* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download economists and economic theories
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Supply-side economics wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
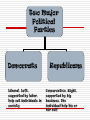
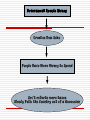
Warm-Up: Review What are the main differences between the Democrats & Republicans economic theories & policies? Which party was: FDR? Adam Smith? Explain… Two Major Political Parties Democrats Republicans Two Major Political Parties Democrats Liberal, Left, supported by labor, help out individuals in society Republicans Conservative, Right, supported by big business, the individual help his or her self UNIT I Economic Theories and Economists Warm Up/Review 1) What is the danger of inflation rising too quickly? 2) What are the dangers of having too high of an unemployment rate in the U.S.? 3) Who are the 3 economic Presidents? And, under what time period did each president serve in office? Economic Presidents: 1. President Hoover (≈early 1930’s) 2. President Carter (≈late 1970’s) 3. President Bush Sr. (≈early 1990s) ~Keep this in mind when we learn about different economists and their theories~ 1. Adam Smith “Classical Economics” Father of Modern Classical Economics Believed in Laissezfaire/Government should not get involved Invisible Hand (profit) drives individuals 2. JOHN MAYNARD KEYNES “Keynesian Economics” Was FDR’s economic advisor “guru” during the Great Depression Unemployment was at a record high of 25% in 1932 He advised FDR that the govt. had to intervene and take action This was a huge departure from classical theory His solution=govt. needs to spend money Spending is the key to creating demand in the economy Government Spends Money Creates New Jobs People Have More Money to Spend Gov’t collects more taxes Slowly Pulls the Country out of a Recession 3. MILTON FRIEDMAN “Monetarism” His ideas became popular in the 1970’s – What president did he influence the most? Money supply (MS) is the key to stabilizing the economy Follow monetary rule-increasing MS at 3-5% every year If the money supply increases a little every year, it balances out the increase in prices every year. Economy will remain stable. 4. Robert Lucas “Rational Expectations Theory” His ideas became popular in the 1990’s – What president did he influence the most? Believed in monetary rule Same as monetarism: increase the MS 3-5% Also believed in balanced budget (govt. spending = total tax revenue) Don’t allow the govt to go into debt. Keep the government accountable to balancing its budget! Wrap Up How are Smith and Keynes different from one another? How are Friedman and Lucas similar to each other? Rank the 4 theorists from best to worst (1-4) and explain your choices – EXPLAIN!! Quick Quiz: True or False 1. Adam Smith is called the father of modern economics. 2. The monetary rule states that the money supply should decrease 3-5% every year. 3. Keynes believed that the government should not intervene during the peak of the Great Depression. Who am I? [Activity] Read through each description and determine which economist and economic theory it is describing. Then, cut and glue under the appropriate column. Also, match each picture with the correct economist and theory. Provide a brief explanation of how the picture illustrates each theory inside your brochure. GRAPHS! Phillips Curve There is an inverse (opposite) relationship between inflation and unemployment. When one is high, the other is low; and vice versa. Graphing: #1 Draw a correctly labeled Phillips Curve from the information give in the following table: Period Unemployment Rate Inflation Rate Last year 4% 9% This Year 7% 5% Laffer Curve When tax rates are lower, the government collects more total tax revenue because spending will go up. Graphing: #2 Draw a correctly labeled Laffer Curve from the information give in the following table: Period Tax Rate Tax Revenue Last year 25% 190 mil. This Year 22% 210 mil. $$CASH QUESTION$$: Would this be a Democratic or Republican tax policy? Explain.