Origin of life - River Dell Regional School District
... space when meteorites and comets crashed into the Earth’s surface – Analysis of present-day meteorites recovered from impact craters on Earth has revealed that some meteorites contain relatively high concentrations of amino acids and other simple organic molecules – When small molecules known to be ...
... space when meteorites and comets crashed into the Earth’s surface – Analysis of present-day meteorites recovered from impact craters on Earth has revealed that some meteorites contain relatively high concentrations of amino acids and other simple organic molecules – When small molecules known to be ...
INTRODUCTION The HSAB concept is an acronym for `hard and soft
... From this analysis, a principle can be derived: Type A metals prefer to bind to Type A ligands and Type B metals prefer to bind to Type B ligands These empirical (experimentally derived) rules tell us that Type A metals are more likely to form oxides, carbonates, nitrides and fluorides, while Type ...
... From this analysis, a principle can be derived: Type A metals prefer to bind to Type A ligands and Type B metals prefer to bind to Type B ligands These empirical (experimentally derived) rules tell us that Type A metals are more likely to form oxides, carbonates, nitrides and fluorides, while Type ...
Respiratory system
... One system that the Respiratory system works with is the digestive system. Food first goes down to the throat, and moves to the digestive system. It then breaks down the food into smaller substances that the body can use consisting of proteins . Both systems end up helping each other. The Digestive ...
... One system that the Respiratory system works with is the digestive system. Food first goes down to the throat, and moves to the digestive system. It then breaks down the food into smaller substances that the body can use consisting of proteins . Both systems end up helping each other. The Digestive ...
document
... Enthalpy is a tricky thing to grasp, but we can look at it this way: • Enthalpy is the macroscopic energy change (in the form of heat) that accompanies changes at the atomic level (bond formation or breaking) • Enthalpy has the same sign convention as work, q and U – If energy is released as heat d ...
... Enthalpy is a tricky thing to grasp, but we can look at it this way: • Enthalpy is the macroscopic energy change (in the form of heat) that accompanies changes at the atomic level (bond formation or breaking) • Enthalpy has the same sign convention as work, q and U – If energy is released as heat d ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... coenzyme (19.7) an organic group required by some enzymes; generally a donor or acceptor of electrons or functional groups in a reaction. cofactor (19.7) metal ions, organic compounds, or organometallic compounds that must be bound to an apoenzyme to maintain the correct configuration of the active ...
... coenzyme (19.7) an organic group required by some enzymes; generally a donor or acceptor of electrons or functional groups in a reaction. cofactor (19.7) metal ions, organic compounds, or organometallic compounds that must be bound to an apoenzyme to maintain the correct configuration of the active ...
2011-A-Level-CH-H2-P3-soln
... delocalisation of the negative charge in the monoanion over the two –CO2H groups, or equated the greater acidity to the presence of two –CO2H groups. Drawing the displayed structure of the monoanion, which few candidates did, would not only have shown them that this delocalisation was impossible, bu ...
... delocalisation of the negative charge in the monoanion over the two –CO2H groups, or equated the greater acidity to the presence of two –CO2H groups. Drawing the displayed structure of the monoanion, which few candidates did, would not only have shown them that this delocalisation was impossible, bu ...
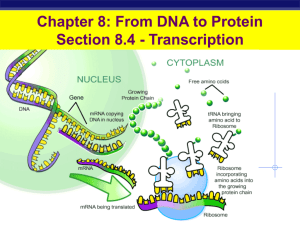
Transcription/translation
... How do cells control Gene Expression? For RNA Polymerase to do its job it has to attach to the DNA molecule ...
... How do cells control Gene Expression? For RNA Polymerase to do its job it has to attach to the DNA molecule ...
Module 1 Lecture 7
... of oxidative reaction occurs in liver and kidney cells, where the peroxisomes detoxify various toxic molecules that enter the bloodstream. 2. Photorespiration: In green leaves, there are peroxisomes that carry out a process called photorespiration which is a light-stimulated production of CO2 that i ...
... of oxidative reaction occurs in liver and kidney cells, where the peroxisomes detoxify various toxic molecules that enter the bloodstream. 2. Photorespiration: In green leaves, there are peroxisomes that carry out a process called photorespiration which is a light-stimulated production of CO2 that i ...
Survey of Kingdoms Notes KEY
... o Phototaxis: the movement of an organism towards or away from light (a stimulus) ...
... o Phototaxis: the movement of an organism towards or away from light (a stimulus) ...
Hydrogen Bonds
... A superscript plus or minus sign following the symbol of an element indicates an ion. A single plus sign indicates a cation with a charge of 1. (The original atom has lost one electron.) A single minus sign indicates an anion with a charge of 1. (The original atom has gained one electron.) If more ...
... A superscript plus or minus sign following the symbol of an element indicates an ion. A single plus sign indicates a cation with a charge of 1. (The original atom has lost one electron.) A single minus sign indicates an anion with a charge of 1. (The original atom has gained one electron.) If more ...
1 NEUROTRANSMITTERS: CRITICAL AMINO ACIDS AFFECTING
... most abundant amino acid in plasma but recent research now regards glutamine as a semiessential amino acid due to its many benefits to healing on the body when in abundance (Wardlaw, 2003). Hippocampus: A shortened explanation is that the hippocampus is a short term memory center of the brain which ...
... most abundant amino acid in plasma but recent research now regards glutamine as a semiessential amino acid due to its many benefits to healing on the body when in abundance (Wardlaw, 2003). Hippocampus: A shortened explanation is that the hippocampus is a short term memory center of the brain which ...
29
... With the procedure, usually between 1 to 4 units of a person's own blood (autologos) are withdrawn, the plasma is removed and immediately reinfused, and the packed red cells are placed in frozen storage. To prevent a dramatic reduction in blood cell concentration, each unit of blood is withdrawn ove ...
... With the procedure, usually between 1 to 4 units of a person's own blood (autologos) are withdrawn, the plasma is removed and immediately reinfused, and the packed red cells are placed in frozen storage. To prevent a dramatic reduction in blood cell concentration, each unit of blood is withdrawn ove ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... - enough ATP NADH accumulates in mitochondrial matrix shuts off E3 enzyme to prevent mitochondria from unnecessarily continuing to oxidize pyruvate to acetyl CoA (which would result in depletion of free coenzyme A supplies) - when mitochondria oxidizing fats large production of NADH and Acetyl ...
... - enough ATP NADH accumulates in mitochondrial matrix shuts off E3 enzyme to prevent mitochondria from unnecessarily continuing to oxidize pyruvate to acetyl CoA (which would result in depletion of free coenzyme A supplies) - when mitochondria oxidizing fats large production of NADH and Acetyl ...
Chemistry 1 - Edexcel
... (ii) Carbon dioxide is used in some fire extinguishers. Explain why carbon dioxide is effective at extinguishing fires. ...
... (ii) Carbon dioxide is used in some fire extinguishers. Explain why carbon dioxide is effective at extinguishing fires. ...
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
... Pyruvate formed in the aerobic conditions undergoes conversion to acetyl CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a bridge between glycolysis and aerobic metabolism – citric acid cycle. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and enzymes of cytric acid cycle are located in the ...
... Pyruvate formed in the aerobic conditions undergoes conversion to acetyl CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a bridge between glycolysis and aerobic metabolism – citric acid cycle. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and enzymes of cytric acid cycle are located in the ...
Ch. 13 end of chapter review
... cause the fly to grow eyes in odd places. This happens despite the fact that mouse eyes and fly eyes are very different. In fact the only reason we describe them as “eyes” is because they make vision possible. How can the Pax6 gene perform the same role in such diverse animals? It probably began very ...
... cause the fly to grow eyes in odd places. This happens despite the fact that mouse eyes and fly eyes are very different. In fact the only reason we describe them as “eyes” is because they make vision possible. How can the Pax6 gene perform the same role in such diverse animals? It probably began very ...
hydrosulfuric
... NonNon-metal with a nonnon-metal When non-metals combine, they form molecules. They may do so in multiple forms: ...
... NonNon-metal with a nonnon-metal When non-metals combine, they form molecules. They may do so in multiple forms: ...
ribosome
... Examine the Genetic Code chart on your handout to find the 1st codon. Now that methionine is delivered, tRNA drops off methionine and the ribosome moves to the next codon. ...
... Examine the Genetic Code chart on your handout to find the 1st codon. Now that methionine is delivered, tRNA drops off methionine and the ribosome moves to the next codon. ...
8.3 What Happens During Cellular Respiration?
... – Muscles that are working hard enough to use up all the available oxygen ferment pyruvate to lactate – To regenerate NAD, muscle cells ferment pyruvate to lactate, using electrons from NADH and hydrogen ions – A variety of microorganisms use lactic acid fermentation, including the bacteria that co ...
... – Muscles that are working hard enough to use up all the available oxygen ferment pyruvate to lactate – To regenerate NAD, muscle cells ferment pyruvate to lactate, using electrons from NADH and hydrogen ions – A variety of microorganisms use lactic acid fermentation, including the bacteria that co ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... a) Bronchus (bronchi): one of two large branches into lungs b) Bronchioles: any of the tiny branches into which a bronchi divides Alveoli: sacs that fill with oxygen when we breath in and carbon dioxide when we breath out. They are the site of gas exchange between the lungs and the circulatory syste ...
... a) Bronchus (bronchi): one of two large branches into lungs b) Bronchioles: any of the tiny branches into which a bronchi divides Alveoli: sacs that fill with oxygen when we breath in and carbon dioxide when we breath out. They are the site of gas exchange between the lungs and the circulatory syste ...
Evolution of Digestive Systems Notes
... Fungi are heterotrophs that feed by absorbing nutrients from the environment. a. Fungi cannot make their own food like plants can. Fungi do not ingest food, however. They secrete digestive enzymes into their surroundings that break down complex molecules into simple molecules that are small enough t ...
... Fungi are heterotrophs that feed by absorbing nutrients from the environment. a. Fungi cannot make their own food like plants can. Fungi do not ingest food, however. They secrete digestive enzymes into their surroundings that break down complex molecules into simple molecules that are small enough t ...
DNA and RNA Chapter 12
... How do genes work? How do genes determine characteristics of organisms? ...
... How do genes work? How do genes determine characteristics of organisms? ...
DNA/RNA Positive Controls - Bio
... As the number and scope of disease-producing pathogens and their genetic variants that cause human disease have continued to increase, there has been a commensurate and rapid increase in the use of nucleic acid based tests for routine clinical diagnosis. Due to the complex nature of nucleic acids, t ...
... As the number and scope of disease-producing pathogens and their genetic variants that cause human disease have continued to increase, there has been a commensurate and rapid increase in the use of nucleic acid based tests for routine clinical diagnosis. Due to the complex nature of nucleic acids, t ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.