Biotechnology
... In addition to the nucleoid, many bacteria often contain small nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or ...
... In addition to the nucleoid, many bacteria often contain small nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or ...
Distinguishing Different DNA Heterozygotes by
... to 1.3 °C for the different SNPs (Table 2 of the online Data Supplement). For single SNPs, heteroduplex destabilization varied from 1.1 to 3.0 °C compared with the most stable homoduplex, or 0.7–2.2 °C compared with the least stable homoduplex. For compound heterozygotes, the respective destabilizat ...
... to 1.3 °C for the different SNPs (Table 2 of the online Data Supplement). For single SNPs, heteroduplex destabilization varied from 1.1 to 3.0 °C compared with the most stable homoduplex, or 0.7–2.2 °C compared with the least stable homoduplex. For compound heterozygotes, the respective destabilizat ...
Eötvös Loránd Science University Faculty of Sciences Department of
... The course intends to introduce students to the principles and applications of gene technology, that is recombinant DNS techniques, based on background knowledge of biochemistry and molecular biology. Our important goal is that the students understand the controversial and often misinterpreted conce ...
... The course intends to introduce students to the principles and applications of gene technology, that is recombinant DNS techniques, based on background knowledge of biochemistry and molecular biology. Our important goal is that the students understand the controversial and often misinterpreted conce ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering
... The Enzymes cut the strands. The cut produces DNA fragments with short strands on each end that are complementary to each other ...
... The Enzymes cut the strands. The cut produces DNA fragments with short strands on each end that are complementary to each other ...
DNA
... Supply of the four nucleotides DNA polymerase (enzyme involved in DNA replication) Primers ...
... Supply of the four nucleotides DNA polymerase (enzyme involved in DNA replication) Primers ...
Cells, Chromosomes, Genes
... their paper entitled The Utility of DNA Typing in Forensic Work. They asserted that even a small amount of migration (gene) across populations is quickly homogenized and contested Lewontin and Hartle’s ideas. • In 1994, Bruce Budowle and Eric Lander published a paper in they concluded that any contr ...
... their paper entitled The Utility of DNA Typing in Forensic Work. They asserted that even a small amount of migration (gene) across populations is quickly homogenized and contested Lewontin and Hartle’s ideas. • In 1994, Bruce Budowle and Eric Lander published a paper in they concluded that any contr ...
DNA Replication
... Each chromosome replicates once in the S phase to produce two sister chromatids (identical DNA molecules). During mitosis the the kinetochore regions of each pair of sister chromatids are attached by chromosome fibers to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosome fibers contract pulling sister chromatid ...
... Each chromosome replicates once in the S phase to produce two sister chromatids (identical DNA molecules). During mitosis the the kinetochore regions of each pair of sister chromatids are attached by chromosome fibers to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosome fibers contract pulling sister chromatid ...
The History of Molecular Genetics
... – Studied fruit fly eye color, determining that trait was sex-linked – Won the Nobel Prize in 1933 for his work on chromosomes and genetics ...
... – Studied fruit fly eye color, determining that trait was sex-linked – Won the Nobel Prize in 1933 for his work on chromosomes and genetics ...
Biologists have learned to manipulate DNA
... B. Plasmids can be shared between bacteria, for example to increase antibiotic resistance C. Humans use plasmids to place DNA to make useful products from bacteria 1. Plasmid is removed and the desired gene is placed in the plasmid recombinant DNA 2. Recombinant plasmid is placed back in bacteria ...
... B. Plasmids can be shared between bacteria, for example to increase antibiotic resistance C. Humans use plasmids to place DNA to make useful products from bacteria 1. Plasmid is removed and the desired gene is placed in the plasmid recombinant DNA 2. Recombinant plasmid is placed back in bacteria ...
SLG MOCK MIDTERM – FOR PRACTICE ONLY
... 19. Thymine makes up 36% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an organism. Approximately what percentage of nucleotides in this sample will be Guanine? a. 36% b. 28% c. ...
... 19. Thymine makes up 36% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an organism. Approximately what percentage of nucleotides in this sample will be Guanine? a. 36% b. 28% c. ...
Topic 2 & 3: Genetics Review
... 2.4.3 Outline how the DNA nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds into a single strand. 2.4.4 Explain how a DNA double helix is formed using complimentary base pairing and hydrogen bonds. 2.4.5 Draw a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA. 2.5.1 State that DNA replication is sem ...
... 2.4.3 Outline how the DNA nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds into a single strand. 2.4.4 Explain how a DNA double helix is formed using complimentary base pairing and hydrogen bonds. 2.4.5 Draw a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA. 2.5.1 State that DNA replication is sem ...
Genetics Practice Test (H)
... D) The parent duplex is left intact and an entirely new double-stranded molecule is formed. ...
... D) The parent duplex is left intact and an entirely new double-stranded molecule is formed. ...
Library screening
... Colonies are replicated on nitrocellulose or other hybridization filter and grown further, whereas plaques are lifted onto filter and processes immediately The filter are processed to lyse the bacterial cells or to break open (disrupt) the phage protein coat and denature and fix the DNA in situ Ther ...
... Colonies are replicated on nitrocellulose or other hybridization filter and grown further, whereas plaques are lifted onto filter and processes immediately The filter are processed to lyse the bacterial cells or to break open (disrupt) the phage protein coat and denature and fix the DNA in situ Ther ...
Genetic engineering : DNA sequencing By: Dr. Hanaa Farhan
... organisms and the primary means of obtaining DNA sequence was so-called reverse genetics in which the amino acid sequence of the gene product of interest is backtranslated into a nucleotide sequence based upon the appropriate codons. Given the degeneracy of the genetic code, this process can be tric ...
... organisms and the primary means of obtaining DNA sequence was so-called reverse genetics in which the amino acid sequence of the gene product of interest is backtranslated into a nucleotide sequence based upon the appropriate codons. Given the degeneracy of the genetic code, this process can be tric ...
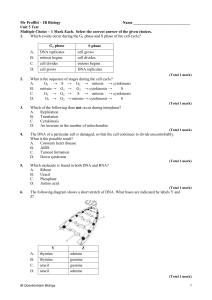
Mr Proffitt – IB Biology Name Unit 3 Test Multiple Choice – 1 Mark
... Essay – CHOOSE ONE. Answer one of the following essay choices. Take note of the command terms, and number of marks awarded for each question. – 11 Marks. 19. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. ...
... Essay – CHOOSE ONE. Answer one of the following essay choices. Take note of the command terms, and number of marks awarded for each question. – 11 Marks. 19. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. ...
Nucleic Acids - New Jersey Institute of Technology
... about how Hershey and chase’s experiment led to the conclusion that DNA and not protein is the hereditary molecule in viruses. Synthesize a complimentary strand that shows base pairing within the DNA molecule, and explain how it allows for the replication of DNA. Create a model to explain the pr ...
... about how Hershey and chase’s experiment led to the conclusion that DNA and not protein is the hereditary molecule in viruses. Synthesize a complimentary strand that shows base pairing within the DNA molecule, and explain how it allows for the replication of DNA. Create a model to explain the pr ...
Activity 10
... supports their hypothesis and the class as a whole can solve the crime. Note: If creating your own DNA strands for this activity seems too tedious, there are some activities on the web which provide downloadable DNA strands that might be adapted to this activity or allow for more efficient creation ...
... supports their hypothesis and the class as a whole can solve the crime. Note: If creating your own DNA strands for this activity seems too tedious, there are some activities on the web which provide downloadable DNA strands that might be adapted to this activity or allow for more efficient creation ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/16/99 NAME
... 8. In the example above, what offspring would be expected if the two genes are 10 map units apart and the heterozygote has the dominant alleles on one chromosome and the recessive alleles on the other? 1. 45% of the offspring will exhibit A and B, 45% will exhibit a and b, 5% will exhibit A and b, a ...
... 8. In the example above, what offspring would be expected if the two genes are 10 map units apart and the heterozygote has the dominant alleles on one chromosome and the recessive alleles on the other? 1. 45% of the offspring will exhibit A and B, 45% will exhibit a and b, 5% will exhibit A and b, a ...
Concept Sheet - Fredericksburg City Public Schools
... homozygous dominant, whereas if they are both recessive alleles it is called homozygous recessive. If there is one of each allele present, that is called heterozygous. In our pea example earlier. The dominant allele is for smooth seeds. So genotypes SS and Ss appear as smooth. The first is homozygou ...
... homozygous dominant, whereas if they are both recessive alleles it is called homozygous recessive. If there is one of each allele present, that is called heterozygous. In our pea example earlier. The dominant allele is for smooth seeds. So genotypes SS and Ss appear as smooth. The first is homozygou ...
document
... be helpful to a molecular biologist who needs to “search” DNA for the right place to divide it into pieces? ...
... be helpful to a molecular biologist who needs to “search” DNA for the right place to divide it into pieces? ...
Variations - Bioinformatics Unit
... Genomic Diversity SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms) base pair substitutions InDels insertion/deletion (frameshifts) occur in 1 in every 300 bp (human) ~3 billion base pairs in mammalian genomes! 3 of 49 ...
... Genomic Diversity SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms) base pair substitutions InDels insertion/deletion (frameshifts) occur in 1 in every 300 bp (human) ~3 billion base pairs in mammalian genomes! 3 of 49 ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.