Topological studies suggest that the pathway of the protons through
... TID-reactive residues in F0• The labeling profilein Fig. 58 was obtaincd after reaction with Neurospora crassa mitochondria in the presence of an oligomycin concentration 10-fold higher than necessary for maximal inhibition. The identical group of residues was TID-reactive in the presence and in the ...
... TID-reactive residues in F0• The labeling profilein Fig. 58 was obtaincd after reaction with Neurospora crassa mitochondria in the presence of an oligomycin concentration 10-fold higher than necessary for maximal inhibition. The identical group of residues was TID-reactive in the presence and in the ...
File
... Eyes, spinal cord, begin life with a tail 6. How do these similarities support the evidence of ancestry? The embryo begins with very similar characteristics showing that they have a common ancestor ...
... Eyes, spinal cord, begin life with a tail 6. How do these similarities support the evidence of ancestry? The embryo begins with very similar characteristics showing that they have a common ancestor ...
11 Cytochrome P450 and the Metabolism and Bioactivation of
... metabolic cascade, P450 metabolizes only free, nonesterified forms of AA and thus, in vivo metabolism requires the release of the fatty acid from selected glycerophospholipid pools. CYP P450, prostaglandin H2 synthase, and lipoxygenases are capable of metabolizing polyunsaturated fatty acids other t ...
... metabolic cascade, P450 metabolizes only free, nonesterified forms of AA and thus, in vivo metabolism requires the release of the fatty acid from selected glycerophospholipid pools. CYP P450, prostaglandin H2 synthase, and lipoxygenases are capable of metabolizing polyunsaturated fatty acids other t ...
Biology Study List - MCAT Prep Course
... ¾ Understand the basic functions and structures of the major chemical components of living cells and their surroundings: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleotides, water and minerals (in order of importance) Enzymes: ¾ Understand the function and mode of action of enzymes ¾ Know the concept and m ...
... ¾ Understand the basic functions and structures of the major chemical components of living cells and their surroundings: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleotides, water and minerals (in order of importance) Enzymes: ¾ Understand the function and mode of action of enzymes ¾ Know the concept and m ...
Presence of Anaplerotic Reactions and Transamination, and the
... Enzymes ofthe TCA cycle. (i) Citrate synthase (EC 4.1.3.7) was assayed by both the methods of Srere (1969) and Stitt (1983~).(ii) Aconitase (EC 4.2.1.3) was assayed by a modification of the method of Goldberg & Ellis (1983). The reaction mixture (1.0 ml) contained 100 mM-HEPES/NaOH (pH 7-4), 1.7 mM- ...
... Enzymes ofthe TCA cycle. (i) Citrate synthase (EC 4.1.3.7) was assayed by both the methods of Srere (1969) and Stitt (1983~).(ii) Aconitase (EC 4.2.1.3) was assayed by a modification of the method of Goldberg & Ellis (1983). The reaction mixture (1.0 ml) contained 100 mM-HEPES/NaOH (pH 7-4), 1.7 mM- ...
Hepatology: Anatomy, Physiology and Dev
... digestion via the production and storage of bile. The liver is also the major organ for metabolism and detoxification. The pancreas also produces digestive enzymes to break down proteins, sugars, and fats. - The processes described above are the exocrine functions of the liver and gallbladder. But t ...
... digestion via the production and storage of bile. The liver is also the major organ for metabolism and detoxification. The pancreas also produces digestive enzymes to break down proteins, sugars, and fats. - The processes described above are the exocrine functions of the liver and gallbladder. But t ...
Objectives 19 - u.arizona.edu
... 1. HEME SYNTHESIS - heme is an iron containing prosthetic group found in hemoglobin, myoglobin, and cytochromes - heme binds O2, participates in electron transfer, or oxidizes exogenous molecule - reaction for synthesis occur both in cytoplasm and mitochondrial matrix; final step of pathway incorp ...
... 1. HEME SYNTHESIS - heme is an iron containing prosthetic group found in hemoglobin, myoglobin, and cytochromes - heme binds O2, participates in electron transfer, or oxidizes exogenous molecule - reaction for synthesis occur both in cytoplasm and mitochondrial matrix; final step of pathway incorp ...
Methods and approaches for the comprehensive characterization
... the method is based on labeling proteins even before tryptic digestion followed by fractionation, it significantly reduces the complexity of the sample but retains sequence coverage in the subsequent mass spectral analysis. This results in improved protein identification that is indispensable for th ...
... the method is based on labeling proteins even before tryptic digestion followed by fractionation, it significantly reduces the complexity of the sample but retains sequence coverage in the subsequent mass spectral analysis. This results in improved protein identification that is indispensable for th ...
Congratulations! You have signed up for AP Chemistry for this year
... AP stands for “Advanced Placement” and AP Chemistry is the equivalent of a college chemistry class. There are some chemistry principles that are important that you remember from Pre-AP Chemistry, so I have compiled some practice notes and assignments that will equip you for the beginning of the year ...
... AP stands for “Advanced Placement” and AP Chemistry is the equivalent of a college chemistry class. There are some chemistry principles that are important that you remember from Pre-AP Chemistry, so I have compiled some practice notes and assignments that will equip you for the beginning of the year ...
Course Map_2011-2012 - Kenwood Academy High School
... 12.11.74 Understand that the magnitude of a force F is defined as F = ma (Force equals Mass times Acceleration). Know how to perform such calculations. Understand that whenever one object exerts force on another, a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction is exerted on the first object. Un ...
... 12.11.74 Understand that the magnitude of a force F is defined as F = ma (Force equals Mass times Acceleration). Know how to perform such calculations. Understand that whenever one object exerts force on another, a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction is exerted on the first object. Un ...
Distinct profiling of antimicrobial peptide families
... AMP families differ among each other in the set of restrictive properties found in different regions of their peptide sequences. Different regions may have different restrictive properties. To select these restrictive properties, we used 544 physicochemical properties of amino acids available in the ...
... AMP families differ among each other in the set of restrictive properties found in different regions of their peptide sequences. Different regions may have different restrictive properties. To select these restrictive properties, we used 544 physicochemical properties of amino acids available in the ...
Yield Potential, Plant Assimilatory Capacity, and Metabolic Efficiencies
... plants. Other benefits include better water-use efficiency than C3 species and, perhaps more important, need for much less rubisco (and thus less N) per unit leaf area for rapid photosynthesis. Genetic control is similar to that for C3 systems, and key enzymes are homologous with ancient C3 genes, b ...
... plants. Other benefits include better water-use efficiency than C3 species and, perhaps more important, need for much less rubisco (and thus less N) per unit leaf area for rapid photosynthesis. Genetic control is similar to that for C3 systems, and key enzymes are homologous with ancient C3 genes, b ...
regulation of fatty acid synthesis
... localized in plastids. Although the biochemistry of this pathway is now well understood, much less is known about how plants control the very different amounts and types of lipids produced in different tissues. Thus, a central challenge for plant lipid research is to provide a molecular understandin ...
... localized in plastids. Although the biochemistry of this pathway is now well understood, much less is known about how plants control the very different amounts and types of lipids produced in different tissues. Thus, a central challenge for plant lipid research is to provide a molecular understandin ...
APPLICATION OF LACTIC ACID BACTERIA TO CONTROL
... The NL-249 isolates was identified as Lactobacillus plantarum showed the highest inhibitory activity against S. Typhimurium. This was allegedly due to presence of lactic acid which was a main product of L. plantarum NL-249 as homofermentatif LAB (Jay 1996). This was supported by a statement of Nousi ...
... The NL-249 isolates was identified as Lactobacillus plantarum showed the highest inhibitory activity against S. Typhimurium. This was allegedly due to presence of lactic acid which was a main product of L. plantarum NL-249 as homofermentatif LAB (Jay 1996). This was supported by a statement of Nousi ...
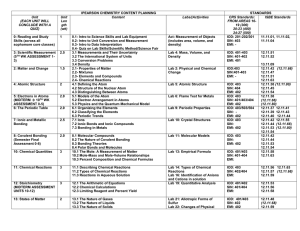
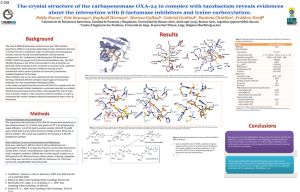
... The class D (OXA) β-lactamases contains more than 400 members classified in different sub-groups depending on their preferred substrates or kinetic behavior, and genetic origin. A particularly interesting group includes enzymes having increased hydrolytic activity towards carbapenems, the “carbapene ...
Dihydrofolate Reductase Assay Kit (CS0340) - Bulletin - Sigma
... present in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, playing a key role in thymidine synthesis. It catalyzes the reduction of 7,8-dihydrofolate (DHF) to 5,6,7,8tetrahydrofolate (THF), utilizing NADPH as cofactor. This reaction is an essential step in the biosynthesis of ...
... present in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, playing a key role in thymidine synthesis. It catalyzes the reduction of 7,8-dihydrofolate (DHF) to 5,6,7,8tetrahydrofolate (THF), utilizing NADPH as cofactor. This reaction is an essential step in the biosynthesis of ...
Boundless Study Slides
... • glycolysis the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source • glycolysis the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source • heterotroph an organism that requires an external supp ...
... • glycolysis the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source • glycolysis the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source • heterotroph an organism that requires an external supp ...
Standard for the presentation of nucleotide and amino acid
... “amino acids” are those L-amino acids commonly found in naturally occurring proteins and are listed in Appendix 2, Table 3. Those amino acid sequences containing at least one D-amino acid are not intended to be embraced by this definition. Any amino acid sequence that contains post-translationally m ...
... “amino acids” are those L-amino acids commonly found in naturally occurring proteins and are listed in Appendix 2, Table 3. Those amino acid sequences containing at least one D-amino acid are not intended to be embraced by this definition. Any amino acid sequence that contains post-translationally m ...
sec chemistry may 2011 marking scheme
... A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Carbon can catenate / form chains of C atoms • An atom of carbon can form stable (or strong) covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Gases (or fuel gas) (Do not accept LPG) Petrol (or gasoline) / naphtha Any two from: • different sized molec ...
... A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Carbon can catenate / form chains of C atoms • An atom of carbon can form stable (or strong) covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Gases (or fuel gas) (Do not accept LPG) Petrol (or gasoline) / naphtha Any two from: • different sized molec ...
Abnormal Renal and Hepatic Glucose Metabolism in Type 2
... However, increased renal glucose release has also been demonstrated in diabetic animals (6–9). Moreover, recent studies (10, 11) indicate that the human kidney may normally account for as much as 25% of postabsorptive glucose production. It is possible, therefore, that renal glucose release may cont ...
... However, increased renal glucose release has also been demonstrated in diabetic animals (6–9). Moreover, recent studies (10, 11) indicate that the human kidney may normally account for as much as 25% of postabsorptive glucose production. It is possible, therefore, that renal glucose release may cont ...
Activation and Stabilization of Penicillin V Acylase from
... potential scope and economic impact of biocatalysis, opening a new field in the biotechnological applications of enzymes (Gupta, 1992). Enzymatic activity sometimes may be improved as a result of the incorporation of a small amount of a water-miscible organic solvent in the reaction mixture (Tan and ...
... potential scope and economic impact of biocatalysis, opening a new field in the biotechnological applications of enzymes (Gupta, 1992). Enzymatic activity sometimes may be improved as a result of the incorporation of a small amount of a water-miscible organic solvent in the reaction mixture (Tan and ...
COMMUNICATION
... strikingly similar isoelec- nectin and other extracellular matrix materials. These tric focusing patterns (1) and functions (2,3. 5. 11, 14, adhesion glycoproteins recognize a common sequence, 21. 22) of the two proteins. Compared with other gene RGD. present in many extracellular matrix proteins, s ...
... strikingly similar isoelec- nectin and other extracellular matrix materials. These tric focusing patterns (1) and functions (2,3. 5. 11, 14, adhesion glycoproteins recognize a common sequence, 21. 22) of the two proteins. Compared with other gene RGD. present in many extracellular matrix proteins, s ...
Chemistry Standard Level Chapter 1
... reactions involve changes in smell, colour and texture and these are difficult to quantify. Lavoisier appreciated the importance of attaching numbers to properties and recognized the need for precise measurement. His use of the balance allowed changes in mass to be used to analyse chemical reactions. ...
... reactions involve changes in smell, colour and texture and these are difficult to quantify. Lavoisier appreciated the importance of attaching numbers to properties and recognized the need for precise measurement. His use of the balance allowed changes in mass to be used to analyse chemical reactions. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.