Chapter 17 Protein Synthesis
... called the template strand, provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript • The template strand is always the same strand for a given gene • During translation, the mRNA base triplets, called codons, are read in the 5 to 3 direction ...
... called the template strand, provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript • The template strand is always the same strand for a given gene • During translation, the mRNA base triplets, called codons, are read in the 5 to 3 direction ...
Statistical analysis of atomic contacts at RNA– protein
... to date for the functions it provides. The database and the update programs may be easily implemented using any other RDBMS which can be coupled with a host language. Statistical analysis Chi-square tests. Two problems must be distinguished: (i) the preferred amino acid types (or nucleotide componen ...
... to date for the functions it provides. The database and the update programs may be easily implemented using any other RDBMS which can be coupled with a host language. Statistical analysis Chi-square tests. Two problems must be distinguished: (i) the preferred amino acid types (or nucleotide componen ...
New Negative Potential Body Energizer
... converted to a signal inside the cell (the 2nd. Messenger). This signal occurs in the cell membrane. 1994 Nobel Prize winners Alfred Gilmand & Martin Rodbell discovered how they work. ...
... converted to a signal inside the cell (the 2nd. Messenger). This signal occurs in the cell membrane. 1994 Nobel Prize winners Alfred Gilmand & Martin Rodbell discovered how they work. ...
Assigning and Using Oxidation Numbers in Biochemistry Lecture
... With respect to oxidation–reduction processes of atoms other than carbon, those of sulfur and oxygen are among the most important. These processes can be analyzed quantitatively by assigning redox numbers to these heteroatoms using the rules given above. The reduction of a disulfide bond to two thio ...
... With respect to oxidation–reduction processes of atoms other than carbon, those of sulfur and oxygen are among the most important. These processes can be analyzed quantitatively by assigning redox numbers to these heteroatoms using the rules given above. The reduction of a disulfide bond to two thio ...
Conceptual Questions C1. Answer: The start codon begins at the
... C11. Answer: An anticodon that was 3′–UUG–5′ would recognize the two codons. To recognize 5′–AAA–3′, it would have to be modified to 3′–UUI–5′. C12. Answer: All tRNA molecules have some basic features in common. They all have a cloverleaf structure with three stem-loop structures. The second stem-l ...
... C11. Answer: An anticodon that was 3′–UUG–5′ would recognize the two codons. To recognize 5′–AAA–3′, it would have to be modified to 3′–UUI–5′. C12. Answer: All tRNA molecules have some basic features in common. They all have a cloverleaf structure with three stem-loop structures. The second stem-l ...
Ch.5
... How many molecules of ammonia are produced when 4.55 x 1018 molecules of hydrogen react? ...
... How many molecules of ammonia are produced when 4.55 x 1018 molecules of hydrogen react? ...
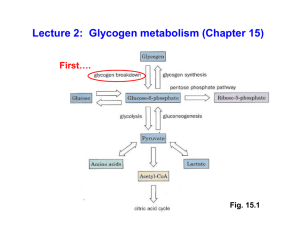
Lecture 2: Glycogen metabolism (Chapter 15)
... GLYGOGENIN and Glycogen “Priming” Glycogen synthesis can only occur by extending an already existing (1 4)-linked glucan chain. Therefore, how can it get started in the first place? Answer: The first step in glycogen synthesis is the attachment of a glucose residue to the -OH group on Tyr-194 of GL ...
... GLYGOGENIN and Glycogen “Priming” Glycogen synthesis can only occur by extending an already existing (1 4)-linked glucan chain. Therefore, how can it get started in the first place? Answer: The first step in glycogen synthesis is the attachment of a glucose residue to the -OH group on Tyr-194 of GL ...
Metabolomics in Nutrition Research, and Implications in Blood Type
... Autism and nutritional supplementation. ...
... Autism and nutritional supplementation. ...
L02_2002
... GLYGOGENIN and Glycogen “Priming” Glycogen synthesis can only occur by extending an already existing a (1 4)-linked glucan chain. Therefore, how can it get started in the first place? Answer: The first step in glycogen synthesis is the attachment of a glucose residue to the -OH group on Tyr-194 of ...
... GLYGOGENIN and Glycogen “Priming” Glycogen synthesis can only occur by extending an already existing a (1 4)-linked glucan chain. Therefore, how can it get started in the first place? Answer: The first step in glycogen synthesis is the attachment of a glucose residue to the -OH group on Tyr-194 of ...
BC 367 Biochemistry of the Cell I
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
Chapter 7-8-9
... 22. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other b. to attain a noble-gas electron configuration c. to become more polar d. to increase their atomic numbers 23. Which molecule has a single covalent bond? a. CO b. Cl c. CO d. N 24. What causes water molecul ...
... 22. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other b. to attain a noble-gas electron configuration c. to become more polar d. to increase their atomic numbers 23. Which molecule has a single covalent bond? a. CO b. Cl c. CO d. N 24. What causes water molecul ...
LITERATURE REVIEW: 1) Citric acid production by Aspergillusniger
... An intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, citric acid is an importantcommercial product with global production reaching 736,000 tons/yr. Furthermore, it isproduced almost through the submerged fermentation of the white rot fungus (Jianlong 2000). Citric acid is widely used in the food, ...
... An intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, citric acid is an importantcommercial product with global production reaching 736,000 tons/yr. Furthermore, it isproduced almost through the submerged fermentation of the white rot fungus (Jianlong 2000). Citric acid is widely used in the food, ...
PREwORkOUT - Advanced Molecular Labs
... of the most effective muscle-building and performance-enhancing compounds available. The first strength-promoting compound in AML Preworkout is creatine monohydrate, which is the most studied form of creatine on the market. In addition, creatine monohydrate is also one of the most heavily used suppl ...
... of the most effective muscle-building and performance-enhancing compounds available. The first strength-promoting compound in AML Preworkout is creatine monohydrate, which is the most studied form of creatine on the market. In addition, creatine monohydrate is also one of the most heavily used suppl ...
Notes: Moles
... Hydrates Notes: Explain what hydrates are and what their structures look like: o Ionic compounds sometimes have water molecules that adhere to the metal ion in the compound. Such compounds are called hydrates. o These water molecules aren’t tightly bonded but rather loosely associated with them. ...
... Hydrates Notes: Explain what hydrates are and what their structures look like: o Ionic compounds sometimes have water molecules that adhere to the metal ion in the compound. Such compounds are called hydrates. o These water molecules aren’t tightly bonded but rather loosely associated with them. ...
Ammonia (plasma, blood) - Association for Clinical Biochemistry
... to reduce the pyruvate present. There are fewer NADPH consuming systems present in blood, so fewer potential sources of interference. 3. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) has been reported to interfere positively with ammonia measurements using the Infinity™ method, and may lead to underestimation ...
... to reduce the pyruvate present. There are fewer NADPH consuming systems present in blood, so fewer potential sources of interference. 3. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) has been reported to interfere positively with ammonia measurements using the Infinity™ method, and may lead to underestimation ...
video slide
... – Pyruvate must first be converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis ...
... – Pyruvate must first be converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis ...
CHAPTER 1 Differentiate b/w Mendeleev`s periodic law and modern
... Why atomic radii decrease from left to right in a period? Ans.The increase of nuclear charge and the no change of shielding effect decreases the atomic radii from left to right. Why atomic radii increase from top to bottom in a group? Ans.The increasing number of shells and increasing. shielding eff ...
... Why atomic radii decrease from left to right in a period? Ans.The increase of nuclear charge and the no change of shielding effect decreases the atomic radii from left to right. Why atomic radii increase from top to bottom in a group? Ans.The increasing number of shells and increasing. shielding eff ...
Chapter 7: Recent advances in enzyme technology
... Some polymerising reactions, for example the polymerisation of phenols catalysed by peroxidase, will produce a higher molecular weight product when carried out in a solution more able to dissolve the products (i.e. oligomers) initially formed. Under normal physiological conditions, hydrolytic enzyme ...
... Some polymerising reactions, for example the polymerisation of phenols catalysed by peroxidase, will produce a higher molecular weight product when carried out in a solution more able to dissolve the products (i.e. oligomers) initially formed. Under normal physiological conditions, hydrolytic enzyme ...
Evolution of Enzymatic Activity in the Enolase Superfamily
... OSBSs may be functionally promiscuous, that is, they catalyze another reaction as well as the OSBS reaction (10). Perhaps the extreme sequence divergence results from convergent evolution from multiple progenitors within the enolase superfamily, so the potential functional promiscuity may provide a ...
... OSBSs may be functionally promiscuous, that is, they catalyze another reaction as well as the OSBS reaction (10). Perhaps the extreme sequence divergence results from convergent evolution from multiple progenitors within the enolase superfamily, so the potential functional promiscuity may provide a ...
Document
... Look at the “atomic masses” on the periodic table. What do these represent? E.g. the atomic mass of C is 12 (atomic # is 6) We know there are 6 protons and 6 neutrons Protons and neutrons have roughly the same mass. So, C weighs 12 u (atomic mass units). What is the actual mass of a C atom? ...
... Look at the “atomic masses” on the periodic table. What do these represent? E.g. the atomic mass of C is 12 (atomic # is 6) We know there are 6 protons and 6 neutrons Protons and neutrons have roughly the same mass. So, C weighs 12 u (atomic mass units). What is the actual mass of a C atom? ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.