Retrofit Provisions in the International Existing Building Code
... written for fired clay brick, but some guidance for unburned clay, adobe, or stone masonry is also provided. The structural analysis requirements are based on reduced seismic forces from those intended for new construction. Special analysis procedures are included to account for the displacement of ...
... written for fired clay brick, but some guidance for unburned clay, adobe, or stone masonry is also provided. The structural analysis requirements are based on reduced seismic forces from those intended for new construction. Special analysis procedures are included to account for the displacement of ...
File
... wave travels through a coiled spring. They cause particles in rocks to move back and forth in the same direction that the wave is traveling. 8. __________________________ (S-waves) move through Earth by causing particles in rocks to move at right angles to the direction of wave travel. 9. __________ ...
... wave travels through a coiled spring. They cause particles in rocks to move back and forth in the same direction that the wave is traveling. 8. __________________________ (S-waves) move through Earth by causing particles in rocks to move at right angles to the direction of wave travel. 9. __________ ...
Earthquake Preparedness
... Aftershock: An earthquake of similar or lesser intensity that follows the main earthquake. Earthquake: A sudden slipping or movement of a portion of the earth’s crust, accompanied and followed by a series of vibrations. Epicenter: The place on earth’s surface directly above the point on the fault wh ...
... Aftershock: An earthquake of similar or lesser intensity that follows the main earthquake. Earthquake: A sudden slipping or movement of a portion of the earth’s crust, accompanied and followed by a series of vibrations. Epicenter: The place on earth’s surface directly above the point on the fault wh ...
Image courtesy of US Geological Survey
... magnitude greater than 6 in Interferogra this area. This includes seven m from earthquakes with a magnitudeinsarap.org of greater than 7.0. ...
... magnitude greater than 6 in Interferogra this area. This includes seven m from earthquakes with a magnitudeinsarap.org of greater than 7.0. ...
Chapter 10 Test Review Notes
... Soils under buildings may settle from severe shaking. Some soils under buildings become liquefied due to severe shaking. An earthquake with Richter magnitude 8 releases 961 times more energy than an earthquake with Richter magnitude 6. ...
... Soils under buildings may settle from severe shaking. Some soils under buildings become liquefied due to severe shaking. An earthquake with Richter magnitude 8 releases 961 times more energy than an earthquake with Richter magnitude 6. ...
Chapter 4
... • Measures the impact of an earthquake event on humans and surface features • Many local factors are considered such as local geology, construction practices, and distance to the epicenter • Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale is widely used in the United States • Intensities are reported as roman num ...
... • Measures the impact of an earthquake event on humans and surface features • Many local factors are considered such as local geology, construction practices, and distance to the epicenter • Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale is widely used in the United States • Intensities are reported as roman num ...
File
... Earthquake Magnitude and Intensity • Magnitude is the measurement of the amount of energy released during an earthquake. • The Richter scale is a numerical scale based on the size of the largest seismic waves generated by a quake that is used to describe its magnitude. – Each successive number in th ...
... Earthquake Magnitude and Intensity • Magnitude is the measurement of the amount of energy released during an earthquake. • The Richter scale is a numerical scale based on the size of the largest seismic waves generated by a quake that is used to describe its magnitude. – Each successive number in th ...
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-ISSN: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X,
... Abstract : Performance Based Seismic Engineering is the modern approach to earthquake resistant design. It is a limit-state based design approach extended to cover complex range of issues faced by structural engineers. Flat slabs are becoming popular and gaining importance as they are economical as ...
... Abstract : Performance Based Seismic Engineering is the modern approach to earthquake resistant design. It is a limit-state based design approach extended to cover complex range of issues faced by structural engineers. Flat slabs are becoming popular and gaining importance as they are economical as ...
Earthquakes - Colorado School of Mines
... • Tectonic plates are moving apart • Lithosphere is stretching ...
... • Tectonic plates are moving apart • Lithosphere is stretching ...
Design Alternatives for Lateral Force
... International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 6(2) 2012 ...
... International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 6(2) 2012 ...
3D Dynamic Soil structure interaction Design of Al
... 1. Static design: in this part we will study the loads and stresses that the structural elements are subjected to, due to the gravity loads and then the appropriate design of the structural elements will be performed. ...
... 1. Static design: in this part we will study the loads and stresses that the structural elements are subjected to, due to the gravity loads and then the appropriate design of the structural elements will be performed. ...
Seismic evaluation and strengthening of reinforced concrete
... 1. Lack of good design in planning lateral load resisting system such as moment resistant frames, frames with shear walls or with infill walls, and the joints. 2. Poor quality of construction materials and technology. 3. Inadequate detailing of reinforcement in beams, columns, beam-column joints, pa ...
... 1. Lack of good design in planning lateral load resisting system such as moment resistant frames, frames with shear walls or with infill walls, and the joints. 2. Poor quality of construction materials and technology. 3. Inadequate detailing of reinforcement in beams, columns, beam-column joints, pa ...
Earthquake Tip 8
... bent back-and-forth. Engineers define the property that allows steel pins to bend back-and-forth by large amounts, as ductility; chalk is a brittle material. Earthquake-resistant buildings, particularly their main elements, need to be built with ductility in them. Such buildings have the ability to ...
... bent back-and-forth. Engineers define the property that allows steel pins to bend back-and-forth by large amounts, as ductility; chalk is a brittle material. Earthquake-resistant buildings, particularly their main elements, need to be built with ductility in them. Such buildings have the ability to ...
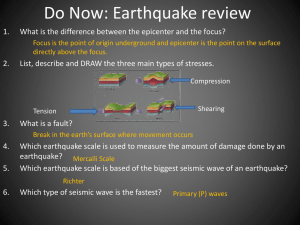
Do Now: Earthquake review
... What type of fault is the result of one rock layer sliding over another at a low angle? Thrust fault surface Rayleigh waves are an example of _______________ waves. Which type of stress pulls and twists the rocks layer is two opposite direction? Shearing ...
... What type of fault is the result of one rock layer sliding over another at a low angle? Thrust fault surface Rayleigh waves are an example of _______________ waves. Which type of stress pulls and twists the rocks layer is two opposite direction? Shearing ...
exchange of seismic/tsunami information between asean member
... real-time among ASEAN member states2. ...
... real-time among ASEAN member states2. ...
Document
... General panic; damage considerable in poorly designed structures, well designed frame structures thrown out of plumb. Damage great in substantial buildings, with partial collapse. Buildings shifted off foundations. ...
... General panic; damage considerable in poorly designed structures, well designed frame structures thrown out of plumb. Damage great in substantial buildings, with partial collapse. Buildings shifted off foundations. ...
Seismic retrofit

Seismic retrofitting is the modification of existing structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity, ground motion, or soil failure due to earthquakes. With better understanding of seismic demand on structures and with our recent experiences with large earthquakes near urban centers, the need of seismic retrofitting is well acknowledged. Prior to the introduction of modern seismic codes in the late 1960s for developed countries (US, Japan etc.) and late 1970s for many other parts of the world (Turkey, China etc.), many structures were designed without adequate detailing and reinforcement for seismic protection. In view of the imminent problem, various research work has been carried out. State-of-the-art technical guidelines for seismic assessment, retrofit and rehabilitation have been published around the world - such as the ASCE-SEI 41 and the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering (NZSEE)'s guidelines. These codes must be regularly updated; the 1994 Northridge earthquake brought to light the brittleness of welded steel frames, for example.The retrofit techniques outlined here are also applicable for other natural hazards such as tropical cyclones, tornadoes, and severe winds from thunderstorms. Whilst current practice of seismic retrofitting is predominantly concerned with structural improvements to reduce the seismic hazard of using the structures, it is similarly essential to reduce the hazards and losses from non-structural elements. It is also important to keep in mind that there is no such thing as an earthquake-proof structure, although seismic performance can be greatly enhanced through proper initial design or subsequent modifications.