Exam 2
... F. ____________ A potassium channel is able to exclude the smaller sodium ion through unfavorable steric interactions. G. ____________ Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because it contains a hemiacetal functional group that is in equilibrium with its open-chain form. H. ____________ It is possible to ...
... F. ____________ A potassium channel is able to exclude the smaller sodium ion through unfavorable steric interactions. G. ____________ Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because it contains a hemiacetal functional group that is in equilibrium with its open-chain form. H. ____________ It is possible to ...
DNA, Proteins and the Proteome - Guiding
... How many nucleotides does the genetic code consist of? What does the genetic code do? How many bases code for one amino acid? How many different amino acids are coded for by the genetic code? How is mRNA generated? ...
... How many nucleotides does the genetic code consist of? What does the genetic code do? How many bases code for one amino acid? How many different amino acids are coded for by the genetic code? How is mRNA generated? ...
2081 Slc35a2 provides a novel role for glycosylation in glucose
... We found that Lec8 cells exhibit enhanced electrophoretic mobility of Glut1 protein, altered lectin binding, and reduced uptake of 2-NBDG, which was time- and concentration-dependent, and reduced whole cell ATP content. Importantly, we found that enhanced Glut1 electrophoretic mobility, altered lect ...
... We found that Lec8 cells exhibit enhanced electrophoretic mobility of Glut1 protein, altered lectin binding, and reduced uptake of 2-NBDG, which was time- and concentration-dependent, and reduced whole cell ATP content. Importantly, we found that enhanced Glut1 electrophoretic mobility, altered lect ...
Name: Genetics Week 7 Review for Test 1. Figure 1 The diagram
... different cells use different parts of the genetic information they contain cells can eliminate the genetic codes that they do not need all other cells in the body lack the genes needed for the production of bile these cells mutated during embryonic development ...
... different cells use different parts of the genetic information they contain cells can eliminate the genetic codes that they do not need all other cells in the body lack the genes needed for the production of bile these cells mutated during embryonic development ...
Cellular Respiration Review
... 6. Lactic acid is the three-carbon waste product of lactic acid fermentation. It causes a burning feeling in your muscles vessels during exercise Fill in the blank. ...
... 6. Lactic acid is the three-carbon waste product of lactic acid fermentation. It causes a burning feeling in your muscles vessels during exercise Fill in the blank. ...
Protein Basics
... • Sequence similarity implies structural, functional, and evolutionary commonality • Small mutations generally well-tolerated by native structure ...
... • Sequence similarity implies structural, functional, and evolutionary commonality • Small mutations generally well-tolerated by native structure ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... iven the rich complexity of life on Earth, we might expect organisms to have an enormous diversity of molecules. Remarkably, however, the critically important large molecules of all living things—from bacteria to elephants—fall into just four main classes: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nuclei ...
... iven the rich complexity of life on Earth, we might expect organisms to have an enormous diversity of molecules. Remarkably, however, the critically important large molecules of all living things—from bacteria to elephants—fall into just four main classes: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nuclei ...
PDF | 816.8KB - New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning
... Emergence of Organic Molecules-Answer Key 1. They created an artificial laboratory model of our ancient atmospheric gases along with electric charges and water formation of the primitive components of organic molecules is possible. Organic molecules are found in all living organisms. 2. Scientist u ...
... Emergence of Organic Molecules-Answer Key 1. They created an artificial laboratory model of our ancient atmospheric gases along with electric charges and water formation of the primitive components of organic molecules is possible. Organic molecules are found in all living organisms. 2. Scientist u ...
workshops: absences: examinations: textbook
... the sequences of these chains, the Primary Structure, are unique to any given protein. To reveal how these chains can form distinct structural features within a protein, the Secondary Structure, including helices and sheet-like structures. The peptide bond is planar and usually trans in conformation ...
... the sequences of these chains, the Primary Structure, are unique to any given protein. To reveal how these chains can form distinct structural features within a protein, the Secondary Structure, including helices and sheet-like structures. The peptide bond is planar and usually trans in conformation ...
Amino acid analysis
... Proteins and peptides are macromolecules consisting of covalently bonded amino acid residues organized as a linear polymer. The sequence of the amino acids in a protein or peptide determines the properties of the molecule. ...
... Proteins and peptides are macromolecules consisting of covalently bonded amino acid residues organized as a linear polymer. The sequence of the amino acids in a protein or peptide determines the properties of the molecule. ...
Chapter 9: Fermentation
... •Both use NAD+ as an electron acceptor. •In fermentation, the electrons of NADH are passed to an organic molecule, regenerating NAD+. • In respiration, the electrons of NADH are ultimately passed to O2, generating ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. •In addition, even more ATP is generated from the o ...
... •Both use NAD+ as an electron acceptor. •In fermentation, the electrons of NADH are passed to an organic molecule, regenerating NAD+. • In respiration, the electrons of NADH are ultimately passed to O2, generating ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. •In addition, even more ATP is generated from the o ...
Deciphering the Genetic Code (Nirenberg)
... • J. H. Matthaei and M. W. Nirenberg (first paper published at 1961) – Decoding the genetic code – DNA and RNA influence on protein synthesis ...
... • J. H. Matthaei and M. W. Nirenberg (first paper published at 1961) – Decoding the genetic code – DNA and RNA influence on protein synthesis ...
(a) (b) - My SMCC
... DNA Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... DNA Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Anaerobic Respiration Gibb`s Free Energy PPT
... • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
... • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
Translation: DNA to mRNA to Protein
... translocation. The tRNA that corresponds to the comprises three steps. second codon can then bind to the A site, a step that requires elongation factors (in E. coli, these are called EF-Tu and EF-Ts), as well as guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as an energy source for the process. Upon binding of the tR ...
... translocation. The tRNA that corresponds to the comprises three steps. second codon can then bind to the A site, a step that requires elongation factors (in E. coli, these are called EF-Tu and EF-Ts), as well as guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as an energy source for the process. Upon binding of the tR ...
Aerobic Energy Systems
... When oxygen is present the complete breakdown of glucose is possible. This occurs in the mitochondria and produces CO2, H2O, and energy. The advantages of aerobic energy production is that there are no fatiguing by-products, the energy sources are usually abundant and lots of ATP can be produced. Th ...
... When oxygen is present the complete breakdown of glucose is possible. This occurs in the mitochondria and produces CO2, H2O, and energy. The advantages of aerobic energy production is that there are no fatiguing by-products, the energy sources are usually abundant and lots of ATP can be produced. Th ...
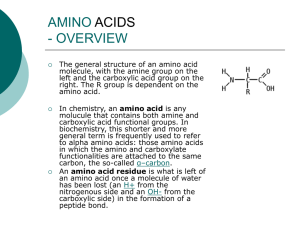
Amino acid
... • Hydrocarbon: consists only of carbon and hydrogen atoms • Functional group: – An atom (other than hydrogen) or small molecular group bonded to a carbon of an organic compound – Imparts a specific chemical property ...
... • Hydrocarbon: consists only of carbon and hydrogen atoms • Functional group: – An atom (other than hydrogen) or small molecular group bonded to a carbon of an organic compound – Imparts a specific chemical property ...
amino acids - UniMAP Portal
... Some of the 20 standard amino acids are called essential amino acids because they cannot be synthesized by the body from other compounds through chemical reactions, but instead must be taken in with food. In humans, the essential amino acids are lysine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, phenylalanine ...
... Some of the 20 standard amino acids are called essential amino acids because they cannot be synthesized by the body from other compounds through chemical reactions, but instead must be taken in with food. In humans, the essential amino acids are lysine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, phenylalanine ...
Principles of sorting and assembly of peroxisomal alcohol
... Proper functioning of living cells involves several regulatory mechanisms controlling protein biosynthesis. The so-called housekeeping proteins are continuously present, whereas other proteins are only made on demand. Synthesis of AO is strictly regulated and dependent on the environmental condition ...
... Proper functioning of living cells involves several regulatory mechanisms controlling protein biosynthesis. The so-called housekeeping proteins are continuously present, whereas other proteins are only made on demand. Synthesis of AO is strictly regulated and dependent on the environmental condition ...
ATP Production
... What happens when cells don’t have enough oxygen? Some organisms live in an oxygen-free environment. The Kreb’s Cycle and Electron Transport How do they get their energy? ...
... What happens when cells don’t have enough oxygen? Some organisms live in an oxygen-free environment. The Kreb’s Cycle and Electron Transport How do they get their energy? ...
An Introduction to Metabolism by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... represents some of the energy that used to be in the glucose molecule. Additionally, some energy released by the fuel is used to make ATP, and some energy is lost as heat. Glycolysis occurs in ...
... represents some of the energy that used to be in the glucose molecule. Additionally, some energy released by the fuel is used to make ATP, and some energy is lost as heat. Glycolysis occurs in ...
Life and Cell
... The three-dimensional structure of macromolecules is formed and maintained primarily through noncovalent interactions. Which one of the following is not considered a noncovalent interaction? A) carbon-carbon bonds B) hydrogen bonds C) hydrophobic interactions D) ionic interactions E) van der Waals ...
... The three-dimensional structure of macromolecules is formed and maintained primarily through noncovalent interactions. Which one of the following is not considered a noncovalent interaction? A) carbon-carbon bonds B) hydrogen bonds C) hydrophobic interactions D) ionic interactions E) van der Waals ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.