In experiments with a 3 base codon system it was shown that the
... major impact depending on: 1) If the codon changed effects a critical amino acid in the polypeptide 2) if the codon is changed to a stop codon 3) if the codon that is changed is the start ...
... major impact depending on: 1) If the codon changed effects a critical amino acid in the polypeptide 2) if the codon is changed to a stop codon 3) if the codon that is changed is the start ...
A. Primary structure: - B. Secondary structure: -
... random coil structure. 3. Proline also prevent forming α – helix because the nitrogen atom is a rigid ring. Thus, no rotation about α – carbon is possible. Also there is no hydrogen atom on the nitrogen of a Proline residue, so no intrachain hydrogen bonds can form. 4. Successive serine residues dis ...
... random coil structure. 3. Proline also prevent forming α – helix because the nitrogen atom is a rigid ring. Thus, no rotation about α – carbon is possible. Also there is no hydrogen atom on the nitrogen of a Proline residue, so no intrachain hydrogen bonds can form. 4. Successive serine residues dis ...
Protein
... that one gene codes for one enzyme. One gene codes for one polypeptide. polypeptide - a chain of covalently bonded amino acids. (proteins are made of one or more polypeptide) ...
... that one gene codes for one enzyme. One gene codes for one polypeptide. polypeptide - a chain of covalently bonded amino acids. (proteins are made of one or more polypeptide) ...
Photosynthetic Reactions
... of rubisco to react with several substrates decreases the efficiency of the protein. This potential means that if an O2 is randomly passing through the various membranes in the chloroplast it might encounter a rubisco enzyme and react with it. Each of these examples shows the way that the two cycles ...
... of rubisco to react with several substrates decreases the efficiency of the protein. This potential means that if an O2 is randomly passing through the various membranes in the chloroplast it might encounter a rubisco enzyme and react with it. Each of these examples shows the way that the two cycles ...
INTRODUCING AMINO ACIDS
... The end of the peptide chain with the -NH2 group is known as the N-terminal, and the end with the -COOH group is the C-terminal. A protein chain (with the N-terminal on the left) will therefore look like this: ...
... The end of the peptide chain with the -NH2 group is known as the N-terminal, and the end with the -COOH group is the C-terminal. A protein chain (with the N-terminal on the left) will therefore look like this: ...
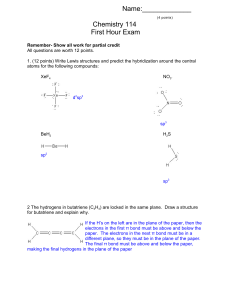
Name:______ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
... Biggest problem is making sure that functional groups don’t overlap and change their functionality my example is: left-to-right, aldehyde,halogen,alcohol,carboxylic acid ...
... Biggest problem is making sure that functional groups don’t overlap and change their functionality my example is: left-to-right, aldehyde,halogen,alcohol,carboxylic acid ...
Pancreatic enzymes basics
... • Mammal – diabetes results • Bird – No diabetes ! Why • Pancreas becomes more discrete as we move from lower vertebrates up to primates. • Diverse in macroscopic structure! • Controlled by parasympathetic and sympathetic inputs but- not primary controls. ...
... • Mammal – diabetes results • Bird – No diabetes ! Why • Pancreas becomes more discrete as we move from lower vertebrates up to primates. • Diverse in macroscopic structure! • Controlled by parasympathetic and sympathetic inputs but- not primary controls. ...
Chapter 26
... – no clear effect on incidence of colorectal cancer – excessive intake can interfere with absorption of elements such as iron, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and other trace ...
... – no clear effect on incidence of colorectal cancer – excessive intake can interfere with absorption of elements such as iron, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and other trace ...
Cell Membrane
... 1. The DNA must replicate before mitosis in order to ________________________ 2. The DNA shuffles and is cut in half during ________________. This is important because _____________. 3. The cell will complete mitosis when making __________________________ 4. The cell will complete meiosis when makin ...
... 1. The DNA must replicate before mitosis in order to ________________________ 2. The DNA shuffles and is cut in half during ________________. This is important because _____________. 3. The cell will complete mitosis when making __________________________ 4. The cell will complete meiosis when makin ...
Lecture 05 Notes: Diffusion, Osmosis and Membranes
... gradients; thus, kinetic energy would actually work against active transport. An outside energy source is needed to cause the necessary shape change; ATP usually does the job. 10. Mechanisms particles that cannot freely cross lipid bilayer use to get across: a. Channel proteins: Ions b. Transport pr ...
... gradients; thus, kinetic energy would actually work against active transport. An outside energy source is needed to cause the necessary shape change; ATP usually does the job. 10. Mechanisms particles that cannot freely cross lipid bilayer use to get across: a. Channel proteins: Ions b. Transport pr ...
Amino Acid Catabolism 2
... Often the first step of amino acid degradation Transfer of amino group from many amino acids to limited number of keto acid acceptors ...
... Often the first step of amino acid degradation Transfer of amino group from many amino acids to limited number of keto acid acceptors ...
Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... The energy taken out can be used to do work, and the rest is given off as heat. One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs without oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic compounds, like sugar, with the parti ...
... The energy taken out can be used to do work, and the rest is given off as heat. One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs without oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic compounds, like sugar, with the parti ...
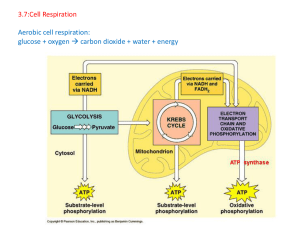
3.7:Cell Respiration Aerobic cell respiration: glucose
... lactic acid neither produced in aerobic respiration; glucose can be the substrate for both; glucose can be the substrate for both; anaerobic entirely in cytoplasm whereas aerobic requires mitochondria/specialized region of membrane; glucose is broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm in both; [5 m ...
... lactic acid neither produced in aerobic respiration; glucose can be the substrate for both; glucose can be the substrate for both; anaerobic entirely in cytoplasm whereas aerobic requires mitochondria/specialized region of membrane; glucose is broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm in both; [5 m ...
NAME_________________ 1 BIO 451 13th
... ammonia toxicity and why this is likely in this case, as well as the composition of collagen.] ...
... ammonia toxicity and why this is likely in this case, as well as the composition of collagen.] ...
Modification of Genes and Proteins - sharonap-cellrepro-p2
... Alteration of ends of transcript: › 5’ end capped with modified guanine Keeps RNA from degrading in the cytoplasm › Cleavage factors and stabilizing factors bind ...
... Alteration of ends of transcript: › 5’ end capped with modified guanine Keeps RNA from degrading in the cytoplasm › Cleavage factors and stabilizing factors bind ...
RNA and Transcription Worksheet File
... Before the RNA can leave the nucleus, it must be modified and edited. Sections on the RNA molecule that are not involved in the making of the protein are called ___20___ and will be ___21___. ...
... Before the RNA can leave the nucleus, it must be modified and edited. Sections on the RNA molecule that are not involved in the making of the protein are called ___20___ and will be ___21___. ...
receptor proteins
... The 3D structure of a protein has an obvious beauty to it – yet it represents an incredible complexity. The 20 amino acids are coupled to one another – thus for a 100 Amino Acid Protein, there is a staggering 20100 different ways one can construct a sequence of such a protein. The conformational s ...
... The 3D structure of a protein has an obvious beauty to it – yet it represents an incredible complexity. The 20 amino acids are coupled to one another – thus for a 100 Amino Acid Protein, there is a staggering 20100 different ways one can construct a sequence of such a protein. The conformational s ...
Enzymes - Hartismere
... allows smaller molecules to fit into them. Enzymes can be used to break down food into nutrients. ...
... allows smaller molecules to fit into them. Enzymes can be used to break down food into nutrients. ...
Chemistry of Life
... b. Because they have the same number of electrons, all ___________________ of an element have the same chemical _____________________. 5. ________________________________ have nuclei that are unstable and break down at a constant rate over time. a. ___________________________ are used to determine t ...
... b. Because they have the same number of electrons, all ___________________ of an element have the same chemical _____________________. 5. ________________________________ have nuclei that are unstable and break down at a constant rate over time. a. ___________________________ are used to determine t ...
Respiration Respiration Respiration - Anoka
... Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis ...
... Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis ...
L12_FAS
... Or the PPP can be used to generate NADPH as an anti-oxidant – Particularly in red blood cells where a deficiency in G6PDH can cause anemia ...
... Or the PPP can be used to generate NADPH as an anti-oxidant – Particularly in red blood cells where a deficiency in G6PDH can cause anemia ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.