Chapter 16 notes
... • Process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself as a result of complementary base pairing: 1) molecule unwinds, then unzips (2 strands separate) due to helicase 2) new DNA nucleotides line up on both strands ...
... • Process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself as a result of complementary base pairing: 1) molecule unwinds, then unzips (2 strands separate) due to helicase 2) new DNA nucleotides line up on both strands ...
Supplementary information (SI) Description of technique The
... streptavidin-coated paramagnetic beads and subjected to several subsequent stringency washes. The enriched library DNA was subsequently eluted from the stable probe fixed to magnetic beads using a strand displacing enzyme at optimum temperature. The targeted enrichment of complex adaptor-ligated DNA ...
... streptavidin-coated paramagnetic beads and subjected to several subsequent stringency washes. The enriched library DNA was subsequently eluted from the stable probe fixed to magnetic beads using a strand displacing enzyme at optimum temperature. The targeted enrichment of complex adaptor-ligated DNA ...
Slide ()
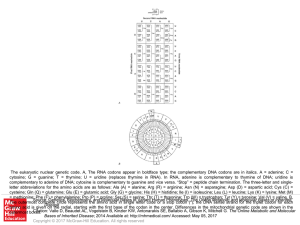
... complementary to adenine of DNA; cytosine is complementary to guanine and vice versa. “Stop” = peptide chain termination. The three-letter and singleletter abbreviations for the amino acids are as follows: Ala (A) = alanine; Arg (R) = arginine; Asn (N) = asparagine; Asp (D) = aspartic acid; Cys (C) ...
... complementary to adenine of DNA; cytosine is complementary to guanine and vice versa. “Stop” = peptide chain termination. The three-letter and singleletter abbreviations for the amino acids are as follows: Ala (A) = alanine; Arg (R) = arginine; Asn (N) = asparagine; Asp (D) = aspartic acid; Cys (C) ...
MolBio Tech Data_new.cdr
... 3. Higher than optimal concentration yields undesired products and if concentration is too low the concentration, no amplification products are ...
... 3. Higher than optimal concentration yields undesired products and if concentration is too low the concentration, no amplification products are ...
Document
... 2) Name the 4 most common RNA bases (spell out) ___________ _____________ ______________ ___________ 3) A fifth common RNA base ________ is used in tRNA for wobble. 4) Name the 5 most common DNA bases (spell out)__________ __________ __________ _________ _________ 5) cDNA is made from mRNA by the en ...
... 2) Name the 4 most common RNA bases (spell out) ___________ _____________ ______________ ___________ 3) A fifth common RNA base ________ is used in tRNA for wobble. 4) Name the 5 most common DNA bases (spell out)__________ __________ __________ _________ _________ 5) cDNA is made from mRNA by the en ...
PGM Quizzes
... Name the enzyme that is used to polish or blunt any overhanging ends of a double strand cDNA. T4 DNA polymerase Name the enzyme that is used to make covalent bonds between vector, in our case pGEM3Z, and insert. DNA ligase What is the name of the process for introducing “naked” DNA into competent ba ...
... Name the enzyme that is used to polish or blunt any overhanging ends of a double strand cDNA. T4 DNA polymerase Name the enzyme that is used to make covalent bonds between vector, in our case pGEM3Z, and insert. DNA ligase What is the name of the process for introducing “naked” DNA into competent ba ...
• Double helix -- twisted ladder shape of DNA, like spiral staircase
... Which letters bind with which? A - T, G - C ...
... Which letters bind with which? A - T, G - C ...
The Living World
... Most restriction enzymes cut the DNA in a staggered fashion This generates “sticky” ends These ends can pair with any other DNA fragment generated by the same enzyme The pairing is aided by DNA ligase ...
... Most restriction enzymes cut the DNA in a staggered fashion This generates “sticky” ends These ends can pair with any other DNA fragment generated by the same enzyme The pairing is aided by DNA ligase ...
Topic 4: Genetics - wfs
... 5. The Human Genome Project sequenced the entire human genome and found there to be 25000 to 30000 genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 6. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability t ...
... 5. The Human Genome Project sequenced the entire human genome and found there to be 25000 to 30000 genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 6. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability t ...
File
... c. is located in the ribosomes. d. is circular. _____ 17. When Mendel crossed true-breeding tall pea plants with true-breeding short pea plants, all the offspring were tall because a. the allele for tall plants is recessive. b. the allele for short plants is ...
... c. is located in the ribosomes. d. is circular. _____ 17. When Mendel crossed true-breeding tall pea plants with true-breeding short pea plants, all the offspring were tall because a. the allele for tall plants is recessive. b. the allele for short plants is ...
Southern Blotting DNA Fingerprinting
... Paper towels Weight Overnight incubation at room temperature ...
... Paper towels Weight Overnight incubation at room temperature ...
GeneMATRIX PCR / DNA Clean-Up Purification Kit
... precipitation, simply warm up in 37 oC water bath, until clarified. Note 2: All solutions should be kept tightly closed to avoid evaporation and resulting components concentration changes. Note 4: This kit selectively removes primers below 40 nt and double-stranded DNA below 20 bp. However, common s ...
... precipitation, simply warm up in 37 oC water bath, until clarified. Note 2: All solutions should be kept tightly closed to avoid evaporation and resulting components concentration changes. Note 4: This kit selectively removes primers below 40 nt and double-stranded DNA below 20 bp. However, common s ...
DNA Ligase Joke (insert laughter here)
... following replication-both strands are identical—recall semi-conservative:— each new DNA double-helix has one parental strand and one newly-formed strand No enzyme activity necessary ...
... following replication-both strands are identical—recall semi-conservative:— each new DNA double-helix has one parental strand and one newly-formed strand No enzyme activity necessary ...
Section 3 - DNA Sequencing
... • ESTs are produced by purifying mRNA from cells and then using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase to convert these to copy DNA (cDNA). The DNA is then cloned in bacteria and sequenced. • The sequence obtained is usually only short (c. 700 base pairs) and may not be very accurate, but ESTs still ...
... • ESTs are produced by purifying mRNA from cells and then using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase to convert these to copy DNA (cDNA). The DNA is then cloned in bacteria and sequenced. • The sequence obtained is usually only short (c. 700 base pairs) and may not be very accurate, but ESTs still ...
Contemporary Biology Per
... a complementary DNA strand. 25. The complementary DNA strand is made using chemically modified nucleotides that _____ the assembly of the new strand at certain places, allowing the pieces to be separated using gel electrophoresis. 26. The gel produces a _________ of bands that shows the sequence of ...
... a complementary DNA strand. 25. The complementary DNA strand is made using chemically modified nucleotides that _____ the assembly of the new strand at certain places, allowing the pieces to be separated using gel electrophoresis. 26. The gel produces a _________ of bands that shows the sequence of ...
Transcription Worksheet
... Write the answer to each question in the blank provided. 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of m ...
... Write the answer to each question in the blank provided. 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of m ...
Transcription Worksheet
... Write the answer to each question in the blank provided. 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of m ...
... Write the answer to each question in the blank provided. 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of m ...
BASIC DNA
... – Regions of DNA which differ from person to person • Locus (plural = loci) – Site or location on a chromosome • Allele – Different variants which can exist at a locus • DNA Profile – The combination of alleles for an individual ...
... – Regions of DNA which differ from person to person • Locus (plural = loci) – Site or location on a chromosome • Allele – Different variants which can exist at a locus • DNA Profile – The combination of alleles for an individual ...
ppt
... – Process is repeated and region of interest is amplified exponentially. – Minutes per cycle ...
... – Process is repeated and region of interest is amplified exponentially. – Minutes per cycle ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.