left axis). Lower panels (c, d): development of P : C ratio (atom : atom; open green circles) and Daphnia egg ratio (filled red circles, left axis). Redrawn, with permission, from Sommer (1992). ...
... green circles; POC (mg-atom L)1): open red circles] and Daphnia biomass (blue triangles, left axis). Lower panels (c, d): development of P : C ratio (atom : atom; open green circles) and Daphnia egg ratio (filled red circles, left axis). Redrawn, with permission, from Sommer (1992). ...
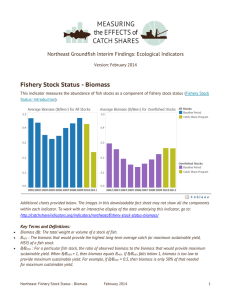
Fishery Stock Status: Biomass – February 2014
... Average biomass has generally increased from a low point in 2005, while the percent of stocks with biomass levels less than 50 percent BMSY has declined, also since 2005. BMSY is the biomass that would maximize long-term average catches. There is no apparent trend in the percent of stocks having bio ...
... Average biomass has generally increased from a low point in 2005, while the percent of stocks with biomass levels less than 50 percent BMSY has declined, also since 2005. BMSY is the biomass that would maximize long-term average catches. There is no apparent trend in the percent of stocks having bio ...
Predation - life.illinois.edu
... In the simplest form of the model, the predator is specialized on just one prey species - therefore in the absence of prey, the predator population declines exponentially: ...
... In the simplest form of the model, the predator is specialized on just one prey species - therefore in the absence of prey, the predator population declines exponentially: ...
A stoichiometric exception to the competitive exclusion principle.
... functions of the limiting factors, an assumption that may not hold in reality. Under this assumption, neither a stable equilibrium nor a stable cycle is possible with n species on fewer than n limiting factors.) As it frequently happens in mathematical biology, the verbal version of a rigorous math ...
... functions of the limiting factors, an assumption that may not hold in reality. Under this assumption, neither a stable equilibrium nor a stable cycle is possible with n species on fewer than n limiting factors.) As it frequently happens in mathematical biology, the verbal version of a rigorous math ...
Aqua Introductory Research Essay 2016:2
... Animal populations have historically often been viewed as groups consisting of identical individuals. However, as almost all animal taxa grow during ontogeny, populations do consist of differently sized individuals which affect their environment in different ways. As growth, survival and reproductio ...
... Animal populations have historically often been viewed as groups consisting of identical individuals. However, as almost all animal taxa grow during ontogeny, populations do consist of differently sized individuals which affect their environment in different ways. As growth, survival and reproductio ...
Guide to Fisheries Science and Stock Assessments
... determine their status, to evaluate how they may be affected by potential management actions, and to forecast their future conditions. In fisheries, determining stock status means estimating one or more biological characteristics of the stock, such as abundance (numbers of fish) or biomass (weight), ...
... determine their status, to evaluate how they may be affected by potential management actions, and to forecast their future conditions. In fisheries, determining stock status means estimating one or more biological characteristics of the stock, such as abundance (numbers of fish) or biomass (weight), ...
recent studies
... the middle of the last century (Nicholson 1933; Andrewortha and Birch 1954). Population limitation occurs when factors, such as predation, reduce the rate of population growth to limit the population below its carry capacity (Sinclair and Pech 1996). Some ecologist held the view that predators had l ...
... the middle of the last century (Nicholson 1933; Andrewortha and Birch 1954). Population limitation occurs when factors, such as predation, reduce the rate of population growth to limit the population below its carry capacity (Sinclair and Pech 1996). Some ecologist held the view that predators had l ...
population
... favored in dependable environments, where adults are more likely to survive to breed again and competition for resources is intense. – In such environments, a few, well-provisioned offspring have a better chance of surviving to reproductive age. • Oak trees and sea urchins are intermediate between t ...
... favored in dependable environments, where adults are more likely to survive to breed again and competition for resources is intense. – In such environments, a few, well-provisioned offspring have a better chance of surviving to reproductive age. • Oak trees and sea urchins are intermediate between t ...
14.1 Habitat And Niche
... Survivorship curves help to describe the reproductive strategy of a species. • A survivorship curve is a diagram showing the number of surviving members over time from a measured set of births. ...
... Survivorship curves help to describe the reproductive strategy of a species. • A survivorship curve is a diagram showing the number of surviving members over time from a measured set of births. ...
Ecosystem fragmentation drives increased diet variation in an
... livebearing fish Gambusia hubbsi (Family Poeciliidae), using both populationand individual-level perspectives. We show that fragmentation-induced release from predation led to increased G. hubbsi population densities, which consequently led to lower mean growth rates, likely as a result of higher in ...
... livebearing fish Gambusia hubbsi (Family Poeciliidae), using both populationand individual-level perspectives. We show that fragmentation-induced release from predation led to increased G. hubbsi population densities, which consequently led to lower mean growth rates, likely as a result of higher in ...
Ecosystem fragmentation drives increased diet variation in an
... livebearing fish Gambusia hubbsi (Family Poeciliidae), using both populationand individual-level perspectives. We show that fragmentation-induced release from predation led to increased G. hubbsi population densities, which consequently led to lower mean growth rates, likely as a result of higher in ...
... livebearing fish Gambusia hubbsi (Family Poeciliidae), using both populationand individual-level perspectives. We show that fragmentation-induced release from predation led to increased G. hubbsi population densities, which consequently led to lower mean growth rates, likely as a result of higher in ...
Population Ecology
... • Some populations fluctuate greatly and make it difficult to define K • Some populations show an Allee effect, in which individuals have a more difficult time surviving or reproducing if the population size is too small ...
... • Some populations fluctuate greatly and make it difficult to define K • Some populations show an Allee effect, in which individuals have a more difficult time surviving or reproducing if the population size is too small ...
LIFE HISTORIES Chapter 12
... After: maintenance, growth, or reproduction. Individuals delaying reproduction will grow faster a reach a larger size. Increased reproduction rate. Molles: Ecology 2nd Ed. ...
... After: maintenance, growth, or reproduction. Individuals delaying reproduction will grow faster a reach a larger size. Increased reproduction rate. Molles: Ecology 2nd Ed. ...
Name_______________ ______ Period _____ Natural Selection
... Where do peppered moths live? ________________________________________________________ Why are peppered moths called ‘peppered’? ______________________________________________ What are common predators of peppered moths? __________________________________________ How do peppered moths avoid these pr ...
... Where do peppered moths live? ________________________________________________________ Why are peppered moths called ‘peppered’? ______________________________________________ What are common predators of peppered moths? __________________________________________ How do peppered moths avoid these pr ...
ODD MODEL PARAMETERS CARIBOU AND WOLF PREDATOR
... other estimates of the biomass energy of a caribou 5.5 million Kcal per caribou Wolves within the range of the Western Arctic Caribou Herd killed 6-7% of this caribou population annually. WAC Population ~ 450,000 caribou over 350,000 sq km for density of 1.5 caribou/sq km Valkenburg et. al. (1996) ...
... other estimates of the biomass energy of a caribou 5.5 million Kcal per caribou Wolves within the range of the Western Arctic Caribou Herd killed 6-7% of this caribou population annually. WAC Population ~ 450,000 caribou over 350,000 sq km for density of 1.5 caribou/sq km Valkenburg et. al. (1996) ...
Theoretical and empirical studies on population dynamics, species
... Laska & Wootton 1998). In the third chapter of the thesis, we will systematically investigate the effects of the foraging parameters on the mean time to extinction of a prey species subjected to constant predation. The generalization of the Lotka-Volterra equations with realistic functional response ...
... Laska & Wootton 1998). In the third chapter of the thesis, we will systematically investigate the effects of the foraging parameters on the mean time to extinction of a prey species subjected to constant predation. The generalization of the Lotka-Volterra equations with realistic functional response ...
Indexically Structured Ecological Communities Abstract. Ecological
... problematic assumption as populations are often highly transient. In one study of 100 biomes across earth, 75% of these systems had at least one in ten species disappear locally per decade (Dornelas, Gotelli et al. 2014). This is often coupled with little change in regional diversity as populations ...
... problematic assumption as populations are often highly transient. In one study of 100 biomes across earth, 75% of these systems had at least one in ten species disappear locally per decade (Dornelas, Gotelli et al. 2014). This is often coupled with little change in regional diversity as populations ...
Wolverine (Gulo gulo), Eastern Population
... to be feasible. The short-term population and distribution objectives consist of determining if individuals of the Wolverine, Eastern population, still persist in Quebec and Labrador and to establish to what degree, if any, a rescue effect from dispersing individuals of the Western population in Ont ...
... to be feasible. The short-term population and distribution objectives consist of determining if individuals of the Wolverine, Eastern population, still persist in Quebec and Labrador and to establish to what degree, if any, a rescue effect from dispersing individuals of the Western population in Ont ...