32_Metabolism of ammonia. Biosynthesis of urea and its disorders
... ammonia causes a decrease in the synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) inhibitory neurotransmitter of the nervous ...
... ammonia causes a decrease in the synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) inhibitory neurotransmitter of the nervous ...
FEBS Letters
... Abstract The present work aimed to proof the functionality of the non-mevalonate pathway in cyanobacteria. It was intended to isolate the 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) reductoisomerase gene (dxr), as this gene encodes the enzyme which catalyzes a pathway-specific, indicative step of this path ...
... Abstract The present work aimed to proof the functionality of the non-mevalonate pathway in cyanobacteria. It was intended to isolate the 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) reductoisomerase gene (dxr), as this gene encodes the enzyme which catalyzes a pathway-specific, indicative step of this path ...
PRODUCTION OF PYRUVATE AND LACTATE BY
... Pyruvic acid and lactic acid are two of the most widely used organic acids in the food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries (Li et al. 2001, Wasewar et al. 2004, Narayanan et al. 2004). Pyruvic acid, also known as 2-oxopropanoic acid, α-ketopropionic acid or acetylformic acid, is one of the most ...
... Pyruvic acid and lactic acid are two of the most widely used organic acids in the food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries (Li et al. 2001, Wasewar et al. 2004, Narayanan et al. 2004). Pyruvic acid, also known as 2-oxopropanoic acid, α-ketopropionic acid or acetylformic acid, is one of the most ...
Reprint
... measured by others varied at about 42-79 M–1·s–1 [34]. Interestingly, reaction (3) is catalyzed by Cu2+, most likely according to the scheme: ...
... measured by others varied at about 42-79 M–1·s–1 [34]. Interestingly, reaction (3) is catalyzed by Cu2+, most likely according to the scheme: ...
The impact of sperm metabolism during in vitro storage: the stallion
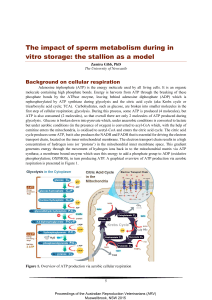
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by all living cells. It is an organic molecule containing high phosphate bonds. Energy is harvests from ATP through the breaking of these phosphate bonds by the ATPase enzyme, leaving behind adenosine diphosphate (ADP) which is rephosphorylate ...
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by all living cells. It is an organic molecule containing high phosphate bonds. Energy is harvests from ATP through the breaking of these phosphate bonds by the ATPase enzyme, leaving behind adenosine diphosphate (ADP) which is rephosphorylate ...
WHEAT GRASS JUICE ( The green revolution)
... have shown chlorophyll to be free of any toxic reaction, the red cell count was returned to normal within 4 to 5 days of the administration of the chlorophyll, even in those animals which were known to be extremely anemic or low in red cell count. 12. Farmers in the Midwest who have sterile cows and ...
... have shown chlorophyll to be free of any toxic reaction, the red cell count was returned to normal within 4 to 5 days of the administration of the chlorophyll, even in those animals which were known to be extremely anemic or low in red cell count. 12. Farmers in the Midwest who have sterile cows and ...
9. Wakil, S. J., Green, DE, Mii, S., and Mahler, HR (1954) Studies on
... subunit contains six catalytic centers, each carrying out a specific reaction and together with the acyl carrier protein (ACP), they generate long-chain fatty acids. Throughout the elongation process, the acyl group is linked as a thioester to the 4’-phosphopantetheinyl-SH of the ACP component of FA ...
... subunit contains six catalytic centers, each carrying out a specific reaction and together with the acyl carrier protein (ACP), they generate long-chain fatty acids. Throughout the elongation process, the acyl group is linked as a thioester to the 4’-phosphopantetheinyl-SH of the ACP component of FA ...
1. A pharmacy analyst supervises the state of a refractometer. For its
... 6. Diethyl ether relates to simple ethers. Prior to its identification by using the boiling temperature an analytical chemist must ensure that there are no: A Peroxides B Reducing substances C Alcohols D Non-volatile residue E Carboxylic acids Before determining the boiling temperature first determ ...
... 6. Diethyl ether relates to simple ethers. Prior to its identification by using the boiling temperature an analytical chemist must ensure that there are no: A Peroxides B Reducing substances C Alcohols D Non-volatile residue E Carboxylic acids Before determining the boiling temperature first determ ...
Maize EMBRYO SAC family peptides interact differentially with
... similarity to other defensins or defensin-like peptides binds to maize pollen tube surfaces, causing swelling prior to burst. This peptide fragment and a second conserved neighbouring fragment showed suppression of fungal germination and growth. The two peptides caused swelling of fungal cells, prod ...
... similarity to other defensins or defensin-like peptides binds to maize pollen tube surfaces, causing swelling prior to burst. This peptide fragment and a second conserved neighbouring fragment showed suppression of fungal germination and growth. The two peptides caused swelling of fungal cells, prod ...
Chemistry Bridging Work
... COURSE OUTLINE This transition work MUST be completed by the time you start your course and it will be assessed in September, you will need to bring it in on your first Chemistry lesson. The aims are for you to understand if you like the course and for you to be ready to start learning at post 16 le ...
... COURSE OUTLINE This transition work MUST be completed by the time you start your course and it will be assessed in September, you will need to bring it in on your first Chemistry lesson. The aims are for you to understand if you like the course and for you to be ready to start learning at post 16 le ...
Role of changes in cardiac metabolism in development - AJP
... FA metabolism includes multiple steps and can be regulated by both acute and chronic mechanisms, with or without modulation of gene expression (Fig. 2). Lipoprotein lipase. Because the heart has limited capacity to synthesize and store FA, it relies on continuous exogenous supply. FA supplied to the ...
... FA metabolism includes multiple steps and can be regulated by both acute and chronic mechanisms, with or without modulation of gene expression (Fig. 2). Lipoprotein lipase. Because the heart has limited capacity to synthesize and store FA, it relies on continuous exogenous supply. FA supplied to the ...
Mechanistic studies on the diazo transfer reaction
... presented in this Letter, would help one prepare specifically labeled proteins/reactants which might be useful for IR spectroscopic tagging of amines. We first confirmed the diazo transfer as opposed to the SNi path which would also result in retention of configuration. To the best of our knowledge, it ...
... presented in this Letter, would help one prepare specifically labeled proteins/reactants which might be useful for IR spectroscopic tagging of amines. We first confirmed the diazo transfer as opposed to the SNi path which would also result in retention of configuration. To the best of our knowledge, it ...
Ammonia destruction in the reaction furnace
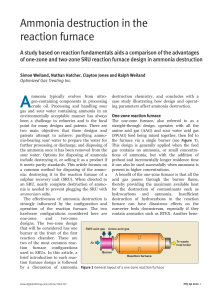
... of ammonia to free nitrogen and water. The second (Reaction 2) is thermal cracking to free nitrogen and hydrogen. Both pathways are well documented and both occur in the reaction furnace. However, there is another pathway that has been reported by Alberta Sulphur Research Limited6 (ASRL), which usua ...
... of ammonia to free nitrogen and water. The second (Reaction 2) is thermal cracking to free nitrogen and hydrogen. Both pathways are well documented and both occur in the reaction furnace. However, there is another pathway that has been reported by Alberta Sulphur Research Limited6 (ASRL), which usua ...
Topology Prediction of Membrane Proteins
... erse the membrane and are tightly packed into bundles (Fig. 2a). They are composed of mainly hydrophobic residues where the side chains can form van der Waals interactions with the fatty acid chains in the membrane core. All polar amide and carbonyl groups in the backbone are hydrogen bonded intern ...
... erse the membrane and are tightly packed into bundles (Fig. 2a). They are composed of mainly hydrophobic residues where the side chains can form van der Waals interactions with the fatty acid chains in the membrane core. All polar amide and carbonyl groups in the backbone are hydrogen bonded intern ...
Taurine 10 sample chapter
... would affect the development of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans, and could have important effects on the pancreatic cell mass and the endocrine function. Abbreviations: PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; Tau, taurine; GAD, glutamic acid decarboxylase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase ...
... would affect the development of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans, and could have important effects on the pancreatic cell mass and the endocrine function. Abbreviations: PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; Tau, taurine; GAD, glutamic acid decarboxylase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase ...
A Complementary Circular Code in the Protein Coding
... GGG and TTT must be excluded from such a code. Indeed, the concatenation of AAA, for example, with itself does not allow to retrieve the frame: . . .AAA,AAA,AAA,. . . , . . . A,AAA,AAA,AA. . . and . . .AA,AAA,AAA,A. . . Similarly, two codons related to circular permutation, e.g. AAC and ACA (or CAA) ...
... GGG and TTT must be excluded from such a code. Indeed, the concatenation of AAA, for example, with itself does not allow to retrieve the frame: . . .AAA,AAA,AAA,. . . , . . . A,AAA,AAA,AA. . . and . . .AA,AAA,AAA,A. . . Similarly, two codons related to circular permutation, e.g. AAC and ACA (or CAA) ...
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Acid–Base
... The hydrogen atom(s) bonded directly to the phosphorus atom is/are not acidic in aqueous solution; only those hydrogen atoms bonded to the oxygen atoms can be released as protons. (b) The acid strength is successively greater as the number of oxygen atoms increases because the very electronegative o ...
... The hydrogen atom(s) bonded directly to the phosphorus atom is/are not acidic in aqueous solution; only those hydrogen atoms bonded to the oxygen atoms can be released as protons. (b) The acid strength is successively greater as the number of oxygen atoms increases because the very electronegative o ...
Multiomics of tomato glandular trichomes reveals
... metabolites are involved in photosynthetic carbon fixation and in starch biosynthesis, which appear to be less active in trichomes than in leaves. Besides this, trichomes of LA1777 and LA4024 accumulated large amounts of inositol polyphosphates (IP5 and IP6) which were not detected in the leaves ...
... metabolites are involved in photosynthetic carbon fixation and in starch biosynthesis, which appear to be less active in trichomes than in leaves. Besides this, trichomes of LA1777 and LA4024 accumulated large amounts of inositol polyphosphates (IP5 and IP6) which were not detected in the leaves ...
Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 15 Polymers
... Classification of Polymers Based on Molecular Forces 1. Elastomers These are rubber like solid polymers in which the polymer chains are held together by weakest intermolecular forces, e.g., natural rubber, buna-S, buna-N etc . The weak binding forces permit the polymers to be stretched. A few ‘cross ...
... Classification of Polymers Based on Molecular Forces 1. Elastomers These are rubber like solid polymers in which the polymer chains are held together by weakest intermolecular forces, e.g., natural rubber, buna-S, buna-N etc . The weak binding forces permit the polymers to be stretched. A few ‘cross ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.