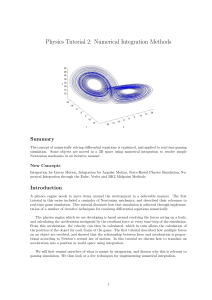
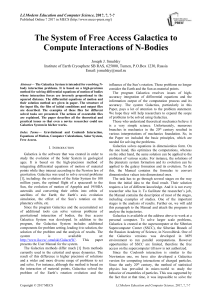
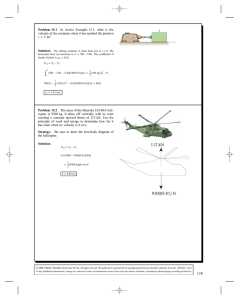
Physics Tutorial 2: Numerical Integration Methods
... of the object – during the first segment with zero acceleration the velocity remains at zero, in the second portion with constant acceleration the velocity increases linearly, the third segment has zero acceleration so the velocity remains constant, in the fourth the velocity decreases linearly due ...
... of the object – during the first segment with zero acceleration the velocity remains at zero, in the second portion with constant acceleration the velocity increases linearly, the third segment has zero acceleration so the velocity remains constant, in the fourth the velocity decreases linearly due ...
Galct14E2
... certain number of steps, characteristics of body motions can be issued; files containing such data are named 1, 2, 3… garez28.dat. The file garez28.dat is always produced on completion of the program. This file contains characteristics of bodies at the final calculation step. This is the main form o ...
... certain number of steps, characteristics of body motions can be issued; files containing such data are named 1, 2, 3… garez28.dat. The file garez28.dat is always produced on completion of the program. This file contains characteristics of bodies at the final calculation step. This is the main form o ...
Complete article - Scientific Reasoning Research Institute
... energy is transformed into gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy associated with the motion of the center of mass, and kinetic energy associated with the motion of the masses relative to the center of mass. At the maximum height, the kinetic energy associated with the motion of the center o ...
... energy is transformed into gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy associated with the motion of the center of mass, and kinetic energy associated with the motion of the masses relative to the center of mass. At the maximum height, the kinetic energy associated with the motion of the center o ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... • Imposed motion resulting from the action of forces that pushed or pulled. • Always had an external cause. • Once objects were in their natural resting places, they could not move by themselves. ...
... • Imposed motion resulting from the action of forces that pushed or pulled. • Always had an external cause. • Once objects were in their natural resting places, they could not move by themselves. ...
HS-SCI-CP -- Chapter 7- Circular Motion and
... Gravitational force always attracts objects to one another, as shown in Figure 7. The force that the moon exerts on Earth is equal and opposite to the force that Earth exerts on the moon. This relationship is an example of Newton's third law of motion. Also, note that the gravitational forces shown ...
... Gravitational force always attracts objects to one another, as shown in Figure 7. The force that the moon exerts on Earth is equal and opposite to the force that Earth exerts on the moon. This relationship is an example of Newton's third law of motion. Also, note that the gravitational forces shown ...
Advanced Classical Mechanics Lecture Notes
... particle described by its trajectory, r(t), is completely determined once its initial position and velocity are known. His famous equation, describing the second law, relates the acceleration d2 r/dt2 to the force on the particle, which is implicitly assumed to depend only on the positions, and poss ...
... particle described by its trajectory, r(t), is completely determined once its initial position and velocity are known. His famous equation, describing the second law, relates the acceleration d2 r/dt2 to the force on the particle, which is implicitly assumed to depend only on the positions, and poss ...
location latitude elevation (m) g (m/s2) north pole 0 9.8322
... of the v − t graph. It is possible, however, to interpret an x − t graph to find out something about the acceleration. An object with zero acceleration, i.e., constant velocity, has an x − t graph that is a straight line. A straight line has no curvature. A change in velocity requires a change in th ...
... of the v − t graph. It is possible, however, to interpret an x − t graph to find out something about the acceleration. An object with zero acceleration, i.e., constant velocity, has an x − t graph that is a straight line. A straight line has no curvature. A change in velocity requires a change in th ...
Momentum
... longer point particles but have extension in space. Up until now we’ve generally limited ourselves to the dynamics of point masses, first in one dimension and then generalized to two and three dimensions. Indeed, not all of the problems we studied were limited to point masses, but the object’s size ...
... longer point particles but have extension in space. Up until now we’ve generally limited ourselves to the dynamics of point masses, first in one dimension and then generalized to two and three dimensions. Indeed, not all of the problems we studied were limited to point masses, but the object’s size ...
Midterm Exam 2
... 4. You’re driving along at 25 m{s with your aunt’s valuable antiques in the back of your pickup truck when suddenly you see a giant hole in the road 55 m ahead of you. Fortunately, your foot is right beside the brake and your reaction time is zero! Will the antiques be as fortunate? Assume that the ...
... 4. You’re driving along at 25 m{s with your aunt’s valuable antiques in the back of your pickup truck when suddenly you see a giant hole in the road 55 m ahead of you. Fortunately, your foot is right beside the brake and your reaction time is zero! Will the antiques be as fortunate? Assume that the ...
problems on mechanics 1 introduction 2 first laws — theoretical basis
... is the net torque acting on the system; here Fi stands for the The application point of contact forces is obviously the contact net force acting on the i-th point mass. In particular, the net point; in the case of body forces, the torque can be calculated by dividing the entire body (system of bodie ...
... is the net torque acting on the system; here Fi stands for the The application point of contact forces is obviously the contact net force acting on the i-th point mass. In particular, the net point; in the case of body forces, the torque can be calculated by dividing the entire body (system of bodie ...
THE LEAST ACTION PRINCIPLE AND THE RELATED CONCEPT
... Unfortunately, at this point it becomes extremely difficult to define the Action in terms of J.l, and so we give up this approach in this paper. The main problem is the lack of dynamics in the description of a generalized flow as a one parameter family of doubly stochastic probability measures (simi ...
... Unfortunately, at this point it becomes extremely difficult to define the Action in terms of J.l, and so we give up this approach in this paper. The main problem is the lack of dynamics in the description of a generalized flow as a one parameter family of doubly stochastic probability measures (simi ...
ODU booklet 1 Teachers booklet (1)
... on a changing mass as fuel is used up. o Resolve forces acting at an angle into two perpendicular forces o Calculate forces acting at an angle to the direction of movement. o Resolve the weight of an object on a slope into a component acting down the slope and a component acting normal to the slope. ...
... on a changing mass as fuel is used up. o Resolve forces acting at an angle into two perpendicular forces o Calculate forces acting at an angle to the direction of movement. o Resolve the weight of an object on a slope into a component acting down the slope and a component acting normal to the slope. ...