Document
... Germany, 1923: banknotes had lost so much value that they were used as wallpaper. Source: wiki ...
... Germany, 1923: banknotes had lost so much value that they were used as wallpaper. Source: wiki ...
Question #2 & Question #4
... Zero percent interest rates help some and hurt others They can help in the short run and potentially due damage in The long run… ...
... Zero percent interest rates help some and hurt others They can help in the short run and potentially due damage in The long run… ...
Money, Inflation and the Business Cycle
... policies is to cut taxes on the savers. Those who are savers are usually labeled as “the rich.” Unfortunately, the prescriptions of “get government out of the market” or a “tax cut for the rich” tend not to be politically popular. Nevertheless, it is the duty of the economist to present the truth. T ...
... policies is to cut taxes on the savers. Those who are savers are usually labeled as “the rich.” Unfortunately, the prescriptions of “get government out of the market” or a “tax cut for the rich” tend not to be politically popular. Nevertheless, it is the duty of the economist to present the truth. T ...
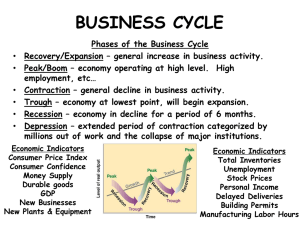
Phases of the Business Cycle Detailed Powerpoint
... • Note: “Years” is on horizontal axis and “real GDP” is on vertical axis. • General trend of economic growth • Recession years are shaded blue: note downward slope on graph indicating that GDP is decreasing. ...
... • Note: “Years” is on horizontal axis and “real GDP” is on vertical axis. • General trend of economic growth • Recession years are shaded blue: note downward slope on graph indicating that GDP is decreasing. ...
Austrian Economics - Auburn University
... subjectivism allow for a straightforward accounting of the gains from trade. Individuals value various goods differently, such that trading goods allows both traders to gain. Direct exchange (goods for goods) leads quite naturally to indirect exchange (goods for more-easily-tradable goods for actual ...
... subjectivism allow for a straightforward accounting of the gains from trade. Individuals value various goods differently, such that trading goods allows both traders to gain. Direct exchange (goods for goods) leads quite naturally to indirect exchange (goods for more-easily-tradable goods for actual ...
economists and economic theories
... Follow monetary rule-increasing MS at 3-5% every year If the money supply increases a little every year, it balances out the increase in prices every year. Economy will remain stable. ...
... Follow monetary rule-increasing MS at 3-5% every year If the money supply increases a little every year, it balances out the increase in prices every year. Economy will remain stable. ...
CLASSICAL THEORY OF EMPLOYMENT
... There is a direct and proportional relation between money wage and real wage. Total output of the economy is divided between consumption and investment expenditure. Labour is homogeneous. Saving is equal to investment. Law of diminishing marginal returns is applicable in agricultural sector. ...
... There is a direct and proportional relation between money wage and real wage. Total output of the economy is divided between consumption and investment expenditure. Labour is homogeneous. Saving is equal to investment. Law of diminishing marginal returns is applicable in agricultural sector. ...
Section 41 - Carsonville Port Sanilac
... Follow the chain reaction on the left as oil prices rise to the end result of recession. The real business cycle theory states that these changes in natural resources and technology are responsible for fluctuations in the economy. Monetarists believe that active control of the money supply causes th ...
... Follow the chain reaction on the left as oil prices rise to the end result of recession. The real business cycle theory states that these changes in natural resources and technology are responsible for fluctuations in the economy. Monetarists believe that active control of the money supply causes th ...
5. Approaches to policy and macroeconomic context
... Keynes shifted macroeconomic thought from a focus on AS to AD. Keynesian economists emphasise the use of demand-side policies, fiscal and monetary, to close gaps between actual and potential output. The 2008 financial crisis caused an increase in popularity of Keynesian beliefs. Keynesians believe t ...
... Keynes shifted macroeconomic thought from a focus on AS to AD. Keynesian economists emphasise the use of demand-side policies, fiscal and monetary, to close gaps between actual and potential output. The 2008 financial crisis caused an increase in popularity of Keynesian beliefs. Keynesians believe t ...
Causes of the Great Depression (1919-1933) - meister
... As people realized their stocks were overvalued, they dumped them, causing panic. ...
... As people realized their stocks were overvalued, they dumped them, causing panic. ...
Course Outline School of Business and Economics ECON 2950
... Illustrate how output is determined in the long run. Describe how interest rates and inflation are determined in the long run. Explain the determinants and consequences of inflation and unemployment in the long run. Discuss the role of capital, population growth and technology in economic growth. Co ...
... Illustrate how output is determined in the long run. Describe how interest rates and inflation are determined in the long run. Explain the determinants and consequences of inflation and unemployment in the long run. Discuss the role of capital, population growth and technology in economic growth. Co ...
“Classical” economic theory and “Keynesian
... • Failure of certain fundamental economic decisions (saving and investment) to be synchronized • In Short Run – prices and wages are inflexible • Extended periods of overproduction and underconsumption …… = ? • Recession or depression will prevail before prices or wages significantly change. ...
... • Failure of certain fundamental economic decisions (saving and investment) to be synchronized • In Short Run – prices and wages are inflexible • Extended periods of overproduction and underconsumption …… = ? • Recession or depression will prevail before prices or wages significantly change. ...
“Classical” economic theory and “Keynesian
... • Failure of certain fundamental economic decisions (saving and investment) to be synchronized • In Short Run – prices and wages are inflexible • Extended periods of overproduction and underconsumption …… = ? • Recession or depression will prevail before prices or wages significantly change. ...
... • Failure of certain fundamental economic decisions (saving and investment) to be synchronized • In Short Run – prices and wages are inflexible • Extended periods of overproduction and underconsumption …… = ? • Recession or depression will prevail before prices or wages significantly change. ...
WHATDUNIT? The Great Depression Mystery
... -->lay offs -->less spending -->lower confidence -->less investment -->less machinery purchased -->higher unemployment • Until surpluses are used up ...
... -->lay offs -->less spending -->lower confidence -->less investment -->less machinery purchased -->higher unemployment • Until surpluses are used up ...
Business cycle - Politechnika Wrocławska
... caused mainly by central government intervention in the money supply. Austrian School economists conclude that, if the interest rate is held artificially low by the government or central bank, then the demand for loans will be higher than the actual supply of willing lenders, and if the interest rat ...
... caused mainly by central government intervention in the money supply. Austrian School economists conclude that, if the interest rate is held artificially low by the government or central bank, then the demand for loans will be higher than the actual supply of willing lenders, and if the interest rat ...
Chapter 30: Business Fluctuations
... - A Trough is the lowest point in a business cycle. - A Depression is a severe trough. Expansion - During a Expansion phase, output expands and income increases. Peak - In a Peak phase, real GDP is at its highest level. Recession - During the Recession phase, income and consumption decline. Length a ...
... - A Trough is the lowest point in a business cycle. - A Depression is a severe trough. Expansion - During a Expansion phase, output expands and income increases. Peak - In a Peak phase, real GDP is at its highest level. Recession - During the Recession phase, income and consumption decline. Length a ...
monetarism & supply
... Monetarists say figures like these support their contention that inflation is a monetary phenomenon: Annual average percentage change 1985 to 1995 in: Country ...
... Monetarists say figures like these support their contention that inflation is a monetary phenomenon: Annual average percentage change 1985 to 1995 in: Country ...
economists and economic theories
... How are Smith and Keynes different from one another? How are Friedman and Lucas similar to each other? ...
... How are Smith and Keynes different from one another? How are Friedman and Lucas similar to each other? ...
historical or evolutionary theory - GCG-42
... period nor just one factor is responsible for its emergence. ...
... period nor just one factor is responsible for its emergence. ...
Ch 18 Milton Friedman
... • Transitory changes in income do not affect consumption spending, only permanent changes do • This implies a small marginal propensity to consume and, therefore, a small multiplier. • This makes Keynesian fiscal policy ineffective ...
... • Transitory changes in income do not affect consumption spending, only permanent changes do • This implies a small marginal propensity to consume and, therefore, a small multiplier. • This makes Keynesian fiscal policy ineffective ...
Notes on Economics
... An economic theory stating that active government intervention in the marketplace and monetary policy is the best method of ensuring economic growth and stability. A supporter of Keynesian economics believes it is the government's job to smooth out the bumps in business cycles. Intervention would co ...
... An economic theory stating that active government intervention in the marketplace and monetary policy is the best method of ensuring economic growth and stability. A supporter of Keynesian economics believes it is the government's job to smooth out the bumps in business cycles. Intervention would co ...
Business Cycles
... cycle, while low levels of investment contribute to contractions (decline in real GDP). Real GDP=The value of a nation’s gross domestic product (GDP) after it has been adjusted for inflation (in increase in overall prices that results from rising wages). ...
... cycle, while low levels of investment contribute to contractions (decline in real GDP). Real GDP=The value of a nation’s gross domestic product (GDP) after it has been adjusted for inflation (in increase in overall prices that results from rising wages). ...
BUSINESS CYCLE, FEDERAL RESERVE, TAXATION
... Business Investment – business decisions If businesses anticipate high sales in the future, they will likely invest; contributes to expansion If businesses anticipate a lower sales, they will reduce production; slows growth Government Activity Policies on taxing and spending (fiscal policy) Control ...
... Business Investment – business decisions If businesses anticipate high sales in the future, they will likely invest; contributes to expansion If businesses anticipate a lower sales, they will reduce production; slows growth Government Activity Policies on taxing and spending (fiscal policy) Control ...
Study Guide - Cobb Learning
... Associate each of the economists studied with their main contributions to the field of Economics: ...
... Associate each of the economists studied with their main contributions to the field of Economics: ...