Gluconeogenesis
... converted to glucose and sucrose and exported to other tissues for starch storage. • In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
... converted to glucose and sucrose and exported to other tissues for starch storage. • In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
Respiration.review.guide.2012.2013w.answers
... 20. Cellular respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce __CO2______ and ____H2O_____ along with ATP. 21.Write the equation for cellular respiration and photosynthesis. C6H12O6 + 6O2 ------------ 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light --------- C6H12O6 + 6O2 22. Electron carriers called __NADH____ ...
... 20. Cellular respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce __CO2______ and ____H2O_____ along with ATP. 21.Write the equation for cellular respiration and photosynthesis. C6H12O6 + 6O2 ------------ 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light --------- C6H12O6 + 6O2 22. Electron carriers called __NADH____ ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: Read Section 2.1 – Atoms
... 10. Elements found in very small amounts in the body but which are needed to survive are called ______________ elements. For example, iron (Fe) is needed to transport oxygen in your blood. Chromium (Cr) is needed for your cells to break down sugars for usable energy. 11. ___________________: A subst ...
... 10. Elements found in very small amounts in the body but which are needed to survive are called ______________ elements. For example, iron (Fe) is needed to transport oxygen in your blood. Chromium (Cr) is needed for your cells to break down sugars for usable energy. 11. ___________________: A subst ...
Biochemistry Ch 37 696-706 [4-20
... intracellular proteins for degradation by covalently binding to E-amino group of lysine residues accomplished by a 3 enzyme system -target is often polyubiquitinylated, forming long ubiquitin tails -a proteasome complex then degrades the targeted protein and releasing intact ubiquitin that can mark ...
... intracellular proteins for degradation by covalently binding to E-amino group of lysine residues accomplished by a 3 enzyme system -target is often polyubiquitinylated, forming long ubiquitin tails -a proteasome complex then degrades the targeted protein and releasing intact ubiquitin that can mark ...
4. Bases are substances that combine with hydrogen ions.
... a. Three important functions of proteins are to serve as structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers. Proteins also function as receptors, antibodies, and enzymes. b. Enzymes are catalysts in living systems. c. Four elements always found in proteins are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen an ...
... a. Three important functions of proteins are to serve as structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers. Proteins also function as receptors, antibodies, and enzymes. b. Enzymes are catalysts in living systems. c. Four elements always found in proteins are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen an ...
1. Hydrogen ion concentration is typically measured in grams of ions
... t. An important steroid found in all body cells is cholesterol. u. Cholesterol is used to synthesize other steroids, sex hormones, and hormones from the adrenal glands. 4. Proteins a. Three important functions of proteins are to serve as structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers ...
... t. An important steroid found in all body cells is cholesterol. u. Cholesterol is used to synthesize other steroids, sex hormones, and hormones from the adrenal glands. 4. Proteins a. Three important functions of proteins are to serve as structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers ...
Cellular respiration - how cells make energy Oxygen is needed for
... The electron transport chain is made up of a sequence of proteins, each of which takes the electron and passes it on to the next one. At each step in the chain, a little energy is released that can be used by the cell. Oxygen is what ultimately pulls on these electrons and powers the chain. If all t ...
... The electron transport chain is made up of a sequence of proteins, each of which takes the electron and passes it on to the next one. At each step in the chain, a little energy is released that can be used by the cell. Oxygen is what ultimately pulls on these electrons and powers the chain. If all t ...
1 slide per page
... - receptors (membrane receptors bind signaling molecules on the outside of cells and transfer the signal to the inside of the cell; cytoplasmic receptors can bind signaling molecules within the cell) - attachment proteins (are exposed on the cell surface and bound to a surface, to the extracellular ...
... - receptors (membrane receptors bind signaling molecules on the outside of cells and transfer the signal to the inside of the cell; cytoplasmic receptors can bind signaling molecules within the cell) - attachment proteins (are exposed on the cell surface and bound to a surface, to the extracellular ...
I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... will react with other molecules. For example, the order of amino acids in a protein will determine the shape and function of the protein just as the order of words in a sentence shapes the meaning of the sentence. ...
... will react with other molecules. For example, the order of amino acids in a protein will determine the shape and function of the protein just as the order of words in a sentence shapes the meaning of the sentence. ...
I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... will react with other molecules. For example, the order of amino acids in a protein will determine the shape and function of the protein just as the order of words in a sentence shapes the meaning of the sentence. ...
... will react with other molecules. For example, the order of amino acids in a protein will determine the shape and function of the protein just as the order of words in a sentence shapes the meaning of the sentence. ...
UNIT 2 : BIOCHEMISTRY
... carbon atoms. The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a _________________ of simple and complex organic compounds. Macromolecules • Large molecules formed by ___________________________, the process of small monomers or subunits joining together to form large macromolecules – Be sure you kno ...
... carbon atoms. The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a _________________ of simple and complex organic compounds. Macromolecules • Large molecules formed by ___________________________, the process of small monomers or subunits joining together to form large macromolecules – Be sure you kno ...
Document
... Fermentation is used outside of the presence of oxygen. It is a series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD+,allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
... Fermentation is used outside of the presence of oxygen. It is a series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD+,allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
Week 2
... Protein Complex Structures - Cryo-Electron Microscopy is becoming an increasingly common way of measuring structures of large protein complexes ...
... Protein Complex Structures - Cryo-Electron Microscopy is becoming an increasingly common way of measuring structures of large protein complexes ...
Document
... d. a plant leaf to turn green. Match the correct definition with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ...
... d. a plant leaf to turn green. Match the correct definition with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ...
Topic 3.7 and Opt C Cell Respiration
... Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products ...
... Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
... A. The study of chemistry is essential for the study of physiology because body functions depend on cellular functions that, in turn, result from chemical changes. B. Biochemistry is the study of chemistry in living organisms. II. Structure of Matter A. Elements and Atoms 1. Matter is anything that ...
... A. The study of chemistry is essential for the study of physiology because body functions depend on cellular functions that, in turn, result from chemical changes. B. Biochemistry is the study of chemistry in living organisms. II. Structure of Matter A. Elements and Atoms 1. Matter is anything that ...
Baird Chem in Your life Chapter 09
... 7. How many three-letter combinations consist of the letters of the four nitrogen bases A, C, G, and T? a. 64 b. 16 c. 32 d. 12 a: Calculating possibilities of four bases A,C,G and T (4 × 4 × 4) gives 64 combinations. ...
... 7. How many three-letter combinations consist of the letters of the four nitrogen bases A, C, G, and T? a. 64 b. 16 c. 32 d. 12 a: Calculating possibilities of four bases A,C,G and T (4 × 4 × 4) gives 64 combinations. ...
Metabolism
... •The H+ ions are then allowed back into the cell by passing them through the ATP synthase protein, which uses the energy of the H+ ions flowing down the gradient to attach phosphate (Pi) to ADP, creating ATP. •the gradient is both chemical: more H+ outside than inside, and electrical: more + ...
... •The H+ ions are then allowed back into the cell by passing them through the ATP synthase protein, which uses the energy of the H+ ions flowing down the gradient to attach phosphate (Pi) to ADP, creating ATP. •the gradient is both chemical: more H+ outside than inside, and electrical: more + ...
worksheet - SCWIBLES - University of California, Santa Cruz
... 1. Cut out the all the shapes from the two pages of cut-outs. 2. Put the three catabolic enzymes aside for later. Anabolic enzymes 3. Build a carbohydrate - Use the appropriate carbohydrate anabolic enzyme as a guide to organize and connect all the sugar (glucose) molecules together. 4. Build a lipi ...
... 1. Cut out the all the shapes from the two pages of cut-outs. 2. Put the three catabolic enzymes aside for later. Anabolic enzymes 3. Build a carbohydrate - Use the appropriate carbohydrate anabolic enzyme as a guide to organize and connect all the sugar (glucose) molecules together. 4. Build a lipi ...
Multiple Choice
... b. (4 points) (i) Explain why phosphoglycerides are capable of spontaneously assembling into the bilayer structure found in biological membranes but triacylglycerols are not. (i) Triacylglycerols have three fatty acyl groups in ester linkage with glycerol; they are very hydrophobic because the carbo ...
... b. (4 points) (i) Explain why phosphoglycerides are capable of spontaneously assembling into the bilayer structure found in biological membranes but triacylglycerols are not. (i) Triacylglycerols have three fatty acyl groups in ester linkage with glycerol; they are very hydrophobic because the carbo ...
Document
... source, eating their way through the food. – For example, maggots burrow into animal carcasses and leaf miners tunnel through the interior of leaves. ...
... source, eating their way through the food. – For example, maggots burrow into animal carcasses and leaf miners tunnel through the interior of leaves. ...
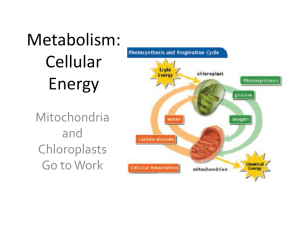
Cellular Energy
... • The life processes of all organisms require energy. • The potential energy held in the bonds of food molecules CANNOT be used directly by the cell. • Energy from food must be converted to the ONLY energy source that cells can use: ATP! ...
... • The life processes of all organisms require energy. • The potential energy held in the bonds of food molecules CANNOT be used directly by the cell. • Energy from food must be converted to the ONLY energy source that cells can use: ATP! ...
Reading Guide: The Origins of Life
... 2. Violent atmospheric conditions caused much lightning; heat from molten rock, and ultraviolet radiation from the sun provided energy for chemical reactions to take place 3. Organic molecules such as Amino acids, lipids and nucleic acids accumulated in the oceans forming an organic soup 4. The orga ...
... 2. Violent atmospheric conditions caused much lightning; heat from molten rock, and ultraviolet radiation from the sun provided energy for chemical reactions to take place 3. Organic molecules such as Amino acids, lipids and nucleic acids accumulated in the oceans forming an organic soup 4. The orga ...
Document
... Organelles in Disease: The Peroxisome -only identified in 1954 -found in all cells – abundant in liver and kidney cells -major function is breakdown of long chain fatty acids -other functions: 1. synthesis of bile acids F-actin and peroxisomes 2. breakdown of alcohol by liver cells 3. anti-oxidant ...
... Organelles in Disease: The Peroxisome -only identified in 1954 -found in all cells – abundant in liver and kidney cells -major function is breakdown of long chain fatty acids -other functions: 1. synthesis of bile acids F-actin and peroxisomes 2. breakdown of alcohol by liver cells 3. anti-oxidant ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.