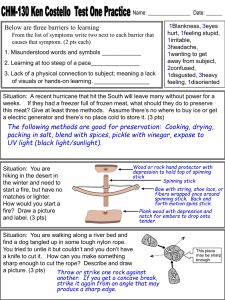
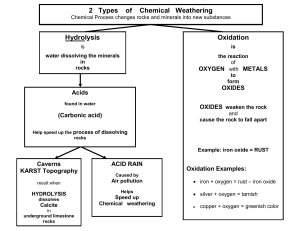
3.4 Cycles of Matter
... stream that carries it to a lake or ocean. -it can also be absorbed into the soil (groundwater) ~enters plants through their roots or flows into larger bodies of water or penetrates deeply enough into the ground to become part of underground reservoirs. ...
... stream that carries it to a lake or ocean. -it can also be absorbed into the soil (groundwater) ~enters plants through their roots or flows into larger bodies of water or penetrates deeply enough into the ground to become part of underground reservoirs. ...
Biochemical Processes Check 3 (Solutions)
... Substrates are materials that are to be processed. The processing could be a breakdown reaction (e.g. digestion) or a synthesis reaction (e.g. making proteins). The material present at the end of the reaction are the products. Enzymes allow the formation of product from substrate in a time that allo ...
... Substrates are materials that are to be processed. The processing could be a breakdown reaction (e.g. digestion) or a synthesis reaction (e.g. making proteins). The material present at the end of the reaction are the products. Enzymes allow the formation of product from substrate in a time that allo ...
100 Important Facts you need to know to pass the
... Living Environment Regents Exam TOPIC 1 1.The ability of an organism to maintain internal stability is known as homeostasis. 2.Metabolism- the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within the cells of an organism. 3.Organic molecules contain both carbon and hydrogen. 4. [smallest] Cells Tiss ...
... Living Environment Regents Exam TOPIC 1 1.The ability of an organism to maintain internal stability is known as homeostasis. 2.Metabolism- the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within the cells of an organism. 3.Organic molecules contain both carbon and hydrogen. 4. [smallest] Cells Tiss ...
AP Biology Study Guide Exam 2
... Metabolism all of the chemical reactions in living organisms Catabolic/Anabolic- Cat= Breaking down of molecules, Ana= Building Molecules broken down by hydrolysis Molecules put together by dehydration Some reactions release energy, some store energy. Exergonic- release energy (Used in d ...
... Metabolism all of the chemical reactions in living organisms Catabolic/Anabolic- Cat= Breaking down of molecules, Ana= Building Molecules broken down by hydrolysis Molecules put together by dehydration Some reactions release energy, some store energy. Exergonic- release energy (Used in d ...
Chapter 15 - Translation of mRNA
... a. Studies involving T4 phage indicated that the genetic code is read in triplets b. Synthetic RNA helped to determine the genetic code c. The use of RNA copolymers and the triplet-binding assay also helped to crack the genetic code 4. Structure and function of tRNA a. The function of a tRNA depends ...
... a. Studies involving T4 phage indicated that the genetic code is read in triplets b. Synthetic RNA helped to determine the genetic code c. The use of RNA copolymers and the triplet-binding assay also helped to crack the genetic code 4. Structure and function of tRNA a. The function of a tRNA depends ...
Effect of pH on Cells 2014
... ionic compounds (+ or - charge) that break apart in water and release hydrogen ion (H+) [positive ion] Stronger acids have MORE H+ (a higher concentration of H+) ...
... ionic compounds (+ or - charge) that break apart in water and release hydrogen ion (H+) [positive ion] Stronger acids have MORE H+ (a higher concentration of H+) ...
Unit 2 Review for Test
... 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule which is the primary component in cellu ...
... 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule which is the primary component in cellu ...
Dynamic visualization of protein molecules in action by highspeed
... Proteins are inherently dynamic molecules. They change the structure and interact with other molecules dynamically, which is largely responsible for the biological functions. Therefore, the direct real-space and real-time visualization of protein molecules at work must be a straightforward approach ...
... Proteins are inherently dynamic molecules. They change the structure and interact with other molecules dynamically, which is largely responsible for the biological functions. Therefore, the direct real-space and real-time visualization of protein molecules at work must be a straightforward approach ...
Cell Respiration Basics
... • 1) Glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate. (This takes 1 ATP to supply the phosphate) • 2) Glucose-6-phosphate splits into 2 3C phosphate compounds: PGALs (This takes another ATP) • 3) Through a series of reactions the 3C phosphates (PGALs) are chemically rearranged into 2 3C pyruvic acid mol ...
... • 1) Glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate. (This takes 1 ATP to supply the phosphate) • 2) Glucose-6-phosphate splits into 2 3C phosphate compounds: PGALs (This takes another ATP) • 3) Through a series of reactions the 3C phosphates (PGALs) are chemically rearranged into 2 3C pyruvic acid mol ...
Slide 1
... Living things use small molecules as building blocks for larger molecules and large compounds as building blocks for very large molecules (macromolecules). What are the two small molecules that build sugars? Carbon dioxide and water Wood is built primarily from cellulose, which is built from the 6-c ...
... Living things use small molecules as building blocks for larger molecules and large compounds as building blocks for very large molecules (macromolecules). What are the two small molecules that build sugars? Carbon dioxide and water Wood is built primarily from cellulose, which is built from the 6-c ...
258927_Fx_DNA-RNA
... 8. Where on an mRNA strand does translation actually begin? Give the term that describes this location along with the correct base sequence. ...
... 8. Where on an mRNA strand does translation actually begin? Give the term that describes this location along with the correct base sequence. ...
Glycolysis - MrOwdijWiki
... Overview of Glycolysis • Before we learn the in depth view of glycolysis lets investigate the overall purpose of glycolysis • Glycolysis is the breaking of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate in the cytoplasm ...
... Overview of Glycolysis • Before we learn the in depth view of glycolysis lets investigate the overall purpose of glycolysis • Glycolysis is the breaking of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate in the cytoplasm ...
Ch 25 and 26 Phylogeny and The History of Life on Earth
... • Morphological- comparing body forms of current and extinct organisms • Molecular- comparing DNA; the closer the sequence the more related – Some analogous structures (wings in insect compared to a bat) may have very different molecular origins. The result of convergent evolution. ...
... • Morphological- comparing body forms of current and extinct organisms • Molecular- comparing DNA; the closer the sequence the more related – Some analogous structures (wings in insect compared to a bat) may have very different molecular origins. The result of convergent evolution. ...
File
... • With an H, glycine is the simplest amino acid • Alanine with a methyl group is the next simplest. • Phenylalanine arises when a phenyl group replaces an H on alanine’s methyl group • Tyrosine evolves by adding an –OH group to the para position on the phenyl ring of phenylalanine ...
... • With an H, glycine is the simplest amino acid • Alanine with a methyl group is the next simplest. • Phenylalanine arises when a phenyl group replaces an H on alanine’s methyl group • Tyrosine evolves by adding an –OH group to the para position on the phenyl ring of phenylalanine ...
Midterm Studyguide Avery L
... A. Darwin’s Principles of Natural Selection Darwin’s Theory states that there are variations in a population and that these variations are inherited from your ancestors. Furthermore, organisms will produce more offspring that are more likely to survive, considering many offspring will die in nature ...
... A. Darwin’s Principles of Natural Selection Darwin’s Theory states that there are variations in a population and that these variations are inherited from your ancestors. Furthermore, organisms will produce more offspring that are more likely to survive, considering many offspring will die in nature ...
Name: Cell Biology Unit Test #1
... 27) True/False: The Michealis-Menten constant (Km) of an enzymatic reaction is the substrate concentration required to achieve half of the maximal reaction velocity. A) True B) False 28) Enzyme function is often regulated by the local environment. For example the four globin subunits of hemoglobin w ...
... 27) True/False: The Michealis-Menten constant (Km) of an enzymatic reaction is the substrate concentration required to achieve half of the maximal reaction velocity. A) True B) False 28) Enzyme function is often regulated by the local environment. For example the four globin subunits of hemoglobin w ...
REVIEW FOR FINALS TT^TT (TEEHEE)x
... tails are bonded using ester bonds. This forms a triglyceride because there are three carbon in the glycerol. Phospholipids- Like a fatty acids, except one of the carbons is bonded to a phosphate group instead of a chain Proteins- structural units in cells, can be used for structure, defense, enzyme ...
... tails are bonded using ester bonds. This forms a triglyceride because there are three carbon in the glycerol. Phospholipids- Like a fatty acids, except one of the carbons is bonded to a phosphate group instead of a chain Proteins- structural units in cells, can be used for structure, defense, enzyme ...
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA
... Join several dipeptides to make a longer peptide. ...
... Join several dipeptides to make a longer peptide. ...
Biochem 2 Recitation #2 Spr 20152102105.pptx
... Biochem 2 Recitation #2 Glycolysis & Gluconeogenesis ...
... Biochem 2 Recitation #2 Glycolysis & Gluconeogenesis ...
Unique plant respiration
... • 2) Citric Acid Cycle (aka Krebs or TCA cycle) – Pyruvate converted to CO2 and electrons • 3) Electron transport chain – Electrons reduce O2 to H20 and create ATP Energy storage • Plants store energy in the form of the carbohydrates sucrose and starch • In stroma of chloroplast, enzymes such as -am ...
... • 2) Citric Acid Cycle (aka Krebs or TCA cycle) – Pyruvate converted to CO2 and electrons • 3) Electron transport chain – Electrons reduce O2 to H20 and create ATP Energy storage • Plants store energy in the form of the carbohydrates sucrose and starch • In stroma of chloroplast, enzymes such as -am ...
Chem 365 Problem set 10 answer key 1. Ketone bodies are formed
... only 6 away from the terminal methyl group. The desaturase enzyme which is used to convert palmitic to other unsaturated fatty acids can not create a double bond on the last 6 carbons in any fatty acid chain. Therefore, the enzyme can not create a double bond at position 12, so the body can not synt ...
... only 6 away from the terminal methyl group. The desaturase enzyme which is used to convert palmitic to other unsaturated fatty acids can not create a double bond on the last 6 carbons in any fatty acid chain. Therefore, the enzyme can not create a double bond at position 12, so the body can not synt ...
Protein Nucleic Acids - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... 1-Which enzyme works best in an acidic pH? 2-Basic pH? 3- What is the optimal pH for each enzyme? 4- Explain Why enzyme 1 does not work in a basic ...
... 1-Which enzyme works best in an acidic pH? 2-Basic pH? 3- What is the optimal pH for each enzyme? 4- Explain Why enzyme 1 does not work in a basic ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.