The Target of Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes
... is not associated with weight gain or hypoglycemia; it is quite friendly to patients. But its mode of action has been very difficult to pinpoint. In animals and humans, metformin is absorbed through the upper small intestine, is concentrated in enterocytes and hepatocytes, circulates essentially unb ...
... is not associated with weight gain or hypoglycemia; it is quite friendly to patients. But its mode of action has been very difficult to pinpoint. In animals and humans, metformin is absorbed through the upper small intestine, is concentrated in enterocytes and hepatocytes, circulates essentially unb ...
Archaeological Dating, Survey and Excavation
... Bones, teeth and shells contain proteins that break down after death, and the most commonly investigated products of decomposition are amino acids. Amino acid racemization dating (AAR) measures changes between these amino acids' L- and D-forms; their ratio is an indication of age. ...
... Bones, teeth and shells contain proteins that break down after death, and the most commonly investigated products of decomposition are amino acids. Amino acid racemization dating (AAR) measures changes between these amino acids' L- and D-forms; their ratio is an indication of age. ...
Practice Test Packet
... [D] 0.10 [E] none of these 18. The correct mathematical expression for finding the molar solubility (S) of Sn(OH) 2 is: [A] 2S3 = Ksp [B] 108S5 = Ksp [C] 2S2 = Ksp [D] 4S3 = Ksp [E] 8S3 = Ksp 19. A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved sodium fluoride, NaF. If HCl is added, which ion will rea ...
... [D] 0.10 [E] none of these 18. The correct mathematical expression for finding the molar solubility (S) of Sn(OH) 2 is: [A] 2S3 = Ksp [B] 108S5 = Ksp [C] 2S2 = Ksp [D] 4S3 = Ksp [E] 8S3 = Ksp 19. A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved sodium fluoride, NaF. If HCl is added, which ion will rea ...
Ch7
... muscle glycogen and on endurance performance during heavy exercise. • Discuss the method of achieving a supercompensation of the muscle glycogen stores. • Describe the importance of blood glucose as a fuel in prolonged exercise, and the role of carbohydrate supplementation during performance. • Desc ...
... muscle glycogen and on endurance performance during heavy exercise. • Discuss the method of achieving a supercompensation of the muscle glycogen stores. • Describe the importance of blood glucose as a fuel in prolonged exercise, and the role of carbohydrate supplementation during performance. • Desc ...
UNIT 1: DNA and the Genome
... produces. The proteins that can be produced are determined by the genetic code (genotype) of the organism. Only a fraction of the genes an organism possesses are actually expressed as not all cells require all proteins e.g. the cells on the palms of your hands do not produce keratin (hair); the cell ...
... produces. The proteins that can be produced are determined by the genetic code (genotype) of the organism. Only a fraction of the genes an organism possesses are actually expressed as not all cells require all proteins e.g. the cells on the palms of your hands do not produce keratin (hair); the cell ...
Multipower Sportsfood launches Fit Protein Lite
... Fit Protein Lite delivers 80% less carbs and sugars than Multipower’s number one selling Fit Protein in the iconic brown bottle. Retailing at just £3.85 a bottle the 500ml drink is available in three delicious flavours of Chocolate, Vanilla and Strawberry. Multipower Nutritionist Drew Price said: “F ...
... Fit Protein Lite delivers 80% less carbs and sugars than Multipower’s number one selling Fit Protein in the iconic brown bottle. Retailing at just £3.85 a bottle the 500ml drink is available in three delicious flavours of Chocolate, Vanilla and Strawberry. Multipower Nutritionist Drew Price said: “F ...
Branched chain aldehydes: production and breakdown pathways
... degradation The Maillard reaction is very important for the formation of brown colour and flavour in especially heat-treated products such as bread and malt. In short, the Maillard reaction starts with the condensation of an amino group with a reducing sugar leading to a so-called Amadori product. R ...
... degradation The Maillard reaction is very important for the formation of brown colour and flavour in especially heat-treated products such as bread and malt. In short, the Maillard reaction starts with the condensation of an amino group with a reducing sugar leading to a so-called Amadori product. R ...
Chemical Equations PowerPoint
... will require trial and error, the following guidelines may be helpful) a) balance the different types of atoms one at a time b) first, balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation ...
... will require trial and error, the following guidelines may be helpful) a) balance the different types of atoms one at a time b) first, balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation ...
Category-4 - HSS-High
... hospitalized and undergo dialysis to remove urea and other wastes from your bloodstream. Further treatments allow your organs to heal and gradually resume their normal function. Which of the label ...
... hospitalized and undergo dialysis to remove urea and other wastes from your bloodstream. Further treatments allow your organs to heal and gradually resume their normal function. Which of the label ...
free energy
... chemical reactions • Metabolism is an emergent property of life that arises from interactions between molecules within the cell • A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product • Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme ...
... chemical reactions • Metabolism is an emergent property of life that arises from interactions between molecules within the cell • A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product • Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme ...
Unit 3
... To ensure maximum conversion the unreacted gases are recycled through the reaction chamber after reaction. ...
... To ensure maximum conversion the unreacted gases are recycled through the reaction chamber after reaction. ...
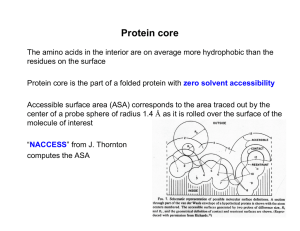
Protein core - Acsu.buffalo.edu
... Lambda repressor : binds DNA from bacteriophage Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) ...
... Lambda repressor : binds DNA from bacteriophage Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) ...
Carbo analysis 040909
... glycan(s), whereas those to the right of HDO originate from #-linked monosaccharide residues in the structure(s). ...
... glycan(s), whereas those to the right of HDO originate from #-linked monosaccharide residues in the structure(s). ...
BOXIN – AN ICHTHYOTOXIC PROTEIN FROM BOXFISHES Research Article
... injections, but highly toxic to fishes if externally applied into the surrounding water. Boxin is 33 times more potent than pahutoxin in its ichthyotoxicity. The protein fraction in the skin secretions of boxfish are responsible for about 15% total ichthyotoxicity of the entire crude secretion in wh ...
... injections, but highly toxic to fishes if externally applied into the surrounding water. Boxin is 33 times more potent than pahutoxin in its ichthyotoxicity. The protein fraction in the skin secretions of boxfish are responsible for about 15% total ichthyotoxicity of the entire crude secretion in wh ...
video slide - Ethical Culture Fieldston School
... • NADH and FADH2 – Donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
... • NADH and FADH2 – Donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
Final Review 2006
... ____ 76. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? a. rule of eights c. configuration rule b. Avogadro principle d. octet rule ____ 77. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or ...
... ____ 76. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? a. rule of eights c. configuration rule b. Avogadro principle d. octet rule ____ 77. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or ...
Biosynthesis of Nucleotides Biosynthesis of Nucleotides
... Cytidine deaminase (activated by dCTP inhibited by dTTP) Of the 4 dNTPs, only dCTP does not interact with the regulatory sites on ribonucleotide reductase, instead it interacts with dCMP deaminase. ...
... Cytidine deaminase (activated by dCTP inhibited by dTTP) Of the 4 dNTPs, only dCTP does not interact with the regulatory sites on ribonucleotide reductase, instead it interacts with dCMP deaminase. ...
File
... The ribosome has two sites for tRNA to attach: the aminoacyl (A) site and the peptidyl (P) site The anticodon (UAC) complimentary to the start codon (AUG) enters the P site The next tRNA carrying the required amino acid enters the A ...
... The ribosome has two sites for tRNA to attach: the aminoacyl (A) site and the peptidyl (P) site The anticodon (UAC) complimentary to the start codon (AUG) enters the P site The next tRNA carrying the required amino acid enters the A ...
The Minimal Nutritional Requirements of Organisms
... defined media. All strains showed an absolute requirement for nicotinic acid and no other vitamin was required for growth. Amino acids were essential for parapertussis and pertussis, but bronchiseptica would grow in either a mixture of amino acids, or lactate or citrate. Two old laboratory strains w ...
... defined media. All strains showed an absolute requirement for nicotinic acid and no other vitamin was required for growth. Amino acids were essential for parapertussis and pertussis, but bronchiseptica would grow in either a mixture of amino acids, or lactate or citrate. Two old laboratory strains w ...
Chapter 8 - HCC Learning Web
... Activation energy may be supplied in the form of heat that the reactant molecules absorb from the surroundings. The bonds of the reactants break only when the molecules have absorbed enough energy to become unstable and, therefore, more reactive. The absorption of thermal energy increases the speed ...
... Activation energy may be supplied in the form of heat that the reactant molecules absorb from the surroundings. The bonds of the reactants break only when the molecules have absorbed enough energy to become unstable and, therefore, more reactive. The absorption of thermal energy increases the speed ...
Presentation biomloecular
... Protein-based biomaterials and biomaterials with Proteins have been attracting more attention recently Protein polymers contain mixtures of molecules with different chain length, lack of control of genetic engineering and chain architecture Genetic Engineering made possible to produce peptide/protei ...
... Protein-based biomaterials and biomaterials with Proteins have been attracting more attention recently Protein polymers contain mixtures of molecules with different chain length, lack of control of genetic engineering and chain architecture Genetic Engineering made possible to produce peptide/protei ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.