respiration_DSE_revi..
... entire process is called cellular respiration. • The chloroplast also produces ATP by chemiosmotic phosphorylation. The energy needed to produce ATP comes from sunlight. ...
... entire process is called cellular respiration. • The chloroplast also produces ATP by chemiosmotic phosphorylation. The energy needed to produce ATP comes from sunlight. ...
INERT GASES -
... contribution. The net force operating on the represel ktative molecule can be expressed as a "two-body" force, acting between the molecule on one hand and its neighbors on the oth er. The bulk property is then obtained by adding up these effects for all the molecules which are present, assuming that ...
... contribution. The net force operating on the represel ktative molecule can be expressed as a "two-body" force, acting between the molecule on one hand and its neighbors on the oth er. The bulk property is then obtained by adding up these effects for all the molecules which are present, assuming that ...
1 Analysis of Polyphenoloxidase Enzyme Activity from Potato Extract
... Analysis of Polyphenoloxidase Enzyme Activity from Potato Extract Biochemistry Lab I (CHEM 4401) Background Enzymes are protein molecules (primarily) that serve as biological catalysts. They are responsible for the synthesis and degradation of lipids, amino acids, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, ...
... Analysis of Polyphenoloxidase Enzyme Activity from Potato Extract Biochemistry Lab I (CHEM 4401) Background Enzymes are protein molecules (primarily) that serve as biological catalysts. They are responsible for the synthesis and degradation of lipids, amino acids, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, ...
Crystal structure of potato tuber ADP‐glucose pyrophosphorylase
... the region around the sulfate 1-binding site in the b subunit does play a role in the allosteric activation of the enzyme. Taken together, these studies indicate that the activator 3-PGA binds at or near the inhibitor-binding site defined in our structure by sulfate 1. Sulfate 2 makes interactions wi ...
... the region around the sulfate 1-binding site in the b subunit does play a role in the allosteric activation of the enzyme. Taken together, these studies indicate that the activator 3-PGA binds at or near the inhibitor-binding site defined in our structure by sulfate 1. Sulfate 2 makes interactions wi ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya No. 2 Raipur
... Mohan took pure water for the electrolytic decomposition of water but did not see any bubbles near the electrodes. Explain why? Rancidity is a process used for spoiling of cooked food materials like vegetables, etc. When kept for long time in open. How can you prevent such process to proceed? Give a ...
... Mohan took pure water for the electrolytic decomposition of water but did not see any bubbles near the electrodes. Explain why? Rancidity is a process used for spoiling of cooked food materials like vegetables, etc. When kept for long time in open. How can you prevent such process to proceed? Give a ...
RNA Structure and the Versatility of RNA
... • Largest class of small non-coding RNA molecules expressed in animal cells. • RNA-protein complexes through interactions with piwi proteins. • These piRNA complexes have been linked to both epigenetic and post-transcriptional gene silencing of retrotransposons and other genetic elements in germ lin ...
... • Largest class of small non-coding RNA molecules expressed in animal cells. • RNA-protein complexes through interactions with piwi proteins. • These piRNA complexes have been linked to both epigenetic and post-transcriptional gene silencing of retrotransposons and other genetic elements in germ lin ...
NH2
... •In the liver:The formation of glutamine can be considered as a mechanism for scavenging NH3 that has not been incorporated into urea. •In the brain: It removes the toxic effect of NH3 in the brain .Then the glutamine goes via the blood to the kidneys where it become hydrolyzed by glutaminase into g ...
... •In the liver:The formation of glutamine can be considered as a mechanism for scavenging NH3 that has not been incorporated into urea. •In the brain: It removes the toxic effect of NH3 in the brain .Then the glutamine goes via the blood to the kidneys where it become hydrolyzed by glutaminase into g ...
16 Chapter
... • Inorganic nutrients—nutrients that lack carbon and regulate many chemical reactions in your body—are called minerals. • Some minerals, called trace minerals, are required only in small amounts. • Copper and iodine usually are listed as trace minerals. ...
... • Inorganic nutrients—nutrients that lack carbon and regulate many chemical reactions in your body—are called minerals. • Some minerals, called trace minerals, are required only in small amounts. • Copper and iodine usually are listed as trace minerals. ...
File
... Mohan took pure water for the electrolytic decomposition of water but did not see any bubbles near the electrodes. Explain why? Rancidity is a process used for spoiling of cooked food materials like vegetables, etc. When kept for long time in open. How can you prevent such process to proceed? Give a ...
... Mohan took pure water for the electrolytic decomposition of water but did not see any bubbles near the electrodes. Explain why? Rancidity is a process used for spoiling of cooked food materials like vegetables, etc. When kept for long time in open. How can you prevent such process to proceed? Give a ...
A novel species of thermoacidophilic archaeon, Sulfolobus
... method of Raha et al. (1990), in which genomic DNA was removed by DNase I treatment (Boehringer Mannheim). The method of Goodman & MacDonald (1979) was then used to synthesize first-strand cDNA with the primer R1 (5'GAGGTGATCCAGCCGCAGG-3') to prime the 3' end (Takayanagi et al., 1996) and AMV revers ...
... method of Raha et al. (1990), in which genomic DNA was removed by DNase I treatment (Boehringer Mannheim). The method of Goodman & MacDonald (1979) was then used to synthesize first-strand cDNA with the primer R1 (5'GAGGTGATCCAGCCGCAGG-3') to prime the 3' end (Takayanagi et al., 1996) and AMV revers ...
Onset of lactation in the bovine mammary gland:
... lactation is different from the significant decrease of anhydrase III expression in mouse mammary gland (Lemkin et al. 2000), indicating different roles of these two enzymes or species differences. The 5’ nucleotidase ecto, mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase 3, pim-1 oncogene, phosphoserine aminotransferas ...
... lactation is different from the significant decrease of anhydrase III expression in mouse mammary gland (Lemkin et al. 2000), indicating different roles of these two enzymes or species differences. The 5’ nucleotidase ecto, mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase 3, pim-1 oncogene, phosphoserine aminotransferas ...
Properties of Enzymes Lab
... reaction. They do this by binding to the reactants (substrates) and changing shape which places the substrates in a position that facilitates bond breaking or bond formation. The product(s) of the reaction form thousands of times more rapidly than they would without the enzyme. Every enzyme has a un ...
... reaction. They do this by binding to the reactants (substrates) and changing shape which places the substrates in a position that facilitates bond breaking or bond formation. The product(s) of the reaction form thousands of times more rapidly than they would without the enzyme. Every enzyme has a un ...
Core 2 Training and performance PowerPoint - MrBettiol
... a three-point start (one hand, two feet) and sprint 15 metres six straight leg bounds and sprint 15 metres ninety-degree jump turn to the left; return to the start and sprint 5 metres medicine ball throw and sprint. ...
... a three-point start (one hand, two feet) and sprint 15 metres six straight leg bounds and sprint 15 metres ninety-degree jump turn to the left; return to the start and sprint 5 metres medicine ball throw and sprint. ...
Essentials of Glycobiology Lecture 42 June 9, 1998 Jeff Esko
... Glycoside primers - Mimicking what already works Inhibitors of glycolipids and GPI anchors ...
... Glycoside primers - Mimicking what already works Inhibitors of glycolipids and GPI anchors ...
Manipulating redox and ATP balancing for improved production of
... pyruvate reduction are cited as the likely causes of the growth defect of this strain (Stols and Donnelly, 1997; Stols et al., 1997). A variety of metabolic engineering strategies including those focused toward the overexpression of pyruvate metabolizing enzymes have been pursued for improving succi ...
... pyruvate reduction are cited as the likely causes of the growth defect of this strain (Stols and Donnelly, 1997; Stols et al., 1997). A variety of metabolic engineering strategies including those focused toward the overexpression of pyruvate metabolizing enzymes have been pursued for improving succi ...
New methods for prediction of Bond order of
... Prediction of bond order is a vitally important to students of chemistry in undergraduate, graduate and also in Post-graduate level for solving different kinds of problems related bond length, bond strength, bond dissociation energy, Thermal stability and Reactivity. The method which is generally us ...
... Prediction of bond order is a vitally important to students of chemistry in undergraduate, graduate and also in Post-graduate level for solving different kinds of problems related bond length, bond strength, bond dissociation energy, Thermal stability and Reactivity. The method which is generally us ...
EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION
... Excretion is the elimination of metabolic wastes and nitrogenous wastes from the body. 2. Mention any one of the chief nitrogenous wastes produced by animals. Ammonia / Urea / Uric acid 3. Mention the most toxic form of nitrogenous waste that requires large amount of water for its elimination. Ammon ...
... Excretion is the elimination of metabolic wastes and nitrogenous wastes from the body. 2. Mention any one of the chief nitrogenous wastes produced by animals. Ammonia / Urea / Uric acid 3. Mention the most toxic form of nitrogenous waste that requires large amount of water for its elimination. Ammon ...
Anabaena - Oxford Academic
... suggested the light activation of fructose- I ,6-bisphosphatase, sedoheptulose- 1,7-bisphosphatase, ribulose-5phosphate kinase and NADP-linked glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, possibly via a thioredoxin-based mechanism [3]. However, there is as yet little detailed information as regards th ...
... suggested the light activation of fructose- I ,6-bisphosphatase, sedoheptulose- 1,7-bisphosphatase, ribulose-5phosphate kinase and NADP-linked glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, possibly via a thioredoxin-based mechanism [3]. However, there is as yet little detailed information as regards th ...
Lecture 19 Membranes 2: Membrane Proteins
... • Timescale of msec to sec, lipids DO diffuse freely in plane of membrane. • On much shorter time scale, 25 µsec intervals, lipids zoom around in a small confined area of membrane, then seem to "hop" to another small confined area, as if there were "fences" they had to hop over (networks of interact ...
... • Timescale of msec to sec, lipids DO diffuse freely in plane of membrane. • On much shorter time scale, 25 µsec intervals, lipids zoom around in a small confined area of membrane, then seem to "hop" to another small confined area, as if there were "fences" they had to hop over (networks of interact ...
PURINE & PYRIMIDINE METABOLISM
... purine synthesis. IMP is synthesized and could make AMP or GMP. It happens in almost most cells’ cytosol except human brain,polymorphonuclear leukocytes and ...
... purine synthesis. IMP is synthesized and could make AMP or GMP. It happens in almost most cells’ cytosol except human brain,polymorphonuclear leukocytes and ...
Stoichiometric Conversions
... gas, the two will combust and form carbon dioxide and water CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O How many moles of H2O will be formed when 28.0 g of methane combusts? ...
... gas, the two will combust and form carbon dioxide and water CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O How many moles of H2O will be formed when 28.0 g of methane combusts? ...
fat-soluble vitamins
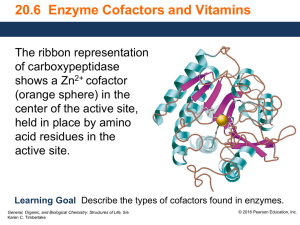
... Enzyme Cofactors • A simple enzyme is an active enzyme that consists only of protein. • Many enzymes are active only when they combine with cofactors such as metal ions or small molecules. • A coenzyme is a cofactor that is a small organic molecule such as a vitamin. Core Chemistry Skill Describing ...
... Enzyme Cofactors • A simple enzyme is an active enzyme that consists only of protein. • Many enzymes are active only when they combine with cofactors such as metal ions or small molecules. • A coenzyme is a cofactor that is a small organic molecule such as a vitamin. Core Chemistry Skill Describing ...
Gas Exchange Live Show
... • Gaseous exchange refers to the exchange of gases, namely Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide and relies on a process called diffusion. • Diffusion is the movement of gases from an area of high pressure to low. The difference between the high and low pressure is called the diffusion gradient • The bigger th ...
... • Gaseous exchange refers to the exchange of gases, namely Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide and relies on a process called diffusion. • Diffusion is the movement of gases from an area of high pressure to low. The difference between the high and low pressure is called the diffusion gradient • The bigger th ...
10 Translocation in the Phloem Chapter
... tional relationship and a ready exchange of solutes between the two cells. The plasmodesmata are often complex and branched on the companion cell side. Companion cells play a role in the transport of photosynthetic products from producing cells in mature leaves to the sieve elements in the minor (sm ...
... tional relationship and a ready exchange of solutes between the two cells. The plasmodesmata are often complex and branched on the companion cell side. Companion cells play a role in the transport of photosynthetic products from producing cells in mature leaves to the sieve elements in the minor (sm ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.