TCA Cycle - eCurriculum
... the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules, not only carbohydrates but also fatty acids and amino acids. Most fuel molecules enter the TCA cycle as acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). In this cycle acetyl CoA is oxidized to CO2. Electrons released in different steps of this pathway ...
... the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules, not only carbohydrates but also fatty acids and amino acids. Most fuel molecules enter the TCA cycle as acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). In this cycle acetyl CoA is oxidized to CO2. Electrons released in different steps of this pathway ...
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... A urea cycle disorder is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation that results in a deficiency of one of the enzymes in the urea cycle. These enzymes are responsible for removing ammonia from the blood stream. Severe deficiency or total absence of activity of any of the first four enzymes (CPS1, OTC, ...
... A urea cycle disorder is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation that results in a deficiency of one of the enzymes in the urea cycle. These enzymes are responsible for removing ammonia from the blood stream. Severe deficiency or total absence of activity of any of the first four enzymes (CPS1, OTC, ...
GCSE PE TEST – Circulatory System, Respiratory System +Energy
... 8. State two risks to the heart and circulatory system from an inactive lifestyle and outline three ways in which physical activity can reduce these risks. (5) ...
... 8. State two risks to the heart and circulatory system from an inactive lifestyle and outline three ways in which physical activity can reduce these risks. (5) ...
Biology_Review-1
... for themselves and also release heat in the process. For these reasons, only 10% of the energy is available to the next higher trophic level of the energy pyramid. ...
... for themselves and also release heat in the process. For these reasons, only 10% of the energy is available to the next higher trophic level of the energy pyramid. ...
THE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ESSAY MUST: be in the FHS Essay
... example - Protein Synthesis occurs in the cell. CM - Commentary (Opinion or your experience) example - It was interesting to use "toys" to demonstrate how protein synthesis occurs to Ms. Antoine. ...
... example - Protein Synthesis occurs in the cell. CM - Commentary (Opinion or your experience) example - It was interesting to use "toys" to demonstrate how protein synthesis occurs to Ms. Antoine. ...
File
... award 2 marks for correct answer if answer is incorrect evidence of selection of 40(% light intensity) either in working or in graph 2 for 1 mark ...
... award 2 marks for correct answer if answer is incorrect evidence of selection of 40(% light intensity) either in working or in graph 2 for 1 mark ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The energy stored in a H+ gradient across a membrane couples the redox reactions of the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis • The H+ gradient is referred to as a protonmotive force, emphasizing its capacity to do ...
... • The energy stored in a H+ gradient across a membrane couples the redox reactions of the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis • The H+ gradient is referred to as a protonmotive force, emphasizing its capacity to do ...
Transcription and Translation
... o tRNA has stem and loop structures via the formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. The stems are short stretches of double-stranded RNA. The loops are single stranded. o *A CCA sequence at the 3’ end of each tRNA offers a site for amino acid attachment, while a triplet on the l ...
... o tRNA has stem and loop structures via the formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. The stems are short stretches of double-stranded RNA. The loops are single stranded. o *A CCA sequence at the 3’ end of each tRNA offers a site for amino acid attachment, while a triplet on the l ...
2. CYCLIC AMINOACIDS 2.1. Aromatic
... weight and 45-50% of dry weight) Play important roles in all biological processes Elementary composition: C 51-55%, O 21-23%, N 15-18%, H 6-7%, S 0.3-2.5% Structure - they are – high-molecular (the mass of single-chain protein is 10-50 kilodaltons (350 dal-1000 kdal); multichain protein complexes >2 ...
... weight and 45-50% of dry weight) Play important roles in all biological processes Elementary composition: C 51-55%, O 21-23%, N 15-18%, H 6-7%, S 0.3-2.5% Structure - they are – high-molecular (the mass of single-chain protein is 10-50 kilodaltons (350 dal-1000 kdal); multichain protein complexes >2 ...
Antiprotozoal agents
... antitrypanosomal arises from absence of nitroreudctase in human and presence of it in the invading organism. 2) so we can say that in metronidazole, tinidazole, secnidazole, nitro group cause both the activity and selectivity. 3) advantages of tinidazole and secnidazole over metronidazole 1) less in ...
... antitrypanosomal arises from absence of nitroreudctase in human and presence of it in the invading organism. 2) so we can say that in metronidazole, tinidazole, secnidazole, nitro group cause both the activity and selectivity. 3) advantages of tinidazole and secnidazole over metronidazole 1) less in ...
Exam #2
... “pacemaker enzyme” steps. What are the major similarities and differences between Glycolysis and Entner-Doudoroff Pathway? Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP); what is its utility for a cell? How is it connected to Glycolysis, at which intermediates? Fermentation as a fate of pyruvate; endogenous organi ...
... “pacemaker enzyme” steps. What are the major similarities and differences between Glycolysis and Entner-Doudoroff Pathway? Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP); what is its utility for a cell? How is it connected to Glycolysis, at which intermediates? Fermentation as a fate of pyruvate; endogenous organi ...
AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... 4. Explain why one FADH2 molecule is worth 2 ATP's. 5. A total of 36 (or 38) molecules of ATP are derived from a glucose molecule via glycolysis followed by aerobic respiration. Describe where these ATP molecules come from. ...
... 4. Explain why one FADH2 molecule is worth 2 ATP's. 5. A total of 36 (or 38) molecules of ATP are derived from a glucose molecule via glycolysis followed by aerobic respiration. Describe where these ATP molecules come from. ...
lecture 13 ppt
... in the process of animal nutrition • In general, animals fall into three categories: – Herbivores eat mainly autotrophs (plants, algae) – Carnivores eat other animals – Omnivores regularly consume animals as well as plants or algal matter ...
... in the process of animal nutrition • In general, animals fall into three categories: – Herbivores eat mainly autotrophs (plants, algae) – Carnivores eat other animals – Omnivores regularly consume animals as well as plants or algal matter ...
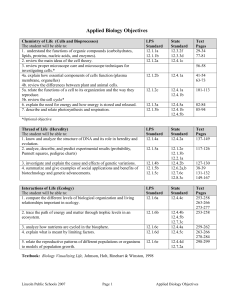
Biology Objectives - Lincoln Public Schools
... Applied Biology Objectives Chemistry of Life (Cells and Bioprocesses) The student will be able to: 1. understand the functions of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and enzymes). 2. review the main ideas of the cell theory. 3. review proper microscope care and microsc ...
... Applied Biology Objectives Chemistry of Life (Cells and Bioprocesses) The student will be able to: 1. understand the functions of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and enzymes). 2. review the main ideas of the cell theory. 3. review proper microscope care and microsc ...
NAME Block________ EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION Background
... vertebrates. All vertebrate embryos start out quite similar in appearance. This similarity has led scientists to infer that these organisms are related through a common ancestor. The diagram below illustrates stages in the embryonic development of a fish, a pig, and a human. Fish ...
... vertebrates. All vertebrate embryos start out quite similar in appearance. This similarity has led scientists to infer that these organisms are related through a common ancestor. The diagram below illustrates stages in the embryonic development of a fish, a pig, and a human. Fish ...
Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information • The information content
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups ...
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups ...
Document
... Cell-free, protein synthesizing machinery isolated from E. coli. (ribosomes, tRNAs, protein factors, radio-labeled amino acids). Synthetic mRNA containing only one type of base: ...
... Cell-free, protein synthesizing machinery isolated from E. coli. (ribosomes, tRNAs, protein factors, radio-labeled amino acids). Synthetic mRNA containing only one type of base: ...
File - Living Environment
... How does Glucose and O2 get to the Mitochondria? Glucose is absorbed by the digestive system Oxygen is taken in by the respiratory system Both systems are connected to the circulatory system which moves materials to and from the cell? ...
... How does Glucose and O2 get to the Mitochondria? Glucose is absorbed by the digestive system Oxygen is taken in by the respiratory system Both systems are connected to the circulatory system which moves materials to and from the cell? ...
03-232 Exam III 2013 Name:__________________________
... Choice A: The mainchain Hbond donors and acceptors will be forming H-bonds with water in the unfolded protein. When the protein folds those H-bonds are broken at a cost of +20 kJ/mol, which is energetically unfavorable. Since there are no H-bond donors and acceptors in the membrane, the protein has ...
... Choice A: The mainchain Hbond donors and acceptors will be forming H-bonds with water in the unfolded protein. When the protein folds those H-bonds are broken at a cost of +20 kJ/mol, which is energetically unfavorable. Since there are no H-bond donors and acceptors in the membrane, the protein has ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.