Chapter 19 - Aerostudents
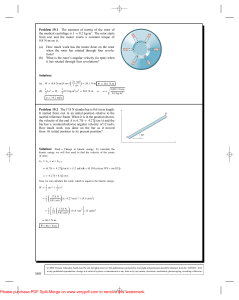
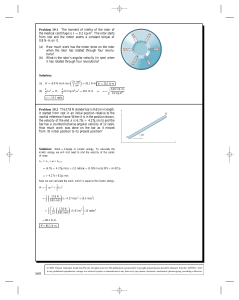
... Problem 19.4 The space station is initially not rotating. Its reaction control system exerts a constant couple on it until it has rotated 90◦ , then exerts a constant couple of the same magnitude in the opposite direction so that its angular velocity has decreased to zero when it has undergone a to ...
... Problem 19.4 The space station is initially not rotating. Its reaction control system exerts a constant couple on it until it has rotated 90◦ , then exerts a constant couple of the same magnitude in the opposite direction so that its angular velocity has decreased to zero when it has undergone a to ...
Problem 19.1 The moment of inertia of the rotor of the medical
... to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or likewise. ...
... to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or likewise. ...
Momentum - eAcademy
... Momentum and Impulse Read the comic and answer the following questions on a separate piece of paper. 1. What is Newton’s Second Law? 2. Can it be written more than one way? If so, what are the other ways? 3. Which equation did Newton believe should be correct? 4. Is force independent of the rate of ...
... Momentum and Impulse Read the comic and answer the following questions on a separate piece of paper. 1. What is Newton’s Second Law? 2. Can it be written more than one way? If so, what are the other ways? 3. Which equation did Newton believe should be correct? 4. Is force independent of the rate of ...
Ch. 1: Introduction of Mechanical Vibrations Modeling
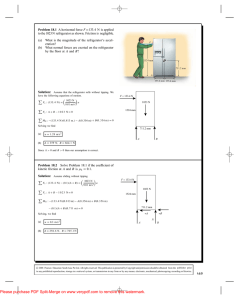
... How to find the equilibrium point? The solution does not change if the system is at the equilibrium. Let that point be x = xe and at that point x = x = … = 0. Substitute into EOM and solve for xe . How to linearize the model? Apply the Taylor’s series expansion to any nonlinear expressions around xe ...
... How to find the equilibrium point? The solution does not change if the system is at the equilibrium. Let that point be x = xe and at that point x = x = … = 0. Substitute into EOM and solve for xe . How to linearize the model? Apply the Taylor’s series expansion to any nonlinear expressions around xe ...
FROM NEWTON`S MECHANICS TO EULER`S EQUATIONS
... Through the eighteenth century, the main contexts for studies of fluid motion were water supply, water-wheels, navigation, wind-mills, artillery, sound propagation, and Descartes’s vortex theory. The most discussed questions were the efflux of water through the short outlet of a vessel, the impact o ...
... Through the eighteenth century, the main contexts for studies of fluid motion were water supply, water-wheels, navigation, wind-mills, artillery, sound propagation, and Descartes’s vortex theory. The most discussed questions were the efflux of water through the short outlet of a vessel, the impact o ...
- D-Scholarship@Pitt
... complex than a mere translation. Euler did not begin with Newton’s laws and derive analytic results from those. Rather, he re-conceived the entire science from top to bottom, taking the occupation of space to be the essential feature of bodies from which the rest of mechanics could be derived neces ...
... complex than a mere translation. Euler did not begin with Newton’s laws and derive analytic results from those. Rather, he re-conceived the entire science from top to bottom, taking the occupation of space to be the essential feature of bodies from which the rest of mechanics could be derived neces ...
ulaby_solved_problems.old
... where x = 0 is the end of the string, which is tied rigidly to a wall, as shown in Fig. (1.1). When wave y1 (x,t) arrives at the wall, a reflected wave y2 (x,t) is generated. Hence, at any location on the string, the vertical displacement ys will be the sum of the incident and reflected waves: ys (x ...
... where x = 0 is the end of the string, which is tied rigidly to a wall, as shown in Fig. (1.1). When wave y1 (x,t) arrives at the wall, a reflected wave y2 (x,t) is generated. Hence, at any location on the string, the vertical displacement ys will be the sum of the incident and reflected waves: ys (x ...
Donna Calhoun Boise State University The Riemann problem
... The need to find a state that simultaneously satisfies both conditions above means we have to solve something... ...
... The need to find a state that simultaneously satisfies both conditions above means we have to solve something... ...
Chapter 11 Equilibrium - Farmingdale State College
... equilibrium states that for a body to be in equilibrium, the vector sum of all the forces acting on that body must be zero. But equation 11.1, the first condition of equilibrium, is just a special case of equation 5.9, Newton’s second law of motion. Hence, bodies in equilibrium are nothing more than ...
... equilibrium states that for a body to be in equilibrium, the vector sum of all the forces acting on that body must be zero. But equation 11.1, the first condition of equilibrium, is just a special case of equation 5.9, Newton’s second law of motion. Hence, bodies in equilibrium are nothing more than ...
Preview Sample 2
... 16) A commercial jet has a mass of 5,000 kg and the thrust of its engine is 10,000 N. The acceleration of the jet when taking off is A) 0.5 m/s2. B) 1 m/s2. C) 2 m/s2. D) 4 m/s2. E) none of the above Answer: C Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Second Law of Motion 17) A jumbo jet has a mass of 100,000 kg. The ...
... 16) A commercial jet has a mass of 5,000 kg and the thrust of its engine is 10,000 N. The acceleration of the jet when taking off is A) 0.5 m/s2. B) 1 m/s2. C) 2 m/s2. D) 4 m/s2. E) none of the above Answer: C Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's Second Law of Motion 17) A jumbo jet has a mass of 100,000 kg. The ...