top408b1_2006
... -KG: Proline biosynthesis was done according to Fig 25.20, page 824. Most texts merge the first two steps into a "Kinase D.H." but learn it as shown here. G.S.A. spontaneously cyclizes, forming a Schiff base, which can then be reduced to give Pro. The Orn pathway (Fig 25.21, p. 825) is similar in m ...
... -KG: Proline biosynthesis was done according to Fig 25.20, page 824. Most texts merge the first two steps into a "Kinase D.H." but learn it as shown here. G.S.A. spontaneously cyclizes, forming a Schiff base, which can then be reduced to give Pro. The Orn pathway (Fig 25.21, p. 825) is similar in m ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 8 8thed - Chemistry
... ○ If a small amount of the enzyme sucrase is added to a solution of sugar, all the su crose is hydrolyzed within seconds. An enzyme is a macromolecule that acts as a catalyst, a chemical agent that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Here we will focus on protein ...
... ○ If a small amount of the enzyme sucrase is added to a solution of sugar, all the su crose is hydrolyzed within seconds. An enzyme is a macromolecule that acts as a catalyst, a chemical agent that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Here we will focus on protein ...
14e8d39db06b481
... Suggest the possible alterations in glucose storage and break down that might occur in this clinical problem. Inhibition of glycogenesis (glycogen synthesis) Stimulation of glycogenolysis (glycogen degradation) ...
... Suggest the possible alterations in glucose storage and break down that might occur in this clinical problem. Inhibition of glycogenesis (glycogen synthesis) Stimulation of glycogenolysis (glycogen degradation) ...
Insulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitus
... retina, and germinal epithelium of gonads most of the glucose between meals is used in the brain glucose can exert high osmotic pressure (cellular dehydration), loss of glucose in urine, osmotic diuresis by the kidneys (loss of fluids and electrolytes), damage to many tissues, especially to blood ve ...
... retina, and germinal epithelium of gonads most of the glucose between meals is used in the brain glucose can exert high osmotic pressure (cellular dehydration), loss of glucose in urine, osmotic diuresis by the kidneys (loss of fluids and electrolytes), damage to many tissues, especially to blood ve ...
BDOL Interactive Chalkboard
... such as the filaments in muscle tissue. • Other proteins, such as enzymes, control chemical reactions that perform key life functions—breaking down glucose molecules in cellular respiration, digesting food, or making spindle fibers during mitosis. ...
... such as the filaments in muscle tissue. • Other proteins, such as enzymes, control chemical reactions that perform key life functions—breaking down glucose molecules in cellular respiration, digesting food, or making spindle fibers during mitosis. ...
Chemistry - SchoolNotes.com
... d) Sr(CH3COO)2 Sr=43% C=23% H=3% O31 7) What is a hydrate? A compound in which the ions are attached to one or more water molecules. 8) How does the empirical formula differ from the molecular formula? Empirical formula is the molecular formula in the lowest ratio 9) Calculate the empirical formula ...
... d) Sr(CH3COO)2 Sr=43% C=23% H=3% O31 7) What is a hydrate? A compound in which the ions are attached to one or more water molecules. 8) How does the empirical formula differ from the molecular formula? Empirical formula is the molecular formula in the lowest ratio 9) Calculate the empirical formula ...
Animals: Structure and Function - Kellar
... simple sugars. As food does not remain long in the mouth, only a little starch is digested by salivary amylase to maltose. No digestion of carbohydrates occurs in the stomach; only proteins are digested in the stomach, however, enzyme activity continues in the stomach, but slows down significantly a ...
... simple sugars. As food does not remain long in the mouth, only a little starch is digested by salivary amylase to maltose. No digestion of carbohydrates occurs in the stomach; only proteins are digested in the stomach, however, enzyme activity continues in the stomach, but slows down significantly a ...
CELLS AS THE LIVING UNITS OF THE BODY
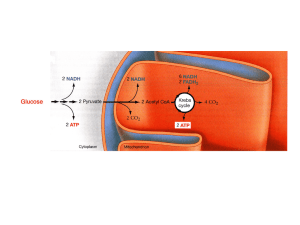
... Another 5% of the cellular energy is obtained by another process called glycolysis. Glycolysis is the set of chemical reactions that convert glucose to pyruvic acid in the cell. Function of the mitochondria: • Mitochondria produces energy packets in the form of ATP molecules so, they are known a ...
... Another 5% of the cellular energy is obtained by another process called glycolysis. Glycolysis is the set of chemical reactions that convert glucose to pyruvic acid in the cell. Function of the mitochondria: • Mitochondria produces energy packets in the form of ATP molecules so, they are known a ...
BC Revision Guide 3
... surrounded by dialysis fluid which contains the same concentration of dissolved ions and glucose as the blood (this ensures that glucose and useful mineral ions are not lost). Ions and waste can pass through, but big molecules like blood cells and proteins can’t pass through (like in the kidneys). D ...
... surrounded by dialysis fluid which contains the same concentration of dissolved ions and glucose as the blood (this ensures that glucose and useful mineral ions are not lost). Ions and waste can pass through, but big molecules like blood cells and proteins can’t pass through (like in the kidneys). D ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... period – ionization energy increases moving right due to increasing nuclear charge, while the number of shielding energy levels remain the same, resulting in greater attraction for the valence electrons in a period ionization energies are lower than expected when the electron is the first one remove ...
... period – ionization energy increases moving right due to increasing nuclear charge, while the number of shielding energy levels remain the same, resulting in greater attraction for the valence electrons in a period ionization energies are lower than expected when the electron is the first one remove ...
+SDS - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Serum albumin - protein used to transport nonsoluble molecules through the bloodstream Carries: bilirubin, fatty acids, hormones, dyes ...
... Serum albumin - protein used to transport nonsoluble molecules through the bloodstream Carries: bilirubin, fatty acids, hormones, dyes ...
Identification of Biological Molecules
... Identification of Biological Molecules Introduction: Molecules of a certain class have similar chemical properties because they have the same functional groups. A chemical test that is sensitive to these groups can be used to identify molecules that are in that class. Practice the following tests by ...
... Identification of Biological Molecules Introduction: Molecules of a certain class have similar chemical properties because they have the same functional groups. A chemical test that is sensitive to these groups can be used to identify molecules that are in that class. Practice the following tests by ...
biogeochemical cycles PP
... (carbohydrates, fats, protein, & nucleic acids)essential to life Currency of energy exchange- chemical energy for life stored as bonds in organic compounds ...
... (carbohydrates, fats, protein, & nucleic acids)essential to life Currency of energy exchange- chemical energy for life stored as bonds in organic compounds ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... The transferase transfers 3 glucose residues from a 4-residue limit branch to the end of another branch, reducing the limit branch to a single glucose residue. ...
... The transferase transfers 3 glucose residues from a 4-residue limit branch to the end of another branch, reducing the limit branch to a single glucose residue. ...
Digestive Enzymes - Goshen Cancer Survivor Network
... Digestive Enzymes Digestive enzymes are what their name implies and more. These enzymes contribute to the 1.5 quarts of pancreatic juice that is dumped into the small intestine daily and aid in the process of digestion. These enzymes include proteases which function to digest proteins into polypepti ...
... Digestive Enzymes Digestive enzymes are what their name implies and more. These enzymes contribute to the 1.5 quarts of pancreatic juice that is dumped into the small intestine daily and aid in the process of digestion. These enzymes include proteases which function to digest proteins into polypepti ...
Chapter 5 Powerpoint Slides
... (carbohydrates, fats, protein, & nucleic acids)essential to life Currency of energy exchange- chemical energy for life stored as bonds in organic compounds ...
... (carbohydrates, fats, protein, & nucleic acids)essential to life Currency of energy exchange- chemical energy for life stored as bonds in organic compounds ...
Glutamate synthase and nitrogen
... converted to NH4+ by the sequential reductive action of the plant enzymes nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase. Some plants, most notably many legumes, can also obtain their nitrogen from atmospheric N2. These legumes form a symbiotic association with rhizobia, which are able to reduce N2 to NH4+ ...
... converted to NH4+ by the sequential reductive action of the plant enzymes nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase. Some plants, most notably many legumes, can also obtain their nitrogen from atmospheric N2. These legumes form a symbiotic association with rhizobia, which are able to reduce N2 to NH4+ ...
OPEN - Cherry Hill Tuition
... Afferent arteriole/ Blood vessel wider than efferent/ (or description of process)/ ORA; Pores/ gaps/ fenestrations in endothelium / capillary wall; Pass through pores, in basement membrane; ...
... Afferent arteriole/ Blood vessel wider than efferent/ (or description of process)/ ORA; Pores/ gaps/ fenestrations in endothelium / capillary wall; Pass through pores, in basement membrane; ...
Chapter 6
... – Enzymes facilitate each step of metabolic pathway – They are proteins acting as chemical catalysts • Accelerate conversion of substrate to product ...
... – Enzymes facilitate each step of metabolic pathway – They are proteins acting as chemical catalysts • Accelerate conversion of substrate to product ...
Breathing - Junior Cert Science
... conversion where the chemical energy in food is changed into other forms of energy. ...
... conversion where the chemical energy in food is changed into other forms of energy. ...
Section 2: Enzymes and Digestion
... basic part of the molecule where it gets the name amino. The carboxyl group (COOH) this is an acid group. The hydrogen atom (H) The r group, this can be a variety of chemicals. Each amino acid has a different r group. The formation of a peptide bond Through the same process by which monosaccharides ...
... basic part of the molecule where it gets the name amino. The carboxyl group (COOH) this is an acid group. The hydrogen atom (H) The r group, this can be a variety of chemicals. Each amino acid has a different r group. The formation of a peptide bond Through the same process by which monosaccharides ...
THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... 11. Calcium (Ca) has an atomic number of 20; chlorine (Cl) has an atomic number of 17. a. The number of electrons in the outer shell of calcium is ______________. b. The number of electrons in the outer shell of chlorine is ______________. c. In a chemical reaction between these two atoms, _________ ...
... 11. Calcium (Ca) has an atomic number of 20; chlorine (Cl) has an atomic number of 17. a. The number of electrons in the outer shell of calcium is ______________. b. The number of electrons in the outer shell of chlorine is ______________. c. In a chemical reaction between these two atoms, _________ ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.