Name: ___________________________ Chapter 6 Notes: Earthquakes Stress
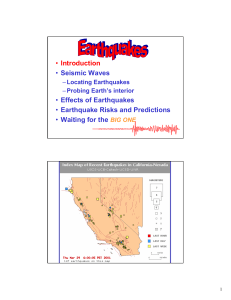
... Seismic Waves: vibrations that travel through Earth _______________ the energy released during an earthquake Types of Seismic waves P waves: the __________ wave to arrive _______________ waves They _______________ and expand Like an accordion ...
... Seismic Waves: vibrations that travel through Earth _______________ the energy released during an earthquake Types of Seismic waves P waves: the __________ wave to arrive _______________ waves They _______________ and expand Like an accordion ...
Earthquake Basics
... – Richter scale measures the total amount of energy released by an earthquake; independent of intensity – Amplitude of the largest wave produced by an event is corrected for distance and assigned a value on an open-ended logarithmic scale – For very large earthquakes, a modified Richter scale is use ...
... – Richter scale measures the total amount of energy released by an earthquake; independent of intensity – Amplitude of the largest wave produced by an event is corrected for distance and assigned a value on an open-ended logarithmic scale – For very large earthquakes, a modified Richter scale is use ...
considerations for future seismic systems - cosmos
... Whatt can be b done d to t make k the th lowl gain components of seismic network data acceptable to our engineering needs? How can our engineering needs drive the low-gain components of ground motion networks? ...
... Whatt can be b done d to t make k the th lowl gain components of seismic network data acceptable to our engineering needs? How can our engineering needs drive the low-gain components of ground motion networks? ...
The Elevated Cube
... detailing of the truss connections and node joint configuration, providing iterative comments in working sessions to provide the most economical and efficient joints. BRBs were the most efficient elements for the coupling system. As they are not intended to be the main energy dissipating mechanism, ...
... detailing of the truss connections and node joint configuration, providing iterative comments in working sessions to provide the most economical and efficient joints. BRBs were the most efficient elements for the coupling system. As they are not intended to be the main energy dissipating mechanism, ...
(2011) AEES Reconnaissance Mission to New
... earthquake (the "rare" event) needs to be reassessed. The Building Code of Australia (Australian Building Codes Board, 2011) stipulates the return period for design level earthquakes to be 500 years for ordinary buildings (importance level 2), with a higher return period for "more important" buildin ...
... earthquake (the "rare" event) needs to be reassessed. The Building Code of Australia (Australian Building Codes Board, 2011) stipulates the return period for design level earthquakes to be 500 years for ordinary buildings (importance level 2), with a higher return period for "more important" buildin ...
Finding an Earthquakes Epicenter
... Earthquakes occur because of a sudden release of stored energy. This energy has built up over long periods of time as a result of tectonic forces within the earth. Most earthquakes take place along faults in the upper 25 miles of the earth's surface when one side rapidly moves relative to the other ...
... Earthquakes occur because of a sudden release of stored energy. This energy has built up over long periods of time as a result of tectonic forces within the earth. Most earthquakes take place along faults in the upper 25 miles of the earth's surface when one side rapidly moves relative to the other ...
Cost Modeling of Reinforced Concrete Buildings Designed for
... parametric study of the cost influencing factors such as; structural and architectural configuration, wind and seismic effects, soil parameters, exposure conditions deciding durability requirements, construction technology, importance of building utility etc. Seismic effect is one of the relatively ...
... parametric study of the cost influencing factors such as; structural and architectural configuration, wind and seismic effects, soil parameters, exposure conditions deciding durability requirements, construction technology, importance of building utility etc. Seismic effect is one of the relatively ...
Adaptation of a Simplified Engineering System for
... helped to increase the stock of safe homes there after the earthquake, a housing seismic evaluation and retrofit program can also be used to help reduce vulnerability in a pre-disaster context. Build Change has worked with partners in Colombia to demonstrate the use of similar guidelines for the sei ...
... helped to increase the stock of safe homes there after the earthquake, a housing seismic evaluation and retrofit program can also be used to help reduce vulnerability in a pre-disaster context. Build Change has worked with partners in Colombia to demonstrate the use of similar guidelines for the sei ...
Jiri Zahradnik
... Serpetsidaki, A., Sokos, E., Tselentis, G.-A., Zahradnik, J. (2010). Seismic sequence near Zakynthos Island, Greece, April 2006: Identification of the activated fault plane. Tectonophysics 480, 23-32. PDF Gallovič, F., Zahradník, J., Křížová, D., Plicka, V., Sokos, E., Serpetsidaki, A., Tselentis, G ...
... Serpetsidaki, A., Sokos, E., Tselentis, G.-A., Zahradnik, J. (2010). Seismic sequence near Zakynthos Island, Greece, April 2006: Identification of the activated fault plane. Tectonophysics 480, 23-32. PDF Gallovič, F., Zahradník, J., Křížová, D., Plicka, V., Sokos, E., Serpetsidaki, A., Tselentis, G ...
Module 5 - Earthquakes - IST Akprind Yogyakarta
... Four types of seismic waves are generated when faulting triggers an earthquake. All the seismic waves are generated at the same time, but travel at different speeds and in different ways. Body waves penetrate the earth and travel through it, while surface waves travel along the surface of the ground ...
... Four types of seismic waves are generated when faulting triggers an earthquake. All the seismic waves are generated at the same time, but travel at different speeds and in different ways. Body waves penetrate the earth and travel through it, while surface waves travel along the surface of the ground ...
Earthquake Notes - Helena High School
... Ground shaking is produced by the waves set in motion by an earthquake’s sudden release of energy. Some of the ground vibrations are up-and-down, but the largest are side-to-side motions. Most buildings can withstand fairly violent up-and-down shaking; however, few buildings can survive violent side ...
... Ground shaking is produced by the waves set in motion by an earthquake’s sudden release of energy. Some of the ground vibrations are up-and-down, but the largest are side-to-side motions. Most buildings can withstand fairly violent up-and-down shaking; however, few buildings can survive violent side ...
Seismic retrofit

Seismic retrofitting is the modification of existing structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity, ground motion, or soil failure due to earthquakes. With better understanding of seismic demand on structures and with our recent experiences with large earthquakes near urban centers, the need of seismic retrofitting is well acknowledged. Prior to the introduction of modern seismic codes in the late 1960s for developed countries (US, Japan etc.) and late 1970s for many other parts of the world (Turkey, China etc.), many structures were designed without adequate detailing and reinforcement for seismic protection. In view of the imminent problem, various research work has been carried out. State-of-the-art technical guidelines for seismic assessment, retrofit and rehabilitation have been published around the world - such as the ASCE-SEI 41 and the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering (NZSEE)'s guidelines. These codes must be regularly updated; the 1994 Northridge earthquake brought to light the brittleness of welded steel frames, for example.The retrofit techniques outlined here are also applicable for other natural hazards such as tropical cyclones, tornadoes, and severe winds from thunderstorms. Whilst current practice of seismic retrofitting is predominantly concerned with structural improvements to reduce the seismic hazard of using the structures, it is similarly essential to reduce the hazards and losses from non-structural elements. It is also important to keep in mind that there is no such thing as an earthquake-proof structure, although seismic performance can be greatly enhanced through proper initial design or subsequent modifications.