Oscillatory Motion
... Our goal this semester is to understand how sound waves travel through the water so that we may exploit them to prosecute a target. We will start with simple models and increase complexity as we go. This course is meant to be directly applicable for the war-fighter. To begin with lets go back to our ...
... Our goal this semester is to understand how sound waves travel through the water so that we may exploit them to prosecute a target. We will start with simple models and increase complexity as we go. This course is meant to be directly applicable for the war-fighter. To begin with lets go back to our ...
6.0 - Introduction 6.1 - Sample problem: a mass on
... Now, you will get some additional practice applying Newton’s laws. More specifically, you will use them in situations where multiple forces are acting on a single object. If the application of multiple forces results in a net force acting on an object, it accelerates. On the other hand, if the force ...
... Now, you will get some additional practice applying Newton’s laws. More specifically, you will use them in situations where multiple forces are acting on a single object. If the application of multiple forces results in a net force acting on an object, it accelerates. On the other hand, if the force ...
1201 lab 6 - U of M Physics
... should not pull the spring past its elastic limit (about 60 cm). Beyond that point you will damage the spring. Decide on a procedure that allows you to measure the extension of the spring in a consistent manner. Decide how many masses ou will need to use to make a reliable measurement of the spring ...
... should not pull the spring past its elastic limit (about 60 cm). Beyond that point you will damage the spring. Decide on a procedure that allows you to measure the extension of the spring in a consistent manner. Decide how many masses ou will need to use to make a reliable measurement of the spring ...
1 Boas, p. 643, problem 13.5-3(b)
... To solve the requested problem, first we put A′ = B ′ = 0 because the temperature would diverge in the center of the plate. Then we apply the boundary condition u(a, θ) = 100H(−θ + π) where H is the Heaviside step function: X an (An sin nθ + Bn cos nθ) ...
... To solve the requested problem, first we put A′ = B ′ = 0 because the temperature would diverge in the center of the plate. Then we apply the boundary condition u(a, θ) = 100H(−θ + π) where H is the Heaviside step function: X an (An sin nθ + Bn cos nθ) ...
Physics 11 - BigEngine
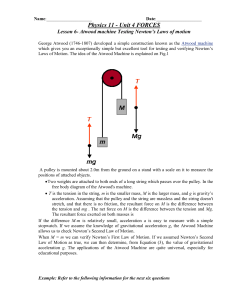
... A pulley is mounted about 2.0m from the ground on a stand with a scale on it to measure the positions of attached objects. Two weights are attached to both ends of a long string which passes over the pulley. In the free body diagram of the Atwood's machine. T is the tension in the string, m is t ...
... A pulley is mounted about 2.0m from the ground on a stand with a scale on it to measure the positions of attached objects. Two weights are attached to both ends of a long string which passes over the pulley. In the free body diagram of the Atwood's machine. T is the tension in the string, m is t ...
Newton`s Third Law 1.0
... push back on you. What you actually “feel” is the electric repulsion between the atoms in the surface of the solid and the tip of your finger. On a larger scale, it is similar to the magnetic repulsion you feel when you push one magnet toward another magnet. It is important to realize that nothing a ...
... push back on you. What you actually “feel” is the electric repulsion between the atoms in the surface of the solid and the tip of your finger. On a larger scale, it is similar to the magnetic repulsion you feel when you push one magnet toward another magnet. It is important to realize that nothing a ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
... - A particle will have an acceleration proportional to the magnitude of the resultant force acting on it and in the direction of the resultant force. - The resultant of the forces acting on a particle is equal to the rate of change of linear momentum of the particle. - The sum of the moments about O ...
... - A particle will have an acceleration proportional to the magnitude of the resultant force acting on it and in the direction of the resultant force. - The resultant of the forces acting on a particle is equal to the rate of change of linear momentum of the particle. - The sum of the moments about O ...
Introduction to Computational Physics
... Expectations of this course This course straddles three subjects: Physics, Computer Science and Mathematics. In ten weeks, we won’t be able to thoroughly cover any one of these. Instead, I will focus on giving you a taste of each of them, and a picture of how you can use math and computers together ...
... Expectations of this course This course straddles three subjects: Physics, Computer Science and Mathematics. In ten weeks, we won’t be able to thoroughly cover any one of these. Instead, I will focus on giving you a taste of each of them, and a picture of how you can use math and computers together ...
Partial solutions from Ch1 to Ch6
... 6.1 Rotation Angle and Angular Velocity .................................................................................. 49 6.2 Centripetal Acceleration ..................................................................................................... 50 6.3 Centripetal Force .................. ...
... 6.1 Rotation Angle and Angular Velocity .................................................................................. 49 6.2 Centripetal Acceleration ..................................................................................................... 50 6.3 Centripetal Force .................. ...
forces - U of M Physics
... Method #1: Select a series of masses that give a usable range of displacements. The smallest mass must be much greater than the mass of the spring to fulfill the massless spring assumption. The largest mass should not pull the spring past its elastic limit (about 60 cm). Beyond that point you will d ...
... Method #1: Select a series of masses that give a usable range of displacements. The smallest mass must be much greater than the mass of the spring to fulfill the massless spring assumption. The largest mass should not pull the spring past its elastic limit (about 60 cm). Beyond that point you will d ...
proofs oofs proofs
... Atoms are extremely tiny. Even though the air is full of oxygen and nitrogen molecules, you cannot see them. We know a lot about atoms and molecules, and this knowledge is invaluable when explaining the properties of substances. But, how do we measure atoms? The scale of atomic size means that chemi ...
... Atoms are extremely tiny. Even though the air is full of oxygen and nitrogen molecules, you cannot see them. We know a lot about atoms and molecules, and this knowledge is invaluable when explaining the properties of substances. But, how do we measure atoms? The scale of atomic size means that chemi ...