Chapter 9 Rotation
... object. You are told to suspend the object from a point, and to suspend a plumb line from the same point. Then draw a vertical line on the object to represent the plumb line. Next, you repeat the process using a different suspension point. The center of gravity will be at the intersection of the dra ...
... object. You are told to suspend the object from a point, and to suspend a plumb line from the same point. Then draw a vertical line on the object to represent the plumb line. Next, you repeat the process using a different suspension point. The center of gravity will be at the intersection of the dra ...
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations
... two systems of forces which are equipollent, i.e., which have the same resultant and the same moment resultant, are also equivalent; that is, they have exactly the same effect on a given rigid body.† Consider in particular the system of the external forces acting on a rigid body (Fig. 16.6a) and the ...
... two systems of forces which are equipollent, i.e., which have the same resultant and the same moment resultant, are also equivalent; that is, they have exactly the same effect on a given rigid body.† Consider in particular the system of the external forces acting on a rigid body (Fig. 16.6a) and the ...
Chapter 9 Rotation
... A spool is free to rotate about a fixed axis, and a string wrapped around the axle of the spool causes the spool to rotate in a counterclockwise direction (see Figure 9-42a). However, if the spool is set on a horizontal tabletop, the spool instead (given sufficient frictional force between the table ...
... A spool is free to rotate about a fixed axis, and a string wrapped around the axle of the spool causes the spool to rotate in a counterclockwise direction (see Figure 9-42a). However, if the spool is set on a horizontal tabletop, the spool instead (given sufficient frictional force between the table ...
CP Physics - Glen Ridge Public Schools
... What forces act on an object as it hangs from a string? How is the net force acting on an object determined? What is the relationship between force and motion? What distinguishes contact forces from field forces? How do free body diagrams represent and how can they be used to find net forc ...
... What forces act on an object as it hangs from a string? How is the net force acting on an object determined? What is the relationship between force and motion? What distinguishes contact forces from field forces? How do free body diagrams represent and how can they be used to find net forc ...
HOLT
... 1. One light-year is the distance light travels in one year. This distance is equal to 9.461 × 1015 m. After the sun, the star nearest to Earth is Alpha Centauri, which is about 4.35 light-years from Earth. Express this distance in a. megameters. b. picometers. ...
... 1. One light-year is the distance light travels in one year. This distance is equal to 9.461 × 1015 m. After the sun, the star nearest to Earth is Alpha Centauri, which is about 4.35 light-years from Earth. Express this distance in a. megameters. b. picometers. ...
... along. That is what you have been doing as you make up your formal notes, outline, etc. What you have done with this systematic approach is to reproduce the notes and outline that the instructor is using. If you are reasonably good at it, you will have as good a source of exam questions as the instr ...
9.5. Particular motions of a rigid body
... propriety in the first part of this mechanics) as a non deformable and continuous system of particles. At the limit the number of these particles tends to infinity. This fact makes as the study of the motion of a body to solve in two ways: -In the first case are considered the points of the body and ...
... propriety in the first part of this mechanics) as a non deformable and continuous system of particles. At the limit the number of these particles tends to infinity. This fact makes as the study of the motion of a body to solve in two ways: -In the first case are considered the points of the body and ...
Newtonian Physics - UFDC Image Array 2
... We Americans assume that our economic system will always scamper to provide us with the products we want. Special orders don’t upset us! I want my MTV! The truth is more complicated, especially in our education system, which is paid for by the students but controlled by the professoriate. Witness th ...
... We Americans assume that our economic system will always scamper to provide us with the products we want. Special orders don’t upset us! I want my MTV! The truth is more complicated, especially in our education system, which is paid for by the students but controlled by the professoriate. Witness th ...
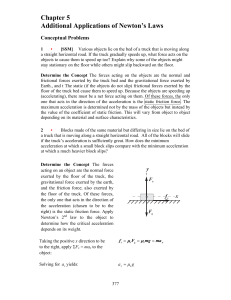
Chapter 5 Additional Applications of Newton`s Laws
... magnetic force acts upwards, slowing it down, so its acceleration will be less than g. Because of this, the magnet will catch up to the iron piece as they fall. 11 ••• [SSM] The following question is an excellent ″braintwister″ invented by Boris Korsunsky. Two identical blocks are attached by a mass ...
... magnetic force acts upwards, slowing it down, so its acceleration will be less than g. Because of this, the magnet will catch up to the iron piece as they fall. 11 ••• [SSM] The following question is an excellent ″braintwister″ invented by Boris Korsunsky. Two identical blocks are attached by a mass ...
CCSS PRECISION Verify that each equation is an identity. 1
... 51. THROWING A BALL In this problem, you will investigate the path of a ball represented by the equation , where θ is the measure of the angle between the ground and the path of the ball, ...
... 51. THROWING A BALL In this problem, you will investigate the path of a ball represented by the equation , where θ is the measure of the angle between the ground and the path of the ball, ...
Document
... velocity – change in position as a function of time acceleration – change in velocity as a function of time centripetal acceleration – Quotient of the velocity squared and the distance from the center of rotation momentum – product of mass and velocity change in momentum = Impulse = change in the pr ...
... velocity – change in position as a function of time acceleration – change in velocity as a function of time centripetal acceleration – Quotient of the velocity squared and the distance from the center of rotation momentum – product of mass and velocity change in momentum = Impulse = change in the pr ...
Boundary-value Problems in Electrostatics I
... charge more complicated1 . Let’s do the simplest problem of this kind. Suppose that we have a spherical cavity of radius a inside of a conductor; within this cavity is a point charge q located a distance r0 from the center of the sphere which is also chosen as the origin of coordinates. Thus the ch ...
... charge more complicated1 . Let’s do the simplest problem of this kind. Suppose that we have a spherical cavity of radius a inside of a conductor; within this cavity is a point charge q located a distance r0 from the center of the sphere which is also chosen as the origin of coordinates. Thus the ch ...