2. CHEMICAL ACTIVITY of the METALS 3. PATTERNS of the
... artillery) achieved new heights (depths?) in warfare and mass destruction. ...
... artillery) achieved new heights (depths?) in warfare and mass destruction. ...
Mechanism of CS, Cont`d
... • It assists in transferring fatty acids from the cytoplasm to mitochondria • A molecule of CoA carrying an acetyl group is also referred to as acetyl-CoA • When it is not attached to an acyl group it is usually referred to as 'CoASH' or 'HSCoA' ...
... • It assists in transferring fatty acids from the cytoplasm to mitochondria • A molecule of CoA carrying an acetyl group is also referred to as acetyl-CoA • When it is not attached to an acyl group it is usually referred to as 'CoASH' or 'HSCoA' ...
Chapter 2: Mass Relations in Formulas, Chemical Reactions, and
... reactions are useful for the chemical analysis of substances containing carbon and hydrogen as they produce CO2 and H2O. Measuring the amount of CO2 and H2O produced by a given amount of substance allows the determination of how much carbon and hydrogen are present in that amount of substance. Examp ...
... reactions are useful for the chemical analysis of substances containing carbon and hydrogen as they produce CO2 and H2O. Measuring the amount of CO2 and H2O produced by a given amount of substance allows the determination of how much carbon and hydrogen are present in that amount of substance. Examp ...
The mitochondrial respiratory chain
... together with a vast amount of information from other spectroscopic methods, have led to understanding of many details of the electron and proton transfer mechanisms involved. For simplicity, the Figure shows one of each major complex and they are described individually below; however, their real or ...
... together with a vast amount of information from other spectroscopic methods, have led to understanding of many details of the electron and proton transfer mechanisms involved. For simplicity, the Figure shows one of each major complex and they are described individually below; however, their real or ...
video slide
... • The stomach stores food and secretes gastric juice, which converts a meal to acid chyme • Gastric juice is made up of hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin • Pepsin is secreted as inactive pepsinogen; pepsin is activated when mixed with hydrochloric acid in the stomach • Mucus protects the stoma ...
... • The stomach stores food and secretes gastric juice, which converts a meal to acid chyme • Gastric juice is made up of hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin • Pepsin is secreted as inactive pepsinogen; pepsin is activated when mixed with hydrochloric acid in the stomach • Mucus protects the stoma ...
video slide - Somers Public Schools
... • The stomach stores food and secretes gastric juice, which converts a meal to acid chyme • Gastric juice is made up of hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin • Pepsin is secreted as inactive pepsinogen; pepsin is activated when mixed with hydrochloric acid in the stomach • Mucus protects the stoma ...
... • The stomach stores food and secretes gastric juice, which converts a meal to acid chyme • Gastric juice is made up of hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin • Pepsin is secreted as inactive pepsinogen; pepsin is activated when mixed with hydrochloric acid in the stomach • Mucus protects the stoma ...
Cerebral Energy Metabolism in Hepatic Encephalopathy and
... NADH+ through its reductive amination to glutamate. Studies by Lai and Cooper (1986) indicated that ammonium salts added in vitro to isolated brain mitochondria significantly inhibited the activity of α-KGDH, while Katanuma et al. (1966) reported inhibition of isocitrate dehydrogenase by ammonia. Co ...
... NADH+ through its reductive amination to glutamate. Studies by Lai and Cooper (1986) indicated that ammonium salts added in vitro to isolated brain mitochondria significantly inhibited the activity of α-KGDH, while Katanuma et al. (1966) reported inhibition of isocitrate dehydrogenase by ammonia. Co ...
Unit 3
... from the atmosphere. This process is called ventilation. Diffusion – Exchange of gases based on concentration levels (High to low). Occurs at a cellular level (In the lungs and in the muscle cell) Cardiac output (Heart rate x stroke volume) - The heart pumps out oxygenated blood to the vascular ...
... from the atmosphere. This process is called ventilation. Diffusion – Exchange of gases based on concentration levels (High to low). Occurs at a cellular level (In the lungs and in the muscle cell) Cardiac output (Heart rate x stroke volume) - The heart pumps out oxygenated blood to the vascular ...
Part 5 Coenzyme-Dependent Enzyme Mechansims
... • It assists in transferring fatty acids from the cytoplasm to mitochondria • A molecule of CoA carrying an acetyl group is also referred to as acetyl-CoA • When it is not attached to an acyl group it is usually referred to as 'CoASH' or 'HSCoA' ...
... • It assists in transferring fatty acids from the cytoplasm to mitochondria • A molecule of CoA carrying an acetyl group is also referred to as acetyl-CoA • When it is not attached to an acyl group it is usually referred to as 'CoASH' or 'HSCoA' ...
Production of exopolysaccharide from mycelial culture of Grifola
... The molecular mass of EPS was determined by HPLC with Shodex OHpak KB-804 column, where a single symmetrical peak was observed (Fig. 2A). The EPS had an extremely high molecular weight (1 · 106 Da) (Fig. 2B), which is considerably higher than those obtained from mycelial extracts of G. frondosa repo ...
... The molecular mass of EPS was determined by HPLC with Shodex OHpak KB-804 column, where a single symmetrical peak was observed (Fig. 2A). The EPS had an extremely high molecular weight (1 · 106 Da) (Fig. 2B), which is considerably higher than those obtained from mycelial extracts of G. frondosa repo ...
Cell Differentiation during Sexual Development of the Fungus
... During sexual development, mycelial cells from most filamentous fungi differentiate into typical fruiting bodies. Here, we describe the isolation and characterization of the Sordaria macrospora developmental mutant per5, which exhibits a sterile phenotype with defects in fruiting body maturation. Cy ...
... During sexual development, mycelial cells from most filamentous fungi differentiate into typical fruiting bodies. Here, we describe the isolation and characterization of the Sordaria macrospora developmental mutant per5, which exhibits a sterile phenotype with defects in fruiting body maturation. Cy ...
accelerated glucose discoloration method
... E-20, (1987), Glucose Color Stability (Analytical Methods of the member Companies of the corn Association, Inc), using the two types of D-glucose, glucose A and glucose B. The addition of different reagents such as HCl, H2SO4, citric acid, H3PO4, chromium chloride, sodium sulphite, ammonium chloride ...
... E-20, (1987), Glucose Color Stability (Analytical Methods of the member Companies of the corn Association, Inc), using the two types of D-glucose, glucose A and glucose B. The addition of different reagents such as HCl, H2SO4, citric acid, H3PO4, chromium chloride, sodium sulphite, ammonium chloride ...
Genetic Engineering for Improved Xylose Fermentation by Yeasts
... in S. cerevisiae but found that the protein had only about 10-3 as much activity as the native protein from E. coli. Over the past 30 years, a few researchers have reported the presence of xylose isomerase in a number of yeasts and fungi capable of rapid xylose metabolism. Because of difficulties in ...
... in S. cerevisiae but found that the protein had only about 10-3 as much activity as the native protein from E. coli. Over the past 30 years, a few researchers have reported the presence of xylose isomerase in a number of yeasts and fungi capable of rapid xylose metabolism. Because of difficulties in ...
Adipocyte metabolic pathways regulated by diet control
... in adipocytes, and the survival of early germline cysts. Enzymes catalyzing fatty acid oxidation and ...
... in adipocytes, and the survival of early germline cysts. Enzymes catalyzing fatty acid oxidation and ...
The Brazilian technology of fuel ethanol fermentation
... 1. The Brazilian process of fuel ethanol production Brazil is the second largest producer of ethanol in the world and the first in the technology of ethanol from sugar cane. The Brazilian production of sugar cane in the 2012/13 harvest was 589 million tons of cane, 38.3 million tons of sugar (5% sup ...
... 1. The Brazilian process of fuel ethanol production Brazil is the second largest producer of ethanol in the world and the first in the technology of ethanol from sugar cane. The Brazilian production of sugar cane in the 2012/13 harvest was 589 million tons of cane, 38.3 million tons of sugar (5% sup ...
C.S.E-Zoology
... of probability that the daughter of the couple is colour blind? (a) 100% (b) 50% (c) 25% (d) 0 14. How many molecules of ATP would be synthesised if one pyruvate moleculepasses through the oxidative steps? (a) 12 (b) 14 (c) 24 (d) 28 16. Consider the following statements: 1. Peroxisomes contain amin ...
... of probability that the daughter of the couple is colour blind? (a) 100% (b) 50% (c) 25% (d) 0 14. How many molecules of ATP would be synthesised if one pyruvate moleculepasses through the oxidative steps? (a) 12 (b) 14 (c) 24 (d) 28 16. Consider the following statements: 1. Peroxisomes contain amin ...
Order date : 24-07-2010
... R. A. Y. Jones, Physical and Mechanistic Organic Chemistry, Cambridge University Press, 1979. ...
... R. A. Y. Jones, Physical and Mechanistic Organic Chemistry, Cambridge University Press, 1979. ...
Sequence and evolutionary analysis of the human trypsin subfamily
... residues Lys15 and Ile16 (chymotrypsinogen numbering). After cleavage, Ile16 forms the new N-terminus of the protein, and Asp194 rotates to interact with it. This rotation and the resulting salt bridge produce a conformational change that completes the formation of the oxyanion hole and the substrat ...
... residues Lys15 and Ile16 (chymotrypsinogen numbering). After cleavage, Ile16 forms the new N-terminus of the protein, and Asp194 rotates to interact with it. This rotation and the resulting salt bridge produce a conformational change that completes the formation of the oxyanion hole and the substrat ...
Trophic ecology of a green turtle breeding population
... al. 2009, Navarro et al. 2011). An isotopic niche is a proxy for an ecological niche and is influenced by what individuals consume (bionomic factors), as well as where they live (scenopoetic factors), and is typically represented by 2 or more stable isotope measurements of tissues from of a consumer ...
... al. 2009, Navarro et al. 2011). An isotopic niche is a proxy for an ecological niche and is influenced by what individuals consume (bionomic factors), as well as where they live (scenopoetic factors), and is typically represented by 2 or more stable isotope measurements of tissues from of a consumer ...
Study Materials
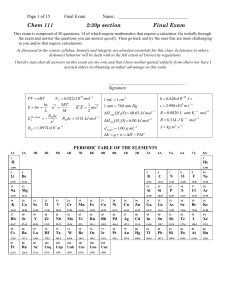
... Chemistry is a branch of science which deals with the composition, structure and properties of matter. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, an atom is the smallest particle of an element, which may or may not have free existence. Moreover it is the smallest particle that take parts in a chemical rea ...
... Chemistry is a branch of science which deals with the composition, structure and properties of matter. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, an atom is the smallest particle of an element, which may or may not have free existence. Moreover it is the smallest particle that take parts in a chemical rea ...
Mini-Series: Modern Metabolic Concepts The Biochemistry of the
... binds E1 at the different site. While E3 interacts with the N-terminal part of the subunit-binding domain, E1 binds to the C-terminal part of the same domain. The binding site for the A. vinelandii E1 was shown to involve not only the subunit-binding domain but also the E2 inner domain [9]. PDK is a ...
... binds E1 at the different site. While E3 interacts with the N-terminal part of the subunit-binding domain, E1 binds to the C-terminal part of the same domain. The binding site for the A. vinelandii E1 was shown to involve not only the subunit-binding domain but also the E2 inner domain [9]. PDK is a ...
Syllabus - Chemistry
... Principle of protection of carbon-hydrogen bonds (in terminal alkynes and hydrogens of aldehydes), carbon-carbon double bonds, alcoholic hydroxyl groups, amine groups, carbonyl and carboxyl groups. Unit-II 12 hrs One Group carbon-carbon Disconnections Examples from simple alcohols, amines (aliphatic ...
... Principle of protection of carbon-hydrogen bonds (in terminal alkynes and hydrogens of aldehydes), carbon-carbon double bonds, alcoholic hydroxyl groups, amine groups, carbonyl and carboxyl groups. Unit-II 12 hrs One Group carbon-carbon Disconnections Examples from simple alcohols, amines (aliphatic ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.