The Geology of the Paleozoic Era
... • Siberia collided with Kazakhstania in the Pennsylvanian, forming the Altai Mountains. • Kazakhstania collided with Baltica in the Permian, forming the Ural Mountains. ...
... • Siberia collided with Kazakhstania in the Pennsylvanian, forming the Altai Mountains. • Kazakhstania collided with Baltica in the Permian, forming the Ural Mountains. ...
Ocean secret (Geography)
... mountains that have their base on the deep floor of the Pacific. Also in the Pacific is the deepest trench on the Earth, the Mariana Trench. It measures eleven kilometers below the sea's surface-seven times the depth of the Grand Canyon. Part 3 How people have learned about the ocean? Introduce the ...
... mountains that have their base on the deep floor of the Pacific. Also in the Pacific is the deepest trench on the Earth, the Mariana Trench. It measures eleven kilometers below the sea's surface-seven times the depth of the Grand Canyon. Part 3 How people have learned about the ocean? Introduce the ...
What does the ocean floor look like
... seafloor that extends around the world’s continents and ranges between 30 and 1300 km wide. At the edge it’s only about 200m deep. A uniform layer of mud and other sediments that originated on land covers most of the continental shelf. Most fish are caught in its teeming waters, which are also home ...
... seafloor that extends around the world’s continents and ranges between 30 and 1300 km wide. At the edge it’s only about 200m deep. A uniform layer of mud and other sediments that originated on land covers most of the continental shelf. Most fish are caught in its teeming waters, which are also home ...
Sedimentary Basins related to Volcanic Arcs
... may overlie either ocean or continental crust oceanic back-arc basins are eventually subducted and destroyed, or preserved in thrust complexes related to ocean closure. • back-arc basins on continental crust - more varied facies, because of terrigenous input; ...
... may overlie either ocean or continental crust oceanic back-arc basins are eventually subducted and destroyed, or preserved in thrust complexes related to ocean closure. • back-arc basins on continental crust - more varied facies, because of terrigenous input; ...
Tectonic Evolution of the Eastern Continental Margins of India and
... Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India, E-mail: [email protected] ...
... Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India, E-mail: [email protected] ...
Cenozoic Era - WordPress.com
... Opinions on the future of climate varies Tectonic movement is certain Some scientist believe that plate movement will eliminate the Atlantic Ocean and create another super continent ...
... Opinions on the future of climate varies Tectonic movement is certain Some scientist believe that plate movement will eliminate the Atlantic Ocean and create another super continent ...
First Midterm Study Guide for Geol-308
... What is Siletzia? When did it form, accrete, and what impact has it subsequently played in Oregon’s history? A large volcanic sea chain that filled up the Columbia embankment. Began forming during early Tertiary. Sileztia “docked” by 50m. Siletzia is a large coherent block of oceanic crust. The accr ...
... What is Siletzia? When did it form, accrete, and what impact has it subsequently played in Oregon’s history? A large volcanic sea chain that filled up the Columbia embankment. Began forming during early Tertiary. Sileztia “docked” by 50m. Siletzia is a large coherent block of oceanic crust. The accr ...
Plate Tectonics Tectonics
... South America and Africa were joined in the past and split apart when the Atlantic Ocean opened ...
... South America and Africa were joined in the past and split apart when the Atlantic Ocean opened ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Todd S. Thuma Homepage
... a. Submerged, inactive volcanoes formed at ridge b. Transported outward and downward as seafloor spreads c. Guyots are flat-topped seamounts 3. Trenches a. Narrow, long, arc-shaped depression b. Deepest part of oceans – 3-4 km depression in sea floor c. Mariana Trench – 11,035 m (36,170 ft) deep O ...
... a. Submerged, inactive volcanoes formed at ridge b. Transported outward and downward as seafloor spreads c. Guyots are flat-topped seamounts 3. Trenches a. Narrow, long, arc-shaped depression b. Deepest part of oceans – 3-4 km depression in sea floor c. Mariana Trench – 11,035 m (36,170 ft) deep O ...
Forschungszentrum für marine
... International science team publishes new data about the history of the Pacific Ring of Fire 10 February 2017/Kiel. The movements of Earth’s tectonic plates shape the face of our planet. The sinking of one plate beneath another, known as subduction, causes volcanism and earthquakes. Subduction zones ...
... International science team publishes new data about the history of the Pacific Ring of Fire 10 February 2017/Kiel. The movements of Earth’s tectonic plates shape the face of our planet. The sinking of one plate beneath another, known as subduction, causes volcanism and earthquakes. Subduction zones ...
Unit 5: Plate Tectonics Review Guide Things you need to know for
... Unit 5: Plate Tectonics Review Guide Things you need to know for the test…… Be able to explain…… Who was Alfred Wegener? What was his theory? What was his evidence (at least 3)? Why did no one believe him? Theory of Continental Drift and Pangaea What are layers of earth and what the Lithosphereic pl ...
... Unit 5: Plate Tectonics Review Guide Things you need to know for the test…… Be able to explain…… Who was Alfred Wegener? What was his theory? What was his evidence (at least 3)? Why did no one believe him? Theory of Continental Drift and Pangaea What are layers of earth and what the Lithosphereic pl ...
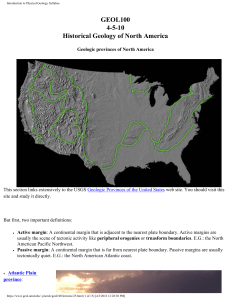
GEOL100 4-5-10 Historical Geology of North America
... By the middle Paleozoic, the east coast was an active margin, fringed by a new active subduction zone. During the Silurian , a small continent called Avalonia rode the oceanic lithosphere into this subduction zone and in the early Devonian , was welded to Laurentia as a microplate terrain. Farther n ...
... By the middle Paleozoic, the east coast was an active margin, fringed by a new active subduction zone. During the Silurian , a small continent called Avalonia rode the oceanic lithosphere into this subduction zone and in the early Devonian , was welded to Laurentia as a microplate terrain. Farther n ...
Sea Floor Spreading – 1956-1963
... 4) What is the mechanism of heat loss of the earth? Conduction or convection? If convection how is it related to geology? ...
... 4) What is the mechanism of heat loss of the earth? Conduction or convection? If convection how is it related to geology? ...
Tectonics 1 - Montville.net
... • Age increased away from ridge • Age of rocks with same magnetism is ...
... • Age increased away from ridge • Age of rocks with same magnetism is ...
Inferring Plate Boundary Deformation Mechanisms from Lithospheric
... Eurasian continental margin is associated with a progressive termination of collision in northern Taiwan as well as subduction of the Eurasian plate underneath the island. It has long been recognized that one model for this flipping of subduction polarity beneath Taiwan is the progressive tearing of ...
... Eurasian continental margin is associated with a progressive termination of collision in northern Taiwan as well as subduction of the Eurasian plate underneath the island. It has long been recognized that one model for this flipping of subduction polarity beneath Taiwan is the progressive tearing of ...
Sea-Floor Spreading Power Point
... produced at mid-ocean ridges, other parts of the ocean floor are sinking back into the mantle. ...
... produced at mid-ocean ridges, other parts of the ocean floor are sinking back into the mantle. ...
Re-examining the evidence from plate-tectonics for the initiation of
... be identified in present-day geology (Figure 1). It has been assumed that these fragments have retained their size and shape since the end of the widespread (Pan-African) orogenic episodes that concluded in early Cambrian times and resulted in a rigid assembly of Gondwana that lasted for almost 400 ...
... be identified in present-day geology (Figure 1). It has been assumed that these fragments have retained their size and shape since the end of the widespread (Pan-African) orogenic episodes that concluded in early Cambrian times and resulted in a rigid assembly of Gondwana that lasted for almost 400 ...
sea-floor spreading
... produced at mid-ocean ridges, other parts of the ocean floor are sinking back into the mantle. ...
... produced at mid-ocean ridges, other parts of the ocean floor are sinking back into the mantle. ...
19.4 Continental United States Geology
... Our story begins late. Most of the history of Earth has already passed. During this time rift valleys formed that split continents into smaller pieces. First the land moved apart on both sides of a rift valley. Then, once the rift valley opened wide enough, water flooded in and a new ocean was born. ...
... Our story begins late. Most of the history of Earth has already passed. During this time rift valleys formed that split continents into smaller pieces. First the land moved apart on both sides of a rift valley. Then, once the rift valley opened wide enough, water flooded in and a new ocean was born. ...
Continental drift script (version 2) File
... By then, the drifting process had made way for creation of the Atlantic Ocean in between the western and eastern landmasses. The continents of South America and Africa are estimated to have drifted apart at this stage. The Indian tectonic plate or the present day India is expected to have drifted no ...
... By then, the drifting process had made way for creation of the Atlantic Ocean in between the western and eastern landmasses. The continents of South America and Africa are estimated to have drifted apart at this stage. The Indian tectonic plate or the present day India is expected to have drifted no ...
Geology of British Columbia and Vancouver Island
... basal units, such as the Malaspina Cut, are no more than 86 m.y. The youngest rocks are probably more than 65 m.y. old, but could be younger. ...
... basal units, such as the Malaspina Cut, are no more than 86 m.y. The youngest rocks are probably more than 65 m.y. old, but could be younger. ...
Physiography of the Seafloor
... 60,000 km long (including back-arc basins) Occupy 1/3 of ocean basin area. Axis depth ~2500 m Parallel ridge and valley structure, with or without axial valley ...
... 60,000 km long (including back-arc basins) Occupy 1/3 of ocean basin area. Axis depth ~2500 m Parallel ridge and valley structure, with or without axial valley ...
Sea-Floor Spreading powerpoint
... were found in the center of the ridge, older rocks were found farther away from the ridge at the trenches. ...
... were found in the center of the ridge, older rocks were found farther away from the ridge at the trenches. ...