USABO Semifinal exam 2006 Answer Key
... A. it may have the same signal-transduction pathway in all organisms B. it may need to be reset on a daily basis C. it may help to cause photoperiodic responses D. it is completely independent of day and night length E. no one knows with certainty the exact mechanisms of biological clocks 24. Joan a ...
... A. it may have the same signal-transduction pathway in all organisms B. it may need to be reset on a daily basis C. it may help to cause photoperiodic responses D. it is completely independent of day and night length E. no one knows with certainty the exact mechanisms of biological clocks 24. Joan a ...
Ions and molecules LO 2.13 Answer Key MC Question
... reactants, and produce O2, ATP, and NADPH as products. The NADPH and ATP are then passed to the stroma to be used in the Calvin cycle, in conjunction with CO2, to produce the G3P sugar that the plant can use. The Calvin cycle also releases NADP+ and ADP + a phosphate, which will be cycled back into ...
... reactants, and produce O2, ATP, and NADPH as products. The NADPH and ATP are then passed to the stroma to be used in the Calvin cycle, in conjunction with CO2, to produce the G3P sugar that the plant can use. The Calvin cycle also releases NADP+ and ADP + a phosphate, which will be cycled back into ...
halogen compounds organic chemistry
... chloride or cuprous bromide dissolved in corresponding halogen acids. Chloro and bromoarenes are formed. Diazonium salts required for this purpose are prepared by treating ice-cold solution of aniline in excess of dilute HCl with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrite at low temperature (0-5oC). This ...
... chloride or cuprous bromide dissolved in corresponding halogen acids. Chloro and bromoarenes are formed. Diazonium salts required for this purpose are prepared by treating ice-cold solution of aniline in excess of dilute HCl with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrite at low temperature (0-5oC). This ...
2, The Glyoxylate Pathway
... Lactate produced by muscle glycolysis is transported by the bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted to glucose by gluconeogenesis. The bloodstream carries glucose back to the muscles, where it may be stored as glycogen. ...
... Lactate produced by muscle glycolysis is transported by the bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted to glucose by gluconeogenesis. The bloodstream carries glucose back to the muscles, where it may be stored as glycogen. ...
Bil 255 – CMB
... 1. PYR --> CO2 + H2O --> NADH/FADH2 Krebs 2. e- of NADH/FADH2 --> O2 to make H2O ...
... 1. PYR --> CO2 + H2O --> NADH/FADH2 Krebs 2. e- of NADH/FADH2 --> O2 to make H2O ...
Document
... Lactate produced by muscle glycolysis is transported by the bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted to glucose by gluconeogenesis. The bloodstream carries glucose back to the muscles, where it may be stored as glycogen. ...
... Lactate produced by muscle glycolysis is transported by the bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted to glucose by gluconeogenesis. The bloodstream carries glucose back to the muscles, where it may be stored as glycogen. ...
Isomerism
... Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3 and methyl propane CH3CH(CH3)CH3 are chain isomers, they have different carbon chains. This is also known as branch isomerism. 1-bromo butane CH3 CH2CH2CH2Br and 2-bromo butane CH3CH2CHBrCH3 are positional isomers. They differ in the position of an atom or group (here the Br atom ...
... Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3 and methyl propane CH3CH(CH3)CH3 are chain isomers, they have different carbon chains. This is also known as branch isomerism. 1-bromo butane CH3 CH2CH2CH2Br and 2-bromo butane CH3CH2CHBrCH3 are positional isomers. They differ in the position of an atom or group (here the Br atom ...
Mitochondrial NRG - Designs for Health
... • Malic, Fumaric, and Succinic Acids - for refilling of key Krebs cycle intermediates • Creatine - to support additional energy production (using Albion’s patented Creatine MagnaPower®, which supplies creatine and magnesium together, both needed for healthy mitochondria) • Resveratrol and Curcumin - ...
... • Malic, Fumaric, and Succinic Acids - for refilling of key Krebs cycle intermediates • Creatine - to support additional energy production (using Albion’s patented Creatine MagnaPower®, which supplies creatine and magnesium together, both needed for healthy mitochondria) • Resveratrol and Curcumin - ...
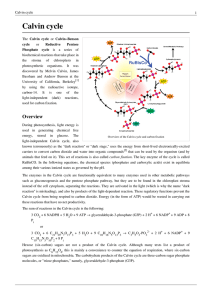
Calvin cycle
... known (erroneously) as the "dark reaction" or "dark stage," uses the energy from short-lived electronically-excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds[2] that can be used by the organism (and by animals that feed on it). This set of reactions is also called carbon fi ...
... known (erroneously) as the "dark reaction" or "dark stage," uses the energy from short-lived electronically-excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds[2] that can be used by the organism (and by animals that feed on it). This set of reactions is also called carbon fi ...
Poster
... process of regulating blood clotting, which is facilitated by platelets sending activation signals. When endothelial cells are damaged, matrix proteins are exposed; hence, activation signals are sent to Rap1b. In its inactive state, Rap1b is bound to GDP. Through the replacement of GDP with GTP, two ...
... process of regulating blood clotting, which is facilitated by platelets sending activation signals. When endothelial cells are damaged, matrix proteins are exposed; hence, activation signals are sent to Rap1b. In its inactive state, Rap1b is bound to GDP. Through the replacement of GDP with GTP, two ...
doc - ray luo
... We begin with a background introduction to the relevant molecular biology of proteins and how they fold, along with a computational formulation of the structure prediction problem. Then we will assess the benefits and costs of current approaches to the problem. Next comes a discussion of our propose ...
... We begin with a background introduction to the relevant molecular biology of proteins and how they fold, along with a computational formulation of the structure prediction problem. Then we will assess the benefits and costs of current approaches to the problem. Next comes a discussion of our propose ...
Trends in Biotechnology
... It is a microbial process which enzymatically changes organic compounds. Fermentation was used for years without knowing the processes. ...
... It is a microbial process which enzymatically changes organic compounds. Fermentation was used for years without knowing the processes. ...
Fatty acids: Review
... catalyzing a series of reactions that sequentially adds C2 units to a growing fatty acid chain covalently attached to the enzyme complex. The mechanism involves the linking malonyl-CoA to an acyl carrier protein, followed by a decarboxylation and condensation reaction that extends the hydrocarbon ch ...
... catalyzing a series of reactions that sequentially adds C2 units to a growing fatty acid chain covalently attached to the enzyme complex. The mechanism involves the linking malonyl-CoA to an acyl carrier protein, followed by a decarboxylation and condensation reaction that extends the hydrocarbon ch ...
lecture08_08
... Different polypeptide chains run alongside each other and are linked together by hydrogen bonds. ...
... Different polypeptide chains run alongside each other and are linked together by hydrogen bonds. ...
Enzymes - africangreyparrott.com
... C. Temp. and pH have no influence on the activity of this enzyme. D. This enzyme works best at a temp. above 50 C and a pH above ...
... C. Temp. and pH have no influence on the activity of this enzyme. D. This enzyme works best at a temp. above 50 C and a pH above ...
From Gene to Protein The Connection Between Genes and Proteins
... 26. Explain what determines the primary structure of a protein and describe how a polypeptide must be modified before it becomes fully functional. ...
... 26. Explain what determines the primary structure of a protein and describe how a polypeptide must be modified before it becomes fully functional. ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... If 2.10 mol N2 and 5.70 mol H2 react, what is the limiting reagent. Ask the question, how many mol of H2 is needed to react with .10 ...
... If 2.10 mol N2 and 5.70 mol H2 react, what is the limiting reagent. Ask the question, how many mol of H2 is needed to react with .10 ...
Learn More - Montgomery County Community College
... Distinguish between organic and inorganic molecules. C. Recognize common functional groups such as: hydrogen, hydroxyl, carboxyl, amine, phosphate. D. Describe possible origins of biological molecules on a primitive earth briefly discussing the significance of Stanley Miller’s work. E. Describe the ...
... Distinguish between organic and inorganic molecules. C. Recognize common functional groups such as: hydrogen, hydroxyl, carboxyl, amine, phosphate. D. Describe possible origins of biological molecules on a primitive earth briefly discussing the significance of Stanley Miller’s work. E. Describe the ...
... in the presence of the aromatic amino a>dmringly and in various combinations. the conclusion that individual end products do not repress specific portions of activity: for example, tymsine does not repress the portion inhibited by tyrosine. It appears likely that, when variation in activity has been ...
Cellular respiration
... You should now be able to: 1. Explain in general terms how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges 2. Name the three stages of cellular respiration; for each, state the region of the eukaryotic cell where it occurs and the products that result 3. In general terms, explain the role of the e ...
... You should now be able to: 1. Explain in general terms how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges 2. Name the three stages of cellular respiration; for each, state the region of the eukaryotic cell where it occurs and the products that result 3. In general terms, explain the role of the e ...
H+ Secretion
... • When the plasma HCO3- concentration is low, all the filtered HCO3- is reabsorbed; but when the plasma HCO3- concentration is high, ie, above 26-28 meq/L (the renal threshold for HCO3-), HCO3- appears in the urine and the urine becomes alkaline. • Conversely, when the plasma HCO3- falls below about ...
... • When the plasma HCO3- concentration is low, all the filtered HCO3- is reabsorbed; but when the plasma HCO3- concentration is high, ie, above 26-28 meq/L (the renal threshold for HCO3-), HCO3- appears in the urine and the urine becomes alkaline. • Conversely, when the plasma HCO3- falls below about ...
9.0 award of the degree
... market job requirements placed on graduates requiring them to have a broad understanding of different fields in Biochemistry and Molecular biology, has forced the Department of Biochemistry to review its current MSc Biochemistry (by research only) Programme. Biochemistry being a cross-cutting scienc ...
... market job requirements placed on graduates requiring them to have a broad understanding of different fields in Biochemistry and Molecular biology, has forced the Department of Biochemistry to review its current MSc Biochemistry (by research only) Programme. Biochemistry being a cross-cutting scienc ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.