Carbohydrates
... - rich in amino-acids, - trace elements and vitamins (Vitamin B-s) - mineral- and trace elements - therapeutically: stimulating, invigorating and exhilarating, restabilizes (a positive effect on the nerves) and generally revitalizes . restore the appetite ...
... - rich in amino-acids, - trace elements and vitamins (Vitamin B-s) - mineral- and trace elements - therapeutically: stimulating, invigorating and exhilarating, restabilizes (a positive effect on the nerves) and generally revitalizes . restore the appetite ...
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... amino acid through glutamate and glutamine Most amino acids obtain their α–amino group from glutamate by transamination. The sidechain nitrogen of glutamine is the nitrogen source for the sidechain nitrogens of tryptophan and histidine. ...
... amino acid through glutamate and glutamine Most amino acids obtain their α–amino group from glutamate by transamination. The sidechain nitrogen of glutamine is the nitrogen source for the sidechain nitrogens of tryptophan and histidine. ...
Slide 1
... There are literally thousands and thousands of different proteins; each one with a different order of amino acids, a different shape, and a different function: Enzymes to perform chemical reactions . . . Actin and myosin (and others) contractile proteins . . . Collagen and fibrin for connective tis ...
... There are literally thousands and thousands of different proteins; each one with a different order of amino acids, a different shape, and a different function: Enzymes to perform chemical reactions . . . Actin and myosin (and others) contractile proteins . . . Collagen and fibrin for connective tis ...
biological molecules of life
... Saturated fats are triglyceride molecules that have only single ...
... Saturated fats are triglyceride molecules that have only single ...
(DNA and RNA).
... ENZYME: A protein that catalyzes biochemical reactions by building, breaking down, or transforming organic compounds. These reactions include digestion, salivation, and fermentation. ...
... ENZYME: A protein that catalyzes biochemical reactions by building, breaking down, or transforming organic compounds. These reactions include digestion, salivation, and fermentation. ...
Chapter 2 Study Guides
... Main Idea: Four main types of carbon-‐based molecules are found in living things. ...
... Main Idea: Four main types of carbon-‐based molecules are found in living things. ...
Today`s Plan: 1/5/09
... to produce an -1,4-glycosidic linkage and water Lactose (a disaccharide) ...
... to produce an -1,4-glycosidic linkage and water Lactose (a disaccharide) ...
CHEMISTRY
... 2. Why do atoms form bonds? a. To change from a gaseous state b. To become more stable c. To build larger molecules d. To gather more electrons ...
... 2. Why do atoms form bonds? a. To change from a gaseous state b. To become more stable c. To build larger molecules d. To gather more electrons ...
Citric Acid Cycle 2
... 2. Carbons from acetyl CoA are transferred to the citric acid cycle. Which is the first round of the citric acid cycle that could possibly release a carbon atom originating from this acetyl CoA? A) First round. B) Second round. C) Third round. D) Fourth round. 3. What type of enzyme is involved in a ...
... 2. Carbons from acetyl CoA are transferred to the citric acid cycle. Which is the first round of the citric acid cycle that could possibly release a carbon atom originating from this acetyl CoA? A) First round. B) Second round. C) Third round. D) Fourth round. 3. What type of enzyme is involved in a ...
AP Biology - Richfield Public Schools
... this atom can make. Using the structural formula draw a molecule of these atoms bonded together to complete their valence electrons. (Hint: you may have to use more than one of each atom) ...
... this atom can make. Using the structural formula draw a molecule of these atoms bonded together to complete their valence electrons. (Hint: you may have to use more than one of each atom) ...
View Sokatch tribute.
... • Fulbright Research Scholarship • Fogarty Senior Research Fellowship • Served on NIH study sections, other grant review panels and editorial boards • Continuous funding from NIH and NSF • Research Interests: Multienzyme complexes involved in amino acid metabolism in Pseudomonas; Regulation of gene ...
... • Fulbright Research Scholarship • Fogarty Senior Research Fellowship • Served on NIH study sections, other grant review panels and editorial boards • Continuous funding from NIH and NSF • Research Interests: Multienzyme complexes involved in amino acid metabolism in Pseudomonas; Regulation of gene ...
June 30, 2009 - Rutgers New Jersey Medical School
... You will shortly begin your work within a new type of curriculum and have a learning experience quite different from what you have known as an undergraduate. First year medical school courses are challenging for many reasons; while all first year students takes the same courses, each brings differen ...
... You will shortly begin your work within a new type of curriculum and have a learning experience quite different from what you have known as an undergraduate. First year medical school courses are challenging for many reasons; while all first year students takes the same courses, each brings differen ...
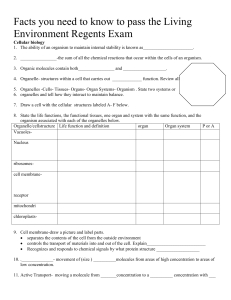
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... 13. Coordination and control of an organism is ______________________ 14. Chemicals produced in the endocrine glands_(_______________) and chemicals produced by nerve cells are primarily responsible for communication between cells. 15. _________________- uses oxygen to oxidize nutrients to produces ...
... 13. Coordination and control of an organism is ______________________ 14. Chemicals produced in the endocrine glands_(_______________) and chemicals produced by nerve cells are primarily responsible for communication between cells. 15. _________________- uses oxygen to oxidize nutrients to produces ...
SMU-DDE-Assignments-Scheme of Evaluation PROGRAM Bachelor
... Liver glycogen functions to store and export glucose to maintain blood glucose level between meals. After 12-18 hours of fasting, liver glycogen is almost totally depleted. Muscle glycogen serves as a fuel reserve for the supply of ATP during muscle contraction. Although muscle glycogen doesn’ ...
... Liver glycogen functions to store and export glucose to maintain blood glucose level between meals. After 12-18 hours of fasting, liver glycogen is almost totally depleted. Muscle glycogen serves as a fuel reserve for the supply of ATP during muscle contraction. Although muscle glycogen doesn’ ...
No Slide Title
... Would you like some Ethyl butyrane ice cream? What is this? “Pineapple” ice cream! Flavor comes from organic compounds. C, N, H, O - these elements make up almost all chemical compounds in living things. Carbon atoms can form long chains and Go to rings. Section: ...
... Would you like some Ethyl butyrane ice cream? What is this? “Pineapple” ice cream! Flavor comes from organic compounds. C, N, H, O - these elements make up almost all chemical compounds in living things. Carbon atoms can form long chains and Go to rings. Section: ...
Section 3 notes
... Peptide bonds link amino acids together to form a polypeptide. Protein - functional molecule built from one or more polypeptides. ...
... Peptide bonds link amino acids together to form a polypeptide. Protein - functional molecule built from one or more polypeptides. ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... The third step is attachment of a second phosphate group to fructose-6-phosphate to form fructose-1,6-diphosphate. This step is driven also by phosphate transfer from ATP and its Go’ is ________________. ...
... The third step is attachment of a second phosphate group to fructose-6-phosphate to form fructose-1,6-diphosphate. This step is driven also by phosphate transfer from ATP and its Go’ is ________________. ...
Slide 1
... _________ for storage Also converted to _____ & _____ for storage, made into _____________ or used to produce ___________ that strengthens cell walls ...
... _________ for storage Also converted to _____ & _____ for storage, made into _____________ or used to produce ___________ that strengthens cell walls ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.