Point Charge Dynamics Near a Grounded Conducting Plane
... There is of course some concern about using a solution for τ that involves superluminal transport. However, we have identified the crossover point where the relativistic expression must be used (see Fig 4). If a particular application falls to the left of the crossover point on Fig. (4), then the no ...
... There is of course some concern about using a solution for τ that involves superluminal transport. However, we have identified the crossover point where the relativistic expression must be used (see Fig 4). If a particular application falls to the left of the crossover point on Fig. (4), then the no ...
uncorrected page proofs
... It must . . . be admitted that very simple relations . . . exist between the volumes of gaseous substances and the numbers of simple or compound molecules which form them. ...
... It must . . . be admitted that very simple relations . . . exist between the volumes of gaseous substances and the numbers of simple or compound molecules which form them. ...
The Gravitational Field
... He postulated that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. In equation form, Newton’s law of universal gravitation states that the force on a p ...
... He postulated that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. In equation form, Newton’s law of universal gravitation states that the force on a p ...
Weakly collisional Landau damping and three-dimensional
... so that one can use some form of gyro-kinetic or drift-kinetic equation24-27. Solutions have also been obtained in the presence of an infinitely strong background magnetic field28-30. In this case, charged particles are constrained to move along magnetic field lines, and thus the 3D problem is effec ...
... so that one can use some form of gyro-kinetic or drift-kinetic equation24-27. Solutions have also been obtained in the presence of an infinitely strong background magnetic field28-30. In this case, charged particles are constrained to move along magnetic field lines, and thus the 3D problem is effec ...
the full course notes are available here in book form for downloading
... focus of continuing research. The problem also involves orbits. The three-body problem: We shall show in this lecture course that an analytical solution in terms of integrals exists for a system of two particles interacting via gravity. No such solution exists for three particles, and the motion can ...
... focus of continuing research. The problem also involves orbits. The three-body problem: We shall show in this lecture course that an analytical solution in terms of integrals exists for a system of two particles interacting via gravity. No such solution exists for three particles, and the motion can ...
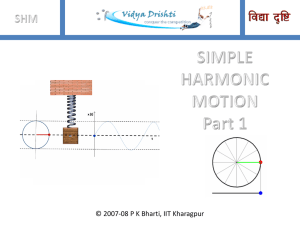
PHYS 1111 Introductory Physics – Mechanics, Waves
... NOTE: In physics, learning can be frustrating and nonlinear. Often you have to work for a long time (many days and even weeks) without feeling that you are making much progress. Then, suddenly, everything falls into place and it all makes sense. But until the “click,” you can’t be sure how much time ...
... NOTE: In physics, learning can be frustrating and nonlinear. Often you have to work for a long time (many days and even weeks) without feeling that you are making much progress. Then, suddenly, everything falls into place and it all makes sense. But until the “click,” you can’t be sure how much time ...
Unit 6: Motion - Youngstown City Schools
... b. (In Physical Science) all motion is limited to objects moving in a straight line (e.g., horizontally, vertically, up/down incline), that can be characterized in a single step (e.g., at rest, constant velocity, constant acceleration) c. motion of two objects may be compared or addressed simultaneo ...
... b. (In Physical Science) all motion is limited to objects moving in a straight line (e.g., horizontally, vertically, up/down incline), that can be characterized in a single step (e.g., at rest, constant velocity, constant acceleration) c. motion of two objects may be compared or addressed simultaneo ...
chapter2 - TTU Physics
... constant positive velocity (shown by red arrows maintaining the same size) Acceleration equals zero ...
... constant positive velocity (shown by red arrows maintaining the same size) Acceleration equals zero ...