Bio 20-Cellular Respiration Assignment Part A
... 4. Identify the stage of cellular respiration where carbon dioxide is given off. State one main function of this stage and where it is located within the cell. (3) ...
... 4. Identify the stage of cellular respiration where carbon dioxide is given off. State one main function of this stage and where it is located within the cell. (3) ...
Food Prelab - TeacherWeb
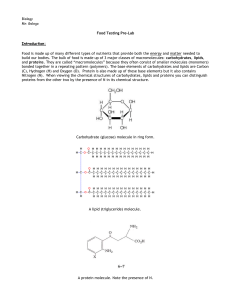
... The body uses lipids for long-term energy storage. Lipids are hydrophobic (“water-hating”) and thus much harder to break down for energy than carbohydrates. Lipids, however, contain more energy per unit weight then carbohydrates. Therefore it is more efficient for the body to use lipids as stored en ...
... The body uses lipids for long-term energy storage. Lipids are hydrophobic (“water-hating”) and thus much harder to break down for energy than carbohydrates. Lipids, however, contain more energy per unit weight then carbohydrates. Therefore it is more efficient for the body to use lipids as stored en ...
Document
... 19. AIDS is a genetic disease which can be transmitted to the next generation 20. Glycolysis is occurred in the cytoplasm and need the O2 . 21. The genotype of an organism refers to its appearance ……. 22. Glycolysis produce energy by oxidizing glucose molecule into 3 pyruvate molecules…. 23. Heterot ...
... 19. AIDS is a genetic disease which can be transmitted to the next generation 20. Glycolysis is occurred in the cytoplasm and need the O2 . 21. The genotype of an organism refers to its appearance ……. 22. Glycolysis produce energy by oxidizing glucose molecule into 3 pyruvate molecules…. 23. Heterot ...
CHAPTER 3-Protein-In Class Activity
... Name some of the protein functions in the body with their examples. Define Primary structure of a protein with example Define Secondary structure of a protein with example Define Tertiary structure of a protein with example Define Quaternary structure of a protein with example Secondary structure, f ...
... Name some of the protein functions in the body with their examples. Define Primary structure of a protein with example Define Secondary structure of a protein with example Define Tertiary structure of a protein with example Define Quaternary structure of a protein with example Secondary structure, f ...
- faculty lounge: non
... also serves as a precursor to steroid hormones, important regulators of growth and development. ...
... also serves as a precursor to steroid hormones, important regulators of growth and development. ...
A. The study of chemistry is essential for the study of physiology
... 10. An atomic number is the number of protons in the atoms of a particular element. 11. Carbon has an atomic number of six. 12. One atom of carbon contains six protons. 13. The weight of an atom is primarily due to the weight of protons and ...
... 10. An atomic number is the number of protons in the atoms of a particular element. 11. Carbon has an atomic number of six. 12. One atom of carbon contains six protons. 13. The weight of an atom is primarily due to the weight of protons and ...
energy2
... The process of glycolysis requires 2 ATP molecules and produces 4, for a net gain of 2 ATPs from each molecule of glucose. Glycolysis does not require oxygen. ...
... The process of glycolysis requires 2 ATP molecules and produces 4, for a net gain of 2 ATPs from each molecule of glucose. Glycolysis does not require oxygen. ...
AMA 108 PowerPoint
... Proteins – contain amino acids, provide energy, help build and repair tissues and assist with antibody production; found in meat, cheese and eggs. The body needs 20 amino acids, 11 are produced by the body, the other 9 are called essential amino acids and you must get them from food ...
... Proteins – contain amino acids, provide energy, help build and repair tissues and assist with antibody production; found in meat, cheese and eggs. The body needs 20 amino acids, 11 are produced by the body, the other 9 are called essential amino acids and you must get them from food ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... protein chain and slowly release energy that is used to form ATP and water molecules • Electron Transport Chain transfers the most energy ...
... protein chain and slowly release energy that is used to form ATP and water molecules • Electron Transport Chain transfers the most energy ...
Cracking the Genetic Code
... analyzed the resulting polypeptides. His data are shown below. “(XY)n” means “XYXYXY ...”, and the resulting amino-acid couplet also repeats indefinitely (e.g., Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu ...). Please use these data (plus Nierenberg’s result) to figure out as much of the code as you can. In particular, ...
... analyzed the resulting polypeptides. His data are shown below. “(XY)n” means “XYXYXY ...”, and the resulting amino-acid couplet also repeats indefinitely (e.g., Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu ...). Please use these data (plus Nierenberg’s result) to figure out as much of the code as you can. In particular, ...
3 Energy Pathways
... • The hydrogen given off at krebs cycle is brought by hydrogen carriers NAD & FAD to the cristae of the mitochondrion. Here it is split into hydrogen ions (H+) and electrons (e-). ...
... • The hydrogen given off at krebs cycle is brought by hydrogen carriers NAD & FAD to the cristae of the mitochondrion. Here it is split into hydrogen ions (H+) and electrons (e-). ...
ppt presentation
... ATOMIC NUMBER • ATOMIC NUMBER OF AN ELEMENT IS THE NUMBER OF PROTONS N THE NUCLEUS • THE ATOMIC NUMBER IDENTIFIES THE ELEMENT AND DISTIGUISHES IT FROM ALL OTHER ELEMENTS • THUS CARBON IS THE ELEMENT WITH ATOMIC NUMBER 6 ...
... ATOMIC NUMBER • ATOMIC NUMBER OF AN ELEMENT IS THE NUMBER OF PROTONS N THE NUCLEUS • THE ATOMIC NUMBER IDENTIFIES THE ELEMENT AND DISTIGUISHES IT FROM ALL OTHER ELEMENTS • THUS CARBON IS THE ELEMENT WITH ATOMIC NUMBER 6 ...
Lecture Slides for Fatty Acid Catabolism
... Peroxisomes • b-Oxidation also occurs in peroxisomes (major site in plants) • In critters, peroxisomes are primary organelles for oxidation of very long chain and branched fatty acids (cerotic acid, phytanic acids) ...
... Peroxisomes • b-Oxidation also occurs in peroxisomes (major site in plants) • In critters, peroxisomes are primary organelles for oxidation of very long chain and branched fatty acids (cerotic acid, phytanic acids) ...
Standard Growth Conditions and Measurement of Growth
... Bacteria need to synthesize macromolecules that allow for their growth and reproduction— what are bacterial cells made up of ? Cells consist of WATER and MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules are made up of smaller monomeric molecules Small monomeric molecules are made up of atoms ...
... Bacteria need to synthesize macromolecules that allow for their growth and reproduction— what are bacterial cells made up of ? Cells consist of WATER and MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules are made up of smaller monomeric molecules Small monomeric molecules are made up of atoms ...
Proteins synthesisand expression
... The information of the messenger RNA (mRNA) describes which amino acids should be in the protein chain. A molecule of transfer RNA (tRNA) will carry in the proper amino acid, one at a time. ...
... The information of the messenger RNA (mRNA) describes which amino acids should be in the protein chain. A molecule of transfer RNA (tRNA) will carry in the proper amino acid, one at a time. ...
Chapter 2 Macromocules
... • General term for compounds which are not soluble in water. • Lipids are soluble in hydrophobic solvents. • Remember: “stores the most energy” • Examples: 1. Fats 2. Phospholipids 3. Oils 4. Waxes 5. Steroid hormones 6. Triglycerides ...
... • General term for compounds which are not soluble in water. • Lipids are soluble in hydrophobic solvents. • Remember: “stores the most energy” • Examples: 1. Fats 2. Phospholipids 3. Oils 4. Waxes 5. Steroid hormones 6. Triglycerides ...
Picture Guide to Chapter 4
... proteins are stored in DNA Each protein has a specific role The shape of proteins can be very ...
... proteins are stored in DNA Each protein has a specific role The shape of proteins can be very ...
PATHWAYS THAT HARVEST CHEMICAL ENERGY CHAPTER 9
... • Links glycolysis and the citric acid cycle; occurs in the mitochondrial matrix • Pyruvate is oxidized to acetate and CO2 is released • NAD+ is reduced to NADH, capturing energy • Some energy is stored by combining acetate and Coenzyme A (CoA) to form acetyl CoA ...
... • Links glycolysis and the citric acid cycle; occurs in the mitochondrial matrix • Pyruvate is oxidized to acetate and CO2 is released • NAD+ is reduced to NADH, capturing energy • Some energy is stored by combining acetate and Coenzyme A (CoA) to form acetyl CoA ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
... Secondary Structure – the chain curls into an alpha helix or folds into a beta sheet Tertiary Structure – alpha helices and beta sheets fold on each ...
... Secondary Structure – the chain curls into an alpha helix or folds into a beta sheet Tertiary Structure – alpha helices and beta sheets fold on each ...
Amino Acids Are the Building Blocks Of Proteins
... b. Compare the two amino acids that have been built. Are they similar? How might two amino acids be different? Amino acids are similar because they share the same “core” structure of NH2CHR-COOH. Amino acids are different because the composition of the “R group” is different for each of the 20 amino ...
... b. Compare the two amino acids that have been built. Are they similar? How might two amino acids be different? Amino acids are similar because they share the same “core” structure of NH2CHR-COOH. Amino acids are different because the composition of the “R group” is different for each of the 20 amino ...
Chapter 11. Protein Structure and Function
... Way that chains of amino acids are coiled or folded (-helix, -sheet, random coil). • Tertiary structure Way -helix, -sheet, random coils fold and coil. ...
... Way that chains of amino acids are coiled or folded (-helix, -sheet, random coil). • Tertiary structure Way -helix, -sheet, random coils fold and coil. ...
Amino Acids are the Building Blocks of Proteins
... b. Compare the two amino acids that have been built. Are they similar? How might two amino acids be different? Amino acids are similar because they share the same “core” structure of NH2CHR-COOH. Amino acids are different because the composition of the “R group” is different for each of the 20 amino ...
... b. Compare the two amino acids that have been built. Are they similar? How might two amino acids be different? Amino acids are similar because they share the same “core” structure of NH2CHR-COOH. Amino acids are different because the composition of the “R group” is different for each of the 20 amino ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.