Aim: What is the structure of the DNA molecule?
... (looks like a ladder) •The molecule is also twisted forming a double helix ...
... (looks like a ladder) •The molecule is also twisted forming a double helix ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily
... • Next step was to examine DNA directly through examination and comparison of restriction fragments (RFLP bands) • Technology evolved to make it feasible to sequence DNA directly • Initially limited to single genes or noncoding regions • Now feasible to sequence large numbers of genes or regions or ...
... • Next step was to examine DNA directly through examination and comparison of restriction fragments (RFLP bands) • Technology evolved to make it feasible to sequence DNA directly • Initially limited to single genes or noncoding regions • Now feasible to sequence large numbers of genes or regions or ...
Repair of Damaged DNA
... • DNA can be damaged by alkylation, methylation, deamination, loss of heterocyclic bases (depurination or depyrimidization) • Glycosylases recognize and remove base (leaves an AP site – abasic site) • Sugar and phosphate not removed yet • AP endonucleases cut backbone • Segment is removed and replac ...
... • DNA can be damaged by alkylation, methylation, deamination, loss of heterocyclic bases (depurination or depyrimidization) • Glycosylases recognize and remove base (leaves an AP site – abasic site) • Sugar and phosphate not removed yet • AP endonucleases cut backbone • Segment is removed and replac ...
No Slide Title
... • DNA from the organism of interest is divided into small pieces that are then placed into individual cells (usually bacterial). • These can then be separated as individual colonies on plates, and they can be screened to find the gene of interest. • This process is also called molecular cloning. ...
... • DNA from the organism of interest is divided into small pieces that are then placed into individual cells (usually bacterial). • These can then be separated as individual colonies on plates, and they can be screened to find the gene of interest. • This process is also called molecular cloning. ...
Immunoreactive trypsinogen based newborn screening for Cystic
... (primers and dNTPs) left over after PCR. Step 3 - Allele-specific primer extension (for CF) The amplified DNA is mixed with short sequences (TAG primers) of DNA specific to each target. If the target is present, the primer will bind and will be lengthened through a process called Allele specific ext ...
... (primers and dNTPs) left over after PCR. Step 3 - Allele-specific primer extension (for CF) The amplified DNA is mixed with short sequences (TAG primers) of DNA specific to each target. If the target is present, the primer will bind and will be lengthened through a process called Allele specific ext ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 25. Explain briefly the molecular interaction between Rhizobium and legume plants. 26. What is Taq DNA polymerase? Write down the steps involved in PCR. 27. Describe any two methods of direct gene transformation in plants. 28. Write notes on phycocolloids. PART C ...
... 25. Explain briefly the molecular interaction between Rhizobium and legume plants. 26. What is Taq DNA polymerase? Write down the steps involved in PCR. 27. Describe any two methods of direct gene transformation in plants. 28. Write notes on phycocolloids. PART C ...
Genetic Association Studies
... • A genetic factor is like any other potential risk factor and the same study design and analysis principles hold – in addition to those specific to GWAs. • Standard case-control (matched or unmatched), cohort-based quantitative trait and longitudinal designs are common. • In what follows, I will ta ...
... • A genetic factor is like any other potential risk factor and the same study design and analysis principles hold – in addition to those specific to GWAs. • Standard case-control (matched or unmatched), cohort-based quantitative trait and longitudinal designs are common. • In what follows, I will ta ...
DNA Technology
... If the cells containing a desired gene translate the gene into protein, then it is possible to identify them by screening for the protein. This if often done by using antibodies that bind to the protein. ...
... If the cells containing a desired gene translate the gene into protein, then it is possible to identify them by screening for the protein. This if often done by using antibodies that bind to the protein. ...
Edvotek Kit #116: Genetically Inherited Disease Detection Using Pre
... and subsequent transport of oxygen is compromised. It also causes the RBC to have a sickle shape. Gregor Mendel predicted that offspring inherited traits by receiving one allele for a trait from each parent. Therefore, offspring receive 2 alleles for each trait. Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ...
... and subsequent transport of oxygen is compromised. It also causes the RBC to have a sickle shape. Gregor Mendel predicted that offspring inherited traits by receiving one allele for a trait from each parent. Therefore, offspring receive 2 alleles for each trait. Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ...
DNA Webquest - Fredericksburg City Schools
... 1. What have people wondered since the beginning of human history? 2. Who discovered that individual traits are passed on from one generation to the next? In what year? On the menu at the right click on Molecules of Genetics tab and then number 19 “The DNA molecule is shaped like a twisted ladder”, ...
... 1. What have people wondered since the beginning of human history? 2. Who discovered that individual traits are passed on from one generation to the next? In what year? On the menu at the right click on Molecules of Genetics tab and then number 19 “The DNA molecule is shaped like a twisted ladder”, ...
References - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
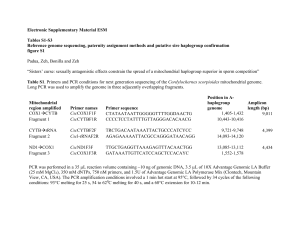
... adults was extracted as described above and PCR was conducted using the ND2 mitochondrial DNA locus forward (5’ – TGTAAGTCTTAAAAYAAAGAAAACC – 3’) and reverse primers (5’ – AAGTCATCGAATAGARACRTTAGC – 3’). PCR reactions were performed, as described above, except that the conditions of the 34 cycles we ...
... adults was extracted as described above and PCR was conducted using the ND2 mitochondrial DNA locus forward (5’ – TGTAAGTCTTAAAAYAAAGAAAACC – 3’) and reverse primers (5’ – AAGTCATCGAATAGARACRTTAGC – 3’). PCR reactions were performed, as described above, except that the conditions of the 34 cycles we ...
Big Questions
... o How are chromosomes, genes, and inheritance related? o How do genes work together to control traits? Word Wall: ...
... o How are chromosomes, genes, and inheritance related? o How do genes work together to control traits? Word Wall: ...
UV-Induced DNA Damage and Repair
... action of sunlight to be primarily attributable to the UV portion of the spectrum near 260 nm. This corresponds to the Amax for the DNA bases, whereas the Amax for proteins is near 280 nm. UV irradiation is a widely used a method for decontamination by "germicidal lamps". UV-induced mutagenicity (as ...
... action of sunlight to be primarily attributable to the UV portion of the spectrum near 260 nm. This corresponds to the Amax for the DNA bases, whereas the Amax for proteins is near 280 nm. UV irradiation is a widely used a method for decontamination by "germicidal lamps". UV-induced mutagenicity (as ...
DNA Review
... Double Helix has two strands: • Complementary – means when you read the message on one strand, you automatically know the message on other strand • Not identical, because in reverse • “Antiparallel” strands • Exact same message on both strands ...
... Double Helix has two strands: • Complementary – means when you read the message on one strand, you automatically know the message on other strand • Not identical, because in reverse • “Antiparallel” strands • Exact same message on both strands ...
review-genetics-final-exam-2016
... 59. What can the sticky ends be used for? 60. What can restriction enzymes that leave straight cuts be used for? 61. List the steps to create recombinant DNA. 62. Explain what a transgenic organism is. 63. How is the foreign gene introduced into the organism to be transformed? ...
... 59. What can the sticky ends be used for? 60. What can restriction enzymes that leave straight cuts be used for? 61. List the steps to create recombinant DNA. 62. Explain what a transgenic organism is. 63. How is the foreign gene introduced into the organism to be transformed? ...
Chapter 20 Notes
... In this lab we will transform E. coli bacterial colonies with recombinant plasmid DNA It will be your job to distinguish between bacterial colonies that have been transformed with the recombinant ...
... In this lab we will transform E. coli bacterial colonies with recombinant plasmid DNA It will be your job to distinguish between bacterial colonies that have been transformed with the recombinant ...
transcription - moleculesoflife1
... End product 2. Proteins are made up of _______________________________, which our bodies either make or come from our food. 3. What is the mRNA strand that would be copied from this DNA strand? G G C ...
... End product 2. Proteins are made up of _______________________________, which our bodies either make or come from our food. 3. What is the mRNA strand that would be copied from this DNA strand? G G C ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.