enzyme
... Absolute specificity:Only catalyze one special kind of substrate and produce one kind of product Relative specificity:Can catalyze one sort of compounds or chemical bonds Stereo specificity:Only act on a single stereoisomer of the substrate ...
... Absolute specificity:Only catalyze one special kind of substrate and produce one kind of product Relative specificity:Can catalyze one sort of compounds or chemical bonds Stereo specificity:Only act on a single stereoisomer of the substrate ...
Glutathione and glutamate levels in the diaphragm of patients with
... (fig. 1c). Besides Glu, the levels of several other amino acids in the COPD group were lower in the quadriceps femoris than in the diaphragm. Furthermore, the Glu/GSH ratio was lower in the quadriceps femoris (pv0.05). However, no difference was observed for glutamine and taurine, amino acids that a ...
... (fig. 1c). Besides Glu, the levels of several other amino acids in the COPD group were lower in the quadriceps femoris than in the diaphragm. Furthermore, the Glu/GSH ratio was lower in the quadriceps femoris (pv0.05). However, no difference was observed for glutamine and taurine, amino acids that a ...
the arithmetical phenomena of symmetry in the genetic code with the
... 5 modules - 40 protons 10 atoms - 40 protons Fig.1. Molecular structure and Petoukhov’s structure of the 20 amino acids (inspired by S. Petoukhov’s paper) So, a module is a grouping of one non-hydrogen atom with from 0 to 3 hydrogen atoms. These modules are described by S. Petoukhov in a number from ...
... 5 modules - 40 protons 10 atoms - 40 protons Fig.1. Molecular structure and Petoukhov’s structure of the 20 amino acids (inspired by S. Petoukhov’s paper) So, a module is a grouping of one non-hydrogen atom with from 0 to 3 hydrogen atoms. These modules are described by S. Petoukhov in a number from ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... 1. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. 2. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag +, Pb2+, or Hg2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those ...
... 1. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. 2. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag +, Pb2+, or Hg2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those ...
Chapter 8
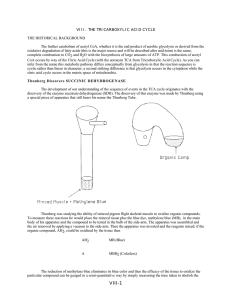
... At this point all of the reactions that result in reduction in carbon chain length are complete, 2 CO2 have been eliminated 2 NADH and 1 ATP have been made and we are back with a 4-carbon acid. However the acid is succinate, whereas to start a new cycle we need oxalacetate. This requires the oxidati ...
... At this point all of the reactions that result in reduction in carbon chain length are complete, 2 CO2 have been eliminated 2 NADH and 1 ATP have been made and we are back with a 4-carbon acid. However the acid is succinate, whereas to start a new cycle we need oxalacetate. This requires the oxidati ...
BIO 100 coursepack FA2015
... What are some current problems facing biology? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
... What are some current problems facing biology? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
Strategies to Overcome Blood-Brain Barrier
... quality assurance/quality control plan. “Additionally, choose simple analysis methods and understand when and why a model may fail.” In vivo molecular imaging can help ...
... quality assurance/quality control plan. “Additionally, choose simple analysis methods and understand when and why a model may fail.” In vivo molecular imaging can help ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... 1. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. 2. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag +, Pb2+, or Hg2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those ...
... 1. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. 2. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag +, Pb2+, or Hg2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those ...
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
... substrates for ANT(4 )JIa previous estimations of the amount of chromosomal DNA per S. aureus cell (11, 15), we estiAntibiotic adeny9% lylated ...
... substrates for ANT(4 )JIa previous estimations of the amount of chromosomal DNA per S. aureus cell (11, 15), we estiAntibiotic adeny9% lylated ...
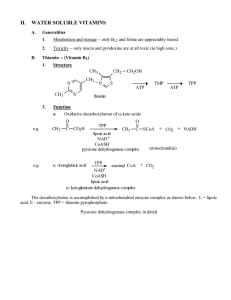
420_06_watersoluble1..
... 11. Toxicity -- nontoxic on oral administration; No UL value. Anaphylactic reactions have been observed in patients receiving repetitive parenteral doses. 12. Patient Counseling/ patient use issues a. Needed to drive carbohydrates to energy b. Rarely needed as a single supplement. Use a multivitamin ...
... 11. Toxicity -- nontoxic on oral administration; No UL value. Anaphylactic reactions have been observed in patients receiving repetitive parenteral doses. 12. Patient Counseling/ patient use issues a. Needed to drive carbohydrates to energy b. Rarely needed as a single supplement. Use a multivitamin ...
Oligomerization and activation of the FliI ATPase
... energy for assembly at the critical location. Whether this energy is used directly for substrate protein translocation and/or protein unfolding or interaction is not known. Crystal structures of the H. pylori and E. coli hexameric type IV export ATPases (Yeo et al., 2000; Gomis-Ruth et al., 2001) sh ...
... energy for assembly at the critical location. Whether this energy is used directly for substrate protein translocation and/or protein unfolding or interaction is not known. Crystal structures of the H. pylori and E. coli hexameric type IV export ATPases (Yeo et al., 2000; Gomis-Ruth et al., 2001) sh ...
cerevisiae - Oxford Academic
... also reported the insertion of tyrosine, lysine and tryptophan at UAG stop codons in yeast Ste6p (28). Most of the available data concerning the nature of the amino acids inserted by readthrough were obtained from in vitro studies on plant tRNAs and viral mRNAs. Very few in vivo data are available, ...
... also reported the insertion of tyrosine, lysine and tryptophan at UAG stop codons in yeast Ste6p (28). Most of the available data concerning the nature of the amino acids inserted by readthrough were obtained from in vitro studies on plant tRNAs and viral mRNAs. Very few in vivo data are available, ...
Chapter 4
... 3. Explain the five physiological reasons for the production of lactic acid. What determines whether or not lactate accumulates in the blood? How is lactate cleared? Pg. 90-92, Figure 4.4 The five physiological reasons for the production of lactate are: a) Muscle contraction- during muscle contract ...
... 3. Explain the five physiological reasons for the production of lactic acid. What determines whether or not lactate accumulates in the blood? How is lactate cleared? Pg. 90-92, Figure 4.4 The five physiological reasons for the production of lactate are: a) Muscle contraction- during muscle contract ...
Anion gap metabolic acidosis
... Acetaldehyde levels increase significantly if acetaldehyde dehydrogenase inhibited by disulfiram, insecticides or a sulfonurea. ...
... Acetaldehyde levels increase significantly if acetaldehyde dehydrogenase inhibited by disulfiram, insecticides or a sulfonurea. ...
The integrity of a cholesterol-binding pocket in Niemann–Pick C2
... and mutant NPC2 proteins, starting from a culture medium into which cells had released NPC2. Previous studies of NPC2 used NPC2-conditioned media (7) or NPC2 purified from porcine epididymal fluid (10). These procedures are not practical for studying a substantial number of mutant proteins, so we de ...
... and mutant NPC2 proteins, starting from a culture medium into which cells had released NPC2. Previous studies of NPC2 used NPC2-conditioned media (7) or NPC2 purified from porcine epididymal fluid (10). These procedures are not practical for studying a substantial number of mutant proteins, so we de ...
03_Worked_Examples
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
v7a29-zhu pgmkr - Molecular Vision
... This kind of genome duplication has been documented in several non-mammalian vertebrates. For example, it has been shown that there are at least seven cry homologs in the zebrafish genome [28]. Since Drosophila and mammalian CRYs have distinct functions, we hypothesized that by studying CRY function ...
... This kind of genome duplication has been documented in several non-mammalian vertebrates. For example, it has been shown that there are at least seven cry homologs in the zebrafish genome [28]. Since Drosophila and mammalian CRYs have distinct functions, we hypothesized that by studying CRY function ...
BTEC National in Applied Science Unit 01 Sample redacted web
... Ionic bonding occurs when an atom of an element loses one or more electron and donates it to an atom of a different element. The atom that loses electrons becomes positively charged and the atom that gains electron(s) become negatively charged because of the imbalance of protons and electrons. For e ...
... Ionic bonding occurs when an atom of an element loses one or more electron and donates it to an atom of a different element. The atom that loses electrons becomes positively charged and the atom that gains electron(s) become negatively charged because of the imbalance of protons and electrons. For e ...
03_Worked_Examples
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... of the equation has the same number of atoms of each element as the right side of the equation. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms of each element, on both each side of the equation should be the same. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ...
... of the equation has the same number of atoms of each element as the right side of the equation. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms of each element, on both each side of the equation should be the same. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ...
The Effect of Oxygen on the Growth and Mannitol
... strains was severely inhibited by oxygen, whereas the others were oxygen-tolerant. The growth of two of the oxygen-tolerant strains was significantly enhanced by oxygen. The activities of superoxide dismutase and NADH oxidase in extracts from aerobically grown bacteria showed a positive correlation ...
... strains was severely inhibited by oxygen, whereas the others were oxygen-tolerant. The growth of two of the oxygen-tolerant strains was significantly enhanced by oxygen. The activities of superoxide dismutase and NADH oxidase in extracts from aerobically grown bacteria showed a positive correlation ...
J B , Mar. 2004, p. 1531–1536 Vol. 186, No. 5
... C40 synthase performance, mutants were transformed into E. coli cells expressing the E. uredovora GGDP synthase CrtE and the C40 desaturase CrtI. Cells containing CrtM variants that have acquired C40 synthase activity accumulate lycopene. The pigmentation level was determined from the peak height (a ...
... C40 synthase performance, mutants were transformed into E. coli cells expressing the E. uredovora GGDP synthase CrtE and the C40 desaturase CrtI. Cells containing CrtM variants that have acquired C40 synthase activity accumulate lycopene. The pigmentation level was determined from the peak height (a ...
Spring 1997 - University of Idaho
... 1828 - active ingredient isolated by Johann Buchner. Found effective for fevers, inflammation, and pains but found to cause stomach irritation. ...
... 1828 - active ingredient isolated by Johann Buchner. Found effective for fevers, inflammation, and pains but found to cause stomach irritation. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.