Slide 1
... that sickle cell haemoglobin varies from wild type by the substitution of one amino acid ...
... that sickle cell haemoglobin varies from wild type by the substitution of one amino acid ...
Electrons - davis.k12.ut.us
... What are the elements in the human body? •Most of the human body is made up of water, H2O, with cells consisting of 65-90% water by weight. Therefore, it isn't surprising that most of a human body's mass is oxygen. Carbon, the basic unit for organic molecules, comes in second. 99% of the mass of th ...
... What are the elements in the human body? •Most of the human body is made up of water, H2O, with cells consisting of 65-90% water by weight. Therefore, it isn't surprising that most of a human body's mass is oxygen. Carbon, the basic unit for organic molecules, comes in second. 99% of the mass of th ...
NOTES: CH 9 pt 1 - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... ● Living cells require ● Some animals, such as the giant panda, obtain energy by ...
... ● Living cells require ● Some animals, such as the giant panda, obtain energy by ...
GHW#10-Questions
... folded - (-helix, -sheet, random coil). 3) Tertiary structure Way -helix, -sheet, random coils fold and coil. ...
... folded - (-helix, -sheet, random coil). 3) Tertiary structure Way -helix, -sheet, random coils fold and coil. ...
Cell.Biology.2. Macromolecules edited
... You have 15 minutes to get as much done as you can. As soon as you’re done, or after 15 minutes (whichever comes first), come back to class. ...
... You have 15 minutes to get as much done as you can. As soon as you’re done, or after 15 minutes (whichever comes first), come back to class. ...
Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism
... removal of the nitrogen Ammonium ion is converted to urea in most mammals. Carbon atoms are converted to other major metabolic intermediates. Inborn errors in metabolism ...
... removal of the nitrogen Ammonium ion is converted to urea in most mammals. Carbon atoms are converted to other major metabolic intermediates. Inborn errors in metabolism ...
G19S Amino Acid code
... 2. Identify the process responsible by writing its mane below the arrow in Column A. 3. Identify the process responsible by writing its name below the arrow in Column C. 4. Complete column D by writing the name of the correct amino acid that is coded by each base sequence. Use the mRNA genetic code ...
... 2. Identify the process responsible by writing its mane below the arrow in Column A. 3. Identify the process responsible by writing its name below the arrow in Column C. 4. Complete column D by writing the name of the correct amino acid that is coded by each base sequence. Use the mRNA genetic code ...
protein - 4J Blog Server
... • How the sequence and subcomponents of proteins determine their properties. • The cellular functions of proteins. (Brief – we will come back to this in other chapters.) • The four structural levels of proteins and how changes at any level can affect the activity of the protein. • How proteins reach ...
... • How the sequence and subcomponents of proteins determine their properties. • The cellular functions of proteins. (Brief – we will come back to this in other chapters.) • The four structural levels of proteins and how changes at any level can affect the activity of the protein. • How proteins reach ...
survey of biochemistry - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... involves noncovalent interactions Binding pocket is wellformed, but induced fitting can occur Substrate or inhibitor binding is usually based on complementarity ...
... involves noncovalent interactions Binding pocket is wellformed, but induced fitting can occur Substrate or inhibitor binding is usually based on complementarity ...
Nucleic Acids Placemat
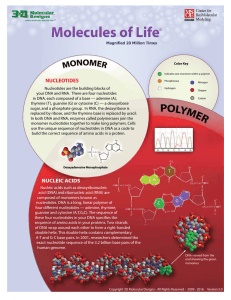
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
Protein Unit Study Guide/Review Sheets
... If you have questions, make sure to ask them. Stop in before or after school. Review questions: 1. What elements comprise proteins? C, H, O, N 2. Are proteins organic? YES – CONTAIN CARBON AND HYDROGEN, THE REQUIREMENT FOR BEING AN ORGANIC MOLECULE 3. What element MAY be present in proteins? SULFUR ...
... If you have questions, make sure to ask them. Stop in before or after school. Review questions: 1. What elements comprise proteins? C, H, O, N 2. Are proteins organic? YES – CONTAIN CARBON AND HYDROGEN, THE REQUIREMENT FOR BEING AN ORGANIC MOLECULE 3. What element MAY be present in proteins? SULFUR ...
biomolecules
... ammonia combine in the presence of an energy source (such as lightning or ultraviolet light from the Sun), inorganic molecules react to form organic molecules, such as amino acids. A competing theory is the RNA-world hypothesis. This hypothesis states that RNA developed first. It may have self-replic ...
... ammonia combine in the presence of an energy source (such as lightning or ultraviolet light from the Sun), inorganic molecules react to form organic molecules, such as amino acids. A competing theory is the RNA-world hypothesis. This hypothesis states that RNA developed first. It may have self-replic ...
Cellular Respiration
... WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE? Anaerobic - Does not require Oxygen Aerobic - Does require Oxygen ...
... WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE? Anaerobic - Does not require Oxygen Aerobic - Does require Oxygen ...
CHAPTERS 23-25
... A series of reactions in which protons and electrons from the oxidation of foods are used to reduce molecular oxygen to water Cytochrome An iron-containing enzyme located in the electron transport chain Fig 23.9 page 721 Oxidative phosphorylation A process coupled with the electron trans ...
... A series of reactions in which protons and electrons from the oxidation of foods are used to reduce molecular oxygen to water Cytochrome An iron-containing enzyme located in the electron transport chain Fig 23.9 page 721 Oxidative phosphorylation A process coupled with the electron trans ...
Grading Rubric: Photosynthesis and Cellular
... the mitochondria for cellular respiration to continue making ATP ...
... the mitochondria for cellular respiration to continue making ATP ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 9
... Preparation for entry to Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle; tricarboxylic acid cycle) C. Fermentation In absence of oxygen Pyruvate is reduced by NADH to regenerate NAD+ Lactate fermentation Lactate dehydrogenase works in either direction depending on prevailing conditions in the cell Lactic acid produ ...
... Preparation for entry to Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle; tricarboxylic acid cycle) C. Fermentation In absence of oxygen Pyruvate is reduced by NADH to regenerate NAD+ Lactate fermentation Lactate dehydrogenase works in either direction depending on prevailing conditions in the cell Lactic acid produ ...
Light-independent reactions - Mrs Jones A
... biological molecules such as saccharides – two molecules of TP can combine to form a hexose sugar, e.g. glucose and such structures can polymerise to form starches, sugars and cellulose molecules of GP can be used to form amino acids and fatty acids TP can also be used to form glycerol, which ca ...
... biological molecules such as saccharides – two molecules of TP can combine to form a hexose sugar, e.g. glucose and such structures can polymerise to form starches, sugars and cellulose molecules of GP can be used to form amino acids and fatty acids TP can also be used to form glycerol, which ca ...
Chemical digestion
... • Macromolecule – Giant molecule made from smaller molecules. • Polymer- Large molecule consisting of similar or identical molecules linked together. • Monomer – Subunit of polymer. • Polymerization - Process of polymer creation ...
... • Macromolecule – Giant molecule made from smaller molecules. • Polymer- Large molecule consisting of similar or identical molecules linked together. • Monomer – Subunit of polymer. • Polymerization - Process of polymer creation ...
18.3 Important Coenzymes
... Pathway of 10 interconnected enzyme Rx Initial substrate: glucose Final product: pyruvate Most ancient metabolic pathway, evolved before O2 levels were high and therefore…. • does not need O2, does not produce CO2 • Takes place in the cytosol of cells • has an energy investing phase (activation E) a ...
... Pathway of 10 interconnected enzyme Rx Initial substrate: glucose Final product: pyruvate Most ancient metabolic pathway, evolved before O2 levels were high and therefore…. • does not need O2, does not produce CO2 • Takes place in the cytosol of cells • has an energy investing phase (activation E) a ...
Light-independent reactions
... biological molecules such as saccharides – two molecules of TP can combine to form a hexose sugar, e.g. glucose and such structures can polymerise to form starches, sugars and cellulose molecules of GP can be used to form amino acids and fatty acids TP can also be used to form glycerol, which ca ...
... biological molecules such as saccharides – two molecules of TP can combine to form a hexose sugar, e.g. glucose and such structures can polymerise to form starches, sugars and cellulose molecules of GP can be used to form amino acids and fatty acids TP can also be used to form glycerol, which ca ...
Biology Final Jeopary 2
... A: The type of memory cell that will produce antibodies quickly in response to a pathogen the body has “seen” before; responsible for immunity. ...
... A: The type of memory cell that will produce antibodies quickly in response to a pathogen the body has “seen” before; responsible for immunity. ...
Amino Acid Analysis - Donald Danforth Plant Science Center
... Analysis of amino acids is required in several areas of research, and it is a fundamental tool in product analysis. The application imposes different requirements on the analytical method because the amino acids play different roles. ...
... Analysis of amino acids is required in several areas of research, and it is a fundamental tool in product analysis. The application imposes different requirements on the analytical method because the amino acids play different roles. ...
Stroma
... 8. Name three(3) ways that pyruvate is modified as it moves into to mitochondrion and prepares to enter Kreb’s cycle. 9. Describe the formation of citric acid in Kreb’s cycle. How many carbons does citric acid have? 10. For glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and electron transport, list the following: locatio ...
... 8. Name three(3) ways that pyruvate is modified as it moves into to mitochondrion and prepares to enter Kreb’s cycle. 9. Describe the formation of citric acid in Kreb’s cycle. How many carbons does citric acid have? 10. For glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and electron transport, list the following: locatio ...
Stroma
... What is the source of electrons for the electron transport chain? Describe how ATP is made in the electron transport chain. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? Provide the summary chemical equation for cellular respiration and explain the origin of each of the reacta ...
... What is the source of electrons for the electron transport chain? Describe how ATP is made in the electron transport chain. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? Provide the summary chemical equation for cellular respiration and explain the origin of each of the reacta ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.