Chemical Composition Notes
... _______ - formed when electrons are lost or gained in ordinary chemical reactions; affect size of atoms dramatically __________ - (+) ions; often metals since metals lose electrons to become positively charged ________ - (—) ions; often nonmetals since nonmetals gain electrons to become negatively c ...
... _______ - formed when electrons are lost or gained in ordinary chemical reactions; affect size of atoms dramatically __________ - (+) ions; often metals since metals lose electrons to become positively charged ________ - (—) ions; often nonmetals since nonmetals gain electrons to become negatively c ...
Metabolism
... Glycerol & Fatty Acids • Fatty acids cannot be used to synthesize glucose: Why is this important?? ...
... Glycerol & Fatty Acids • Fatty acids cannot be used to synthesize glucose: Why is this important?? ...
Organic Chemistry
... Maitotoxin, a complex organic biological toxin Biomolecular chemistry is a major category within organic chemistry which is frequently studied by biochemists. Many complex multi-functional group molecules are important in living organisms. Some are long-chain biopolymers, and these include peptides, ...
... Maitotoxin, a complex organic biological toxin Biomolecular chemistry is a major category within organic chemistry which is frequently studied by biochemists. Many complex multi-functional group molecules are important in living organisms. Some are long-chain biopolymers, and these include peptides, ...
Chapter 7 How Cells Make ATP: Energy
... catabolism enter same metabolic pathways as glucose • Amino acids are deaminated ...
... catabolism enter same metabolic pathways as glucose • Amino acids are deaminated ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: TRANSLATION AND
... Ribosomes Are Workbenches for Protein Biosynthesis Proteins are assembled on particles called ribosomes. These have two dissimilar subunits, each of which contains RNA and many proteins. With one exception, each protein is present in a single copy per ribosome, as is each RNA species. The compositio ...
... Ribosomes Are Workbenches for Protein Biosynthesis Proteins are assembled on particles called ribosomes. These have two dissimilar subunits, each of which contains RNA and many proteins. With one exception, each protein is present in a single copy per ribosome, as is each RNA species. The compositio ...
Influence of milk source and ripening time on free amino
... concentrations of all free amino acids, except asparagine, y-aminobutytic acid, and cysteine, generally increased as ripening time elapsed. Analyses of variance have indicated that ripening time and, to a lesser extent, milk composition have significant effects on the overall concentration of free a ...
... concentrations of all free amino acids, except asparagine, y-aminobutytic acid, and cysteine, generally increased as ripening time elapsed. Analyses of variance have indicated that ripening time and, to a lesser extent, milk composition have significant effects on the overall concentration of free a ...
1-2 wks - OpenWetWare
... genes to make them compatible with E. Coli; if they’re small, we won’t need to synthesize the whole sequence. Instead of synthesizing entire 3kb sequence, break into smaller sequences to be synthesized separately to save on cost, and recombine by PCR. ...
... genes to make them compatible with E. Coli; if they’re small, we won’t need to synthesize the whole sequence. Instead of synthesizing entire 3kb sequence, break into smaller sequences to be synthesized separately to save on cost, and recombine by PCR. ...
Complete nucleotide sequence of RNA 4 of rice stripe virus isolate T
... that of purified S protein (data not shown), confirming that the 20K protein is the S protein. The other O R F , in the Y-proximal region of the v c R N A , encoded a protein of 286 amino acids with an Mr of 32474 (32K protein) (Fig. 1, ORF2). No O R F of significant length was deduced to exist in t ...
... that of purified S protein (data not shown), confirming that the 20K protein is the S protein. The other O R F , in the Y-proximal region of the v c R N A , encoded a protein of 286 amino acids with an Mr of 32474 (32K protein) (Fig. 1, ORF2). No O R F of significant length was deduced to exist in t ...
Folding minimal sequences: the lower bound for sequence
... two reduced-alphabet sequences: a simpli¢ed sarc homology 3 (SH3) domain [3] and a designed helical protein, DHP1 [5]. Simpli¢ed SH3 domains were selected by their biological binding function and characterized by circular dichroism and other methods as folding into a structure similar to that found ...
... two reduced-alphabet sequences: a simpli¢ed sarc homology 3 (SH3) domain [3] and a designed helical protein, DHP1 [5]. Simpli¢ed SH3 domains were selected by their biological binding function and characterized by circular dichroism and other methods as folding into a structure similar to that found ...
17C-SynthesisOfProtein
... 3. RNA plays multiple roles in the cell: a review • The cellular machinery of protein synthesis and ER targeting is dominated by various kinds of RNA. • The diverse functions of RNA are based, in part, on its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other nucleic acid molecules (DNA or RNA). • It can al ...
... 3. RNA plays multiple roles in the cell: a review • The cellular machinery of protein synthesis and ER targeting is dominated by various kinds of RNA. • The diverse functions of RNA are based, in part, on its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other nucleic acid molecules (DNA or RNA). • It can al ...
17C-SynthesisOfProtein
... 3. RNA plays multiple roles in the cell: a review • The cellular machinery of protein synthesis and ER targeting is dominated by various kinds of RNA. • The diverse functions of RNA are based, in part, on its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other nucleic acid molecules (DNA or RNA). • It can al ...
... 3. RNA plays multiple roles in the cell: a review • The cellular machinery of protein synthesis and ER targeting is dominated by various kinds of RNA. • The diverse functions of RNA are based, in part, on its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other nucleic acid molecules (DNA or RNA). • It can al ...
PowerPoint
... • Carrier proteins transport molecules too large to fit through channel proteins (glucose, amino acids): – molecule binds to receptor site on carrier protein – protein changes shape, molecules pass through – receptor site is specific to certain molecules ...
... • Carrier proteins transport molecules too large to fit through channel proteins (glucose, amino acids): – molecule binds to receptor site on carrier protein – protein changes shape, molecules pass through – receptor site is specific to certain molecules ...
PowerPoint
... • Carrier proteins transport molecules too large to fit through channel proteins (glucose, amino acids): – molecule binds to receptor site on carrier protein – protein changes shape, molecules pass through – receptor site is specific to certain molecules ...
... • Carrier proteins transport molecules too large to fit through channel proteins (glucose, amino acids): – molecule binds to receptor site on carrier protein – protein changes shape, molecules pass through – receptor site is specific to certain molecules ...
Chapter 12
... •Organic compounds: cpds which contain hydrogen & carbon (thus, hydrocarbons & derivatives) (~ 7 million) •“Organic Chemistry” started, as a branch of chemistry, when F. Wohler disproved the idea of “vital force.” Carbon Atoms Carbon atoms generally form 4 bonds (think about their electron configura ...
... •Organic compounds: cpds which contain hydrogen & carbon (thus, hydrocarbons & derivatives) (~ 7 million) •“Organic Chemistry” started, as a branch of chemistry, when F. Wohler disproved the idea of “vital force.” Carbon Atoms Carbon atoms generally form 4 bonds (think about their electron configura ...
Coenzymes and Cofactors (PDF Available)
... blocks of proteins are characterized by their side-chains, which can range from simple aliphatic groups such as that found in alanine to more complex, functionalized side groups such as that of histidine. All of the amino acids play important roles in determining the three-dimensional structure of p ...
... blocks of proteins are characterized by their side-chains, which can range from simple aliphatic groups such as that found in alanine to more complex, functionalized side groups such as that of histidine. All of the amino acids play important roles in determining the three-dimensional structure of p ...
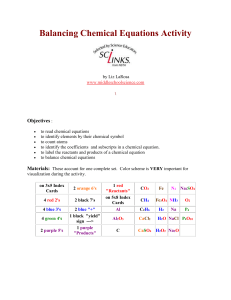
Balancing Chemical Equations Activity by Liz LaRosa www
... Print activity cards on card stock instead of making index cards for quicker set up. The color coding is very important for visualization. It is easier and quicker to locate the elements that you are trying to balance. If everything is in black ink, its harder to distinguish the equation contents. I ...
... Print activity cards on card stock instead of making index cards for quicker set up. The color coding is very important for visualization. It is easier and quicker to locate the elements that you are trying to balance. If everything is in black ink, its harder to distinguish the equation contents. I ...
Docking Studies in Target Proteins Involved in Antibacterial Action
... compounds scored lower than 1 μM. Regarding PBP1a, the best results were obtained with neogrifoline and 3,11-dioxolanosta-8,24(Z)-diene-26-oic acid; the latter also presented the highest score for Ddl. Otherwise, the score of the mentioned compound for Alr was low, being the highest score obtained w ...
... compounds scored lower than 1 μM. Regarding PBP1a, the best results were obtained with neogrifoline and 3,11-dioxolanosta-8,24(Z)-diene-26-oic acid; the latter also presented the highest score for Ddl. Otherwise, the score of the mentioned compound for Alr was low, being the highest score obtained w ...
XVIII. Biology, High School
... Read the information below and use it to answer the four multiple-choice questions and one open-response question that follow. ...
... Read the information below and use it to answer the four multiple-choice questions and one open-response question that follow. ...
File
... acid, acid (carboxyl) group, adenine, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), alpha helix, amine group, amino acid, base, beta pleated sheet, bonding, buffer, carbohydrate, cellulose, complementary base pairing, cytosine, dehydration synthesis, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), deoxyribose, dipeptide, disaccharide ...
... acid, acid (carboxyl) group, adenine, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), alpha helix, amine group, amino acid, base, beta pleated sheet, bonding, buffer, carbohydrate, cellulose, complementary base pairing, cytosine, dehydration synthesis, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), deoxyribose, dipeptide, disaccharide ...
Lecture 2
... hard, borderline or soft. According to Pearson's hard soft [Lewis] acid base (HSAB) principle: Hard [Lewis] acids prefer to bind to hard [Lewis] bases and Soft [Lewis] acids prefer to bind to soft [Lewis] bases ...
... hard, borderline or soft. According to Pearson's hard soft [Lewis] acid base (HSAB) principle: Hard [Lewis] acids prefer to bind to hard [Lewis] bases and Soft [Lewis] acids prefer to bind to soft [Lewis] bases ...
Proteins
... an excellent food for the very young, but humans have also adapted milk, specifically cow’s milk, as a food substance for persons of all ages. ...
... an excellent food for the very young, but humans have also adapted milk, specifically cow’s milk, as a food substance for persons of all ages. ...
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
... fractions from soybean and amaranth. The protein fractions shared some common electrophoretic bands as well as a similar amino acid composition. The larger percent of denaturation in protein fractions, which is associated with enthalpy and the number of ruptured hydrogen bonds, corresponds to disapp ...
... fractions from soybean and amaranth. The protein fractions shared some common electrophoretic bands as well as a similar amino acid composition. The larger percent of denaturation in protein fractions, which is associated with enthalpy and the number of ruptured hydrogen bonds, corresponds to disapp ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.